Sensei
Senior Members
-
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Currently
Viewing Topic: Age of consent (split from Epstein files reveal deeper ties to scientists than previously known.)
Everything posted by Sensei
-
How should I set about actually learning science?
Start by rereading the old school textbooks. But this time not only to pass the exam, but to gain knowledge.
-
A random universe
@geordief It reminded me this: https://www.google.com/search?q=radioactive+random+number+generator Hardware random number generator: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hardware_random_number_generator "In computing, a hardware random number generator (HRNG) or true random number generator (TRNG) is a device that generates random numbers from a physical process, rather than by means of an algorithm. Such devices are often based on microscopic phenomena that generate low-level, statistically random "noise" signals, such as thermal noise, the photoelectric effect, involving a beam splitter, and other quantum phenomena. These stochastic processes are, in theory, completely unpredictable, and the theory's assertions of unpredictability are subject to experimental test. This is in contrast to the paradigm of pseudo-random number generation commonly implemented in computer programs."
-
Mystery Carbohydrates??
Isn't purpose of E-numbers table? e.g. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/analytical-chromatography/analytical-products.html?TablePage=109806885 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/E_number
-
Computer Chess
In 1996, CPUs had one core per CPU. So I assume you meant "to match 200 machines in 1996" (e.g. server-room). The first Intel/Xeon with a dual-core was released in late 2005. The efficiency of modern CPUs apart of increased frequency, and more built-in cores, is the result of the introduction of new instructions which process more data in single instruction. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SIMD SIMD = Single Instruction Multiple Data But it requires 1) writing machine code manually 2) writing assembler snippets manually 3) enabling option in compiler (so it must to have such an option in the first place). Doubtful ancient Pascal compiler will utilize power of new instructions.. 4) writing multi-threaded algorithm.. A significant bottleneck is how fast the processor can read and write data from and to physical memory. To help with the bottleneck, many new technologies have been introduced: multi-level cache, dual-channel and triple-channel memory slots (so, when you have dual-channel memory on the motherboard, instead of buying a single 8 GB memory, you should buy 2x 4 GB, or 2x 8 GB.. and if triple-channel, buy 3x at a time, to have 3x faster memory transfers) These days, when somebody wants to have fast code, converts the most time consuming part of application to GPU/CUDA/OpenCL. We have GFX cards with literally thousands cores. Usage of ancient languages with ancient abandoned compilers won't help you fully utilize power of a modern machine. Hmm.. I have sense this sentence can be equivalent of "is modern 8 core CPU faster than 200 machines in 1996", correct? Yes. Modern single computer with 8 core CPU can be faster than 200 old machines from the past. You can check it using e.g. CPU benchmark website, which list CPUs: Compare AMD Ryzen (Cores: 64 Threads: 128). Score 88731. https://www.cpubenchmark.net/cpu.php?cpu=AMD+Ryzen+Threadripper+PRO+3995WX&id=3837 with Pentium 4 from 2000 (Cores: 1, Threads: 1). Score 77. https://www.cpubenchmark.net/cpu.php?cpu=Intel+Pentium+4+1300MHz&id=1058 (the worstest on this website) 88731/77 = 1152 times faster But it requires 1) multi-threaded code (not all algorithms are easily scalable) 2) no significant transfers from CPU to physical memory 3) no significant transfers from physical memory to data storage e.g. HDD/SSD/M.2
-
Computer Chess
Chess algorithm does not have to be AI at all. '90 chess algorithms were not AI at all. And I doubt modern chess programs are A.I. (even if the creators claim it is A.I. in ads) because developers don't want to give such advanced technology to everybody (if you release software on CD/DVD/program downloaded through Internet, anybody can reverse-engineer what is there). e.g. when you talk to Google Assistant, or Siri, your voice is sent in real-time to central server to analyze, and they return just plain text. Why? Because Google/Apple don't want to include (reveal) A.I. voice recognition code in OS, because everybody ("programmers") will see it, and get it, and will use in their own projects.. AI means Artificial Intelligence, which should mean "teacher gives it data samples, and let it learn from them". The more data are given, the more knowledge gained. If you put A.I. inside of box without any signals from outer world, it won't learn anything. There will be no data to analyze and gain some knowledge. If teacher gives wrong data, A.I. learns bad things, and there are consequences: https://www.independent.co.uk/life-style/facebook-artificial-intelligence-ai-chatbot-new-language-research-openai-google-a7869706.html https://www.cbsnews.com/news/microsoft-shuts-down-ai-chatbot-after-it-turned-into-racist-nazi/ "Microsoft had to shut Tay down because the bot started spewing a series of lewd and racist tweets." Search for "[company name] chatbot shutdown" for other similar stories. (chatbot is kinda like parrot repeating what he/she heard from humans, and repeating unaware what it means) Analyze of the all possible movement is not AI, it is brute force algorithm. Engineers just have to add more and more machines (or increase frequency of CPU) to have better results. Modern GPU cards have 1024/2048/4096+ cores on them. $5k and you have 4096 cores: https://www.acmemicro.com/Product/14963/NVIDIA-Tesla-M60-GPU-4096-cores-PCI-Express-3-0-16GB-GDDR5-GPU-Accelerator?c_id=573 $9k and you have 5120 cores: https://www.acmemicro.com/Product/16529/NVIDIA-900-2G500-0000-000-Tesla-V100-GPU-for-PCIe-16GB-HBM2-640-Tensor-Cores-Passive-Cooling True AI/human don't even think about "obviously wrong movements". Brute-force algorithm does through the all movements and judges them. Maybe "obviously wrong movement" at the beginning of play (rejected at the begging by everybody, by AI and human), maybe later have some unexpected consequences.. A.I./human can't know that, because rejected movement at early stage as wrong/pointless/stupid..
