Everything posted by Sensei
-
Fracking Methane Alarm
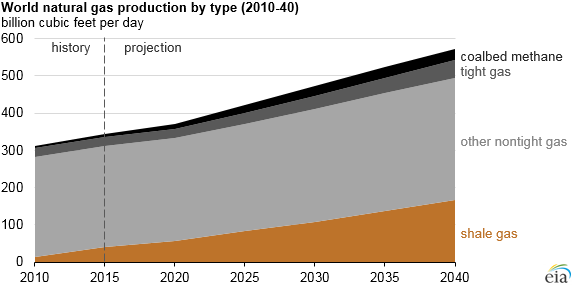
Are you against shale gas and fracking technology only? Or against drilling tradidional way natural gas too? In your posts you are mixing them. 39 mln tones worldwide is leakage from both technologies. Fracking is minority of worldwide production of gas. Contrary to US were it is dominant technology. (People in US are often forgetting that World is not only US..) Decide if you want to talk about US or World. Don't mix World data with US data. Keywords for search engine "natural gas market share" "shale gas market share". https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=27512
-
Fracking Methane Alarm
It is easy to dismiss it as "prime trigger of global warming". Anthropogenic methane emissions worldwide in 2019 was 363 mln tons. 33% of it was coal, oil and gas production, distribution and usage. USA had 6.2% share of methane emissions in 2012. In 1970 it was over 11%. (in absolute numbers it also dropped). See table in below article. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methane_emissions Coal, oil and gas industry by themselves should be the most interested in methods limiting leakage of methane because they simply can't sell leaked product to end customers and lose money. If entire US would stop coal, oil and gas production and usage (regardless of whether it is using fracking or not), methane emissions worldwide would drop only by 2%. Attempt to fight with anthropogenic global warming is job of entire worldwide population, not just one country, or group of countries. Personally I think attempt to fight with it by taxation is silly and instead of solving existing problems, it makes new ones, economical e.g. movement of investors to countries without this silly CO2 emission tax. Which ends up with people being fired (unhappy and rejecting AGW), production unprofitable, reduction of country export (higher costs of production) etc. etc.
-
Separating Hydrogen gas into protium and deuterium hydrogen molecules
If aim is to have Deuterium, search net how to make heavy water. Once you have heavy water you can just do electrolysis of water. Typical source of Hydrogen in lab is electrolysis of water. Normal tap water has very little amount of Deuterium. Sea water has a bit more. Search net for "abundance of Deuterium". It is 1 per 6400. So there are three possible combinations H2, DH and D2. H2 is the most abundant and D2 is the least abundant. Similar situation is with water. There are three combinations H2O, HDO and D2O. From normal water you make semiheavy water and then semiheavy water is enriched to heavy water. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semiheavy_water From more info read production of the heavy-water https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heavy_water
-
Artificial Intelligence with n-gram(Python 2.7 (64 bits) Scripts)
Caching thousands the most used words in ASCII would take a few dozen kilobytes. Not MB. Not GB. But KB. In Unicode 2-4x more. You are caching to not have to lookup things like "I", "you", "it", etc. etc.
-
Artificial Intelligence with n-gram(Python 2.7 (64 bits) Scripts)
Make cache in memory. Check if word is present in dynamically allocated array or key-value pair associative array, if it is, increase usage counter of the entry. If it is not present, lookup the database and put the new entry in the cache. Have 1000, 10000, or so, the most used entries. From time to time flush cache of the least used entries. The most frequently used words-entries-phrases will be cached at all times during execution of the script. You can make separate caches for words, phrase with two words. three words. Each with user configurable max number of entries. In OOP language you should just make class for cache which will cover entire database code.
-
Artificial Intelligence with n-gram(Python 2.7 (64 bits) Scripts)
Do you have SSD? Do you have NVMe? What is transfer of data during db access? How many GB of memory does your computer have? Try using virtual disk in memory to see whether there will be change in speed. How are you storing, querying and updating db? Show SQL query string for them all. You can try: - calculate md5 (or so) of phrase text first. It will be hash code. - phrase table. Use above hash as unique key together with each phrase text. - frequency table. Use above hash code in second table with quantities / frequencies as integer. Therefore update should be faster. Won't require adding or replacing entire string. Alternatively don't store phrases as plain text. Have dictionary with words with unique indices. 4 bytes integer is enough to have 4.2 bln words. Then make phrase dictionary table. One with two columns for word indexes. Second table with three columns for word indexes. etc. in the future you will add more.
-
Question light and UV and cardboard box
@MigL You can't /shouldn't trash old CDs, DVDs, HDDs, pendrives, computers, laptops, tablets, smartphones, anything with your personal data. Especially if they were damaged. E.g. many people thoughtlessly throw away a smartphone with a cracked screen. If the device will be intercepted by a competent person such as a hacker, he/she will fix it and get the all data from it. Possible consequences are stolen identity, yours, a family member or other person (do you have contacts in smartphone with phone numbers and emails? content of emails with long discussion about private subjects). If you can't remove data storage from a device e.g. smartphone or table, you shouldn't use electronic repair service either if you can't see entire process personally. If a hacker works in a repair service, they will get your personal data. You can get an unwanted unauthorised loan, interception of bank accounts, and similar accidents..
-
Question light and UV and cardboard box
Paper is made of wood. Freshly cut tree contains trace amount of radioactive isotope of Carbon C-14 with half life ~ 5730 years. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon-14 There is aluminum foil in each kitchen. It is used to cover cakes in the oven. You can buy it at almost any grocery store around the corner.
-
Biden and the $15 minimum wage
Grow up my child, grow up..