-
Office Chairs
I would instantly dismiss idea of getting chair without armrest.. BTW, when we are at things which increase the comfort of programmer's work and life, one of the first things in my top ten would be blackout curtains. When you work at night (as it is almost 4:00 pm in Europe now. Summer would be sunrise) and you sleep during the day, you need blackout curtains to have a good rest. Daylight does not enter the bedroom and does not interrupt sleep.
-
Water on the red planet
..and I replied: if you have cosmic rays, you have some free neutrons created by them, transmuting one element into another.. and causing them to be radioactive.. OP, in a sloppy way, asked whether radioactive elements are created by cosmic rays and are in Marsian's water e.g. Tritium H-3 or Oxygen-19 etc. OP should ask about C-14 too (because abundance of CO2) in Mars atmosphere.. If water exist on Mars and is irradiated by cosmic rays for billions of years, yes, it contains radioactive isotopes. The thinner atmosphere layer, the worser for water.. So the next question for scientists searching for "water on Mars" (or any other planet): is it radioactive and how much more than terrestrial.
-
Water on the red planet
I did not say N-14 is on Mars, or it is transmuted to C-14 on Mars, or any other planet. It was just an example of what happens in Earth's atmosphere due to cosmic rays. The first reaction is universal: [math]p^+ + p^+ \rightarrow p^+ + n^0 + \pi^+[/math] (because you asked about neutron source in your post) Further secondary reaction(s) are specific to planet's atmosphere. Free neutrons are result of collisions of cosmic rays with matter. It can happen even without any atmosphere.
-
Water on the red planet
Obviously once Nitrogen N-14 transmutes into Carbon C-14, it does not need anymore one of electrons which is also ejected.
-
Water on the red planet
??? Nitrogen has 7 protons, free neutron has 0, Carbon has 6 protons, free proton is 1. 7 = 7 as far as I can see.. isn't?
-
Water on the red planet
In the case of the Earth's atmosphere, they are created by: [math]p^+ + p^+ \rightarrow p^+ + n^0 + \pi^+[/math] i.e. a highly accelerated proton ("cosmic ray") colliding with a gas molecule in the atmosphere creates a secondary pi-meson and neutron, that can be absorbed by another molecule. It transforms Nitrogen-14 to Carbon-14: [math]N^{14} + n^0 \rightarrow C^{14} + p^+[/math] Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon-14#Natural_production_in_the_atmosphere Analogous reaction can happen in Mars or other planet atmosphere.
-
Compare Signs
If you won't initialize to some integers, entire procedure of checking integers won't have data to compare them, isn't? If you don't know length of the array, you should use dynamic lists/ dynamic arrays instead. Long story, short version: they have no initial length, but grow as developer is appending/inserting elements to them. You should *check* if lengths are equal and return error (e.g. throw exception telling about the problem). That would be the nicest/cleanest thing to do. I would use: int length = 4; int [] a1 = new int[ length ]; int [] a2 = new int[ length ]; [...initialize them to some values...] for( int i = 0; i < length; i++ ) { No, it is wrong! What are you doing here? Do you have any idea? Then compare signs of integers ("element" of array)... How to read element of an array/list? Completely wrong answer. If it would be C/C++ or assembler, you could cast from signed integer, to unsigned integer (so shift operations will work correctly), and then shift RIGHT 31 times (32 bit integer as sign bit at #31 bit), and then use bit-wise AND operation, and then you have "sign bit" which you can compare with something else). BUT, BUT.. You SHOULD NOT do it this way, as there is 100 times easier way to find out whether integer is positive or negative! Think! Wrong again. Counter of matching comparisons shall be incremented... You should not return ANY NULL. Your procedure have to return an integer of quantity ("counter") of matched comparisons!!