-
Question light and UV and cardboard box
Repeat the question after 10, 15 or 20 years when there will be no working CD/DVD reader/writer anymore. Who cares about UV light? Write 10+ copies of the same files with checksums every 1 kb or so. If you will have in 2030-2040 working reader which will work with PC you will be able to recover data from 10 copies.. but most likely your readers will be broken and modern in 2030-2040 PC won't allow plugging ancient CD/DVD readers anymore..
-
Question light and UV and cardboard box
If you are concerned about the safety of data storage after years, you should answer the question of whether you are able to load data from a tape recorded in the 80's or 90's... In my laptop there is no built-in CD/DVD reader at all.. (in my PC I don't have it either plugged all the time) Do you have it in your laptop? It increases weight of the device therefore it is used less and less.. Do you have external CD/DVD reader/writer? Soon it will be hard to get them at all. Like tapes. Or similar things from the past years.
-
The fast forward key for retro game(I want to apply it to Python)
I don't think so. It would boost opponents movements as well as the main player movements, possibly rendering entire game unable to play anymore by human. The all real time games refresh at constant rate (if game has wait for vblank) or adaptive rate (if has not wait for vblank). Contrary to games with rounds in which objects don't move therefore don't require periodical screen refreshes. Refresh is needed when there is movement to update state. There are special electronic displays which update only when there is change of pixels. Used mostly with ebooks. This reduces electric power usage only to switch states and saves battery.
-
The fast forward key for retro game(I want to apply it to Python)
You don't seem to understand what he did on the video... Game was not run in some turbo speed. Just frequency of key events was increased.. On Windows OS is sending events WM_KEYDOWN when user pressed key and WM_KEYUP after releasing key button. However when user pressed key button and holds it, there are send WM_CHAR with small delay between them. Application (emulator) and/or external keyboard utility (e.g. keylogger) can inject more WM_CHAR into input events queue and increase frequency. Buggy application will be cheated because programmer did not think about such situation in advance.. Similar situation is with games which did not wait for vertical blank (VBlank interrupt). Emulator get this functionality to fight with such not waiting for vblank games, so they still could be usable after increasing delay of key events. If you want to increase speed of execution of your programs 1) stop using Python and write code in C/C++ 2) use multithreading. Modern CPUs have 8+ HT threads and more. 3) use CUDA/OpenCL and use GPU for heavy computing. Modern GPUs have 1024-8192 cores on GFX. Looking on questions asked on the forum, doubtful that his Python programs are multithreaded. So he could instantly have 8-12 boost after using the all cores of CPU.. If script is just calculating.. But the most of the scripts are loading data from storage etc. etc. Getting M2 NVMe would speedup 3-7x in comparison to ordinary SSD, and 70x in comparison to traditional HDD.
-
Is the earth really our planet? Or the planet of fishes?
-
is it possible to harness gravity to power a motor
Yes.. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydropower https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydroelectricity
-
A rather unique idea to room cooling (radiant cooling + peltier array)
What is color of building and room walls? White color reflects light preventing it from being absorbed. But check if it is not having Titanium Oxide. https://www.sustainability-times.com/green-consumerism/a-new-white-paint-can-keep-buildings-naturally-cooler/ You can get IR camera for smartphone to see which part of wall is heating the most.
-
New exoplanet candidate found in the habitable zone of the closest star system
The closer to Earth properties i.e. mass and radius (thus closer to 1g), the better for human body. Moon or asteroid will have too weak gravitation (astronauts on ISS are suffering from too weak gravitation. To fight with it have to spend many hours per day heavily training).
-
Celsius vs Fahrenheit
There were couple airplane crashes and accidents due to metric-imperial conversion errors including fatal costing people lives.. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gimli_Glider In See Also section in the article above there is list of accidents which were not so happy ending as this story..
-
Rural Roadsigns
Here they are called "sleeping policeman".
-
Question sound hammer damage objects in room
Chances comparable to winning on the lottery..
-
Question sound hammer damage objects in room
Finding appropriate resonance for specific object can have fatal consequences https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tacoma_Narrows_Bridge_(1940)#Resonance_(due_to_Von_Kármán_vortex_street)_hypothesis There might be places in the room where are existing constructive interferences.
-
Quick question about perpetual motion.
Watch video from his other thread. The idea is simple. Heat substance with low boiling point so it will change to gaseous state and move to the other end of closed container where it will liquify. Repeat with other end.
-
Methylene Chloride motor
People with idea build prototype. Nobody will do it for you. Once you have prototype you can show it on YouTube and Vimeo and make crowdfunding project on e.g. Kickstarter or similar website. If people will see value in your idea, they will give you money to build more professional motors utilizing relatively low boiling temperature 39.6 C of methyl chloride or whatever else you will choose. It will be heat by sunlight I suppose so? I enjoy the idea. But you did not even spend time on description of your idea.. Sounds like you want everything to be done for you by us.. If you will continue this, somebody will use idea without you participating in it at all.. You can start from 3D model. Download 3D application e.g. Blender, LightWave etc. model motor and animate it. Render to image sequence. Then render video. Make professional appealing video with lecturer and present it on Kickstarter. The first stage of building a prototype could be 1) buy 3D printer. Once you will have it, remake what you presented on previous showcase in the real world. This way people will see that it is serious project and will give you even more money to e.g. buy CNC and make metalic prototype. Or invest these initial ~ 500 usd in 3D printer by yourself.
-
CPU Architecture
To implement MMU you need knowledge how to program MMU. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Memory_management_unit To implement FPU you need knowledge how to program FPU. And how to store IEEE 754 in memory. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_754
-
Increase tall
I can help you: "grow up"..