-
Assembly code explain MIPS
Then why you used right shift in equivalent comment? "t3 = t3 >> 1"
-
Compare Signs
In which language do you want to code it? You (almost) allocated arrays, but not initialized their fields yet. new [] takes a parameter, the length of the array, which you did not provide. Newly allocated memory block has 1) uninitialized data (always forgotten by newbies) 2) initialized to default values (if you allocated array of C++ objects, and default constructor was called, and it filled the all C++ object members by some default value e.g. zero). So far, so good. ..but it showed possible issue: what if arrays have different lengths..? This way you compare entire object with other object integer e.g. compare their pointers (which will always fail in this case) Why do you want to return here from subroutine? You should count elements. Return quantity of matched elements should be at the end of function, outside of for loops. Should not you compare one element from array #1 with one element from array #2 ("pairs of 32-bit numbers from two arrays of numbers")? So arrays should have equal length (ask teacher), and utilize just one for-loop. Shouldn't you be comparing SIGNS of integers? How to check the sign of a single integer? How to compare if the signs of two integers are equal? How to treat zero element? As positive sign?
-
Assembly code explain MIPS
You can learn machine code without actually having any manual or tutorial. Basically open debugger, in disassembly mode, and step-by-step execute instructions. Watch the registers change. Observe memory and how it changes. slt means "Set on Less Than". sltu means "Set on Less Than Unsigned". Because it is an argument to the function?
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
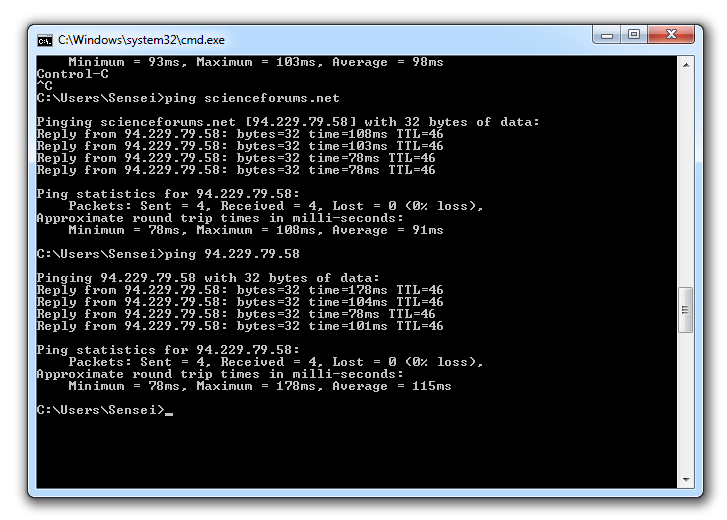
Simply open terminal/shell/console, and ping giving name e.g. ping google.com ping scienceforums.net and in output will be numerical IP address, like on my screen-shot above. You can select it in console and copy (either on Windows and Linux)
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
How about you @Ghideon and @MigL .... ? Repeat above.. On Windows, you can do it using command "arp -a". https://www.google.com/search?q=arp+on+linux https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/arp.8.html and https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/route.8.html Because you can't visit HTTPS via IP address.. It has no info about SSL certificates which are given to specific "host name".. Additionally, like I said, server with IP 94.229.79.58 has multiple other websites.. https://ipinfo.io/94.229.79.58
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromiumos/docs/+/master/developer_mode.md
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
IP "153.229.14.155" is in Japan. For me "scienceforums.net" resolves to "94.229.79.58"..
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
Physical HTTP server can have virtual servers. They share the same IP address. But have different "host name". If we have custom made server, with HTTP like Apache installed, and we are alone, it would work, http://our_ip and http://hostname will give the same (because no Virtual Servers are configured https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_hosting ) but most of HTTP servers these days, are hosted on 3rd party machines i.e. clouds in server rooms in foreign country. And single IP has multiple (e.g. thousands) virtual servers on it.. You can learn what are these virtual servers by using reverse-DNS (search net for keyword)
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
..If I visit https://8.8.8.8 it automatically converts to https://dns.google/ ... (some kind forwarder) If you can check it: make your DNS unreachable in router (i.e. wrong IP data), then visit https://8.8.8.8 to see what happens... Yeah... On Windows you should use "ping [IP] -t" and leave it.. and if Ethernet cable has problems i.e. is physically damaged e.g. by walking on it... having it through doors which are frequently closed and opened and similar things.. basically damaged cable.. then in such a case, continuous ping will have some lost packets..
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
Good advice +1. Easier for newbie. ping it in terminal (or equivalent) instead.. ping other machine from your LAN (to see if it is reachable). And vice versa from other machine to yet another machine. (learn what are IPs of the all machines in your LAN first) (on some devices, they can have disabled ICMP packets so ICMP ping won't work at all unless you use TCP/IP ping and/or enable ICMP ping manually)
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
Problems are universal. Just commands/tools have different names with different arguments.. Tutorial made for one OS will work with other OS if you will look up what is equivalent command on different OS.
-
DNS error... ethernet connected, no internet :-(
The first thing any "idiot" should do when there is no internet connection is to use the "ping" command. A Windows user would do: Click on Start menu, enter "cmd" to open console. Then enter "ping". It is the most widely used command for network analysis. What to ping? e.g. gateway IP, DNS IP address, host given by name, host given by IP address, device IP etc. etc. So first you need to know what is your gateway IP address. Do you know your IP address? If not, before ping, use "ipconfig /all" https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/ipconfig which will show you all your interfaces, e.g. WiFi (even if not used / disabled), Ethernet, Bluetooth etc. Run "cmd", then "ipconfig /all >data.txt" and attach in the reply, so we can see it. You should have rows with "Default Gateway" which will have address that you should enter to "ping" command as argument. e.g. "ping 192.168.0.1", use "-t" to have continuous flow of data. There will be also DNS servers mentioned in output. You can ping Google DNS. Do you know Google DNS addresses? 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 How somebody can know what are Google DNS addresses? Because will use Google to find out: https://www.google.com/search?q=google+dns+address (you can do the same with other companies which provide DNS servers, just change name of company in the above query..) Any network admin will tell you "if your own DNS don't work, use Google DNS". So better remember their IPs in advance.. ping 8.8.8.8 ping 8.8.4.4 What can we see? That they are slooow. Do you know how to set DNS address to different one? If you connect through network which has configured DHCP, DNS address(es) will be given by DHCP server. However if there is something wrong with DNS servers, Internet will stop working in web browsers, but will work through IP given manually. e.g. ping google.com will fail, but ping 172.217.22.14 (or whatever google.com resolves to) will work. Linux obviously has equivalent commands for "ping" and "ipconfig": https://www.google.com/search?q=ipconfig+on+linux which is "ifconfig" https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/ifconfig.8.html and "ping" command manual: https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/ping.8.html ps. When you see Windows tutorial "how to solve some problem", you can still use that knowledge on Linux or whatever else, just use "what is equivalent of XXX on linux/whatever" as search keyword.. e.g. https://www.google.com/search?q=ifconfig+gateway I see user answered that "ifconfig" is depreciated, and user should use "ip" instead... So: https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/ip.8.html and https://www.google.com/search?q=ip+command+linux+examples Forget it. The problem is unknown. e.g. somebody (hacker) could give you fake DNS servers (because intercepted your router).. so you may be connecting to his/her machine, instead of true DNS servers.. Or somebody in company which is providing you net, is restarting DNS servers, or they are restarted automatically every xxx minutes/hours to update for new DNS records... Even if you may be connected via cable Ethernet, it does not guarantee that your ISP provider does not use radiowave Internet further in route. e.g. if there is bad weather (i.e. snow especially), radio Internet has issues, because snowflakes and raindrops with heavy wind reflects signal (I always have problems with net (LTE, WiFi) during heavy snow or heavy rain). You can detect if you DNS servers have been intercepted by hacker. How? Learn what are DNS servers that your computer is using, and search that IP in Google. Or use reverse-DNS on that IP address. Results should show that they are legit DNS servers of ISP that you're using (big ISP providers mention what are their DNS servers on their websites). This subject is so huuge, that your asking to give idiot-proof tutorial, is like asking to give idiot-proof tutorial of surgery of brain, but on steroids.. If you find that your ISP DNS is down by pinging it (better be prepared to in advance), but pinging Google DNS servers work.. you can change DNS servers to Google DNS e.g. https://www.google.com/search?q=how+to+set+dns+linux
-
How should I design Algorithm?
Sounds like modified Ultimate Tic Tac Toe. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ultimate_tic-tac-toe