Everything posted by joigus
-
What is the mechanism for the BIG BANG ?
A mechanism can only be proposed once you have a theory. At least in physics and chemistry. I've told you in another thread, but you didn't answer. Newton's laws of motion don't come from a mechanism Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism don't come from a mechanism Einstein's equations of gravity don't come from a mechanism And so on. In the case of cosmology, the big bang is an inevitable consequence of Einstein's equations plus reasonable --and observationally sound-- cosmological hypotheses (cosmological principle, Hubble's law...). When extrapolated backwards in time, an expanding universe leads to a time in the remote past when everything was much, much closer together. There's your bang. Seems to make sense, doesn't it?
-
Mechanism for TIRED LIGHT
My sarcasmometer is going through the roof!
-
What is the mechanism for SPACE EXPANSION ?
You're right if what you mean is that there are physical reasons to reject those solutions: A static universe would be unstable. But solutions they are. Einstein looked for that, and found it, because he had the prejudice of a static universe. In fact, the whole reason why he introduced the cosmological constant is precisely because it allowed him to tailor-make the universe as static. He did find that solution, but it's a freak universe. Then he regretted that he could have found the expansion of the universe as the biggest blunder of his life. Or so the story goes.
-
What is the mechanism for SPACE EXPANSION ?
Some hopefully helpful ideas much related to what @studiot and @beecee have told you: Explaining a phenomenon via a mechanism: A well-established theory is already there that should explain the phenomenon, simply because it's its job to do so. Example: Rayleigh scattering (mechanism) and Maxwell's equations (fundamental law) explain why the sky is generally blue, but red during the sunset, or the other way around in Mars. Example: Light turning redder and redder the farther away from you it comes from in the sky. Non-examples: Accelerated expansion of space, entropy of black holes, existence of different families or generations of (quark, lepton) in the standard model of elementary particles. We know they can be accomodated in the laws easily. But we haven't the faintest idea why they should be there. It would be just as easy to plug in contraction of space, or just no expansion or contraction at all; there could be several models of what's inside a black hole that gave the same entropy for all we know; there could be just one family of (quark, lepton) or 3, or 103. Why not?
-
Don't Look Up (Film)
I think you're spot on with this. I haven't seen the movie, so I can't opine. Here's an updated version of it, very relevant today, which you may consider taking into account:
-
Our civilization lifespan as per Copernican Principle
Other questions that make the argument very little compelling, if at all, are: how do we define civilization? Do we all belong to the same 'civilisation': Sumerians, Etruscans, Egyptians, and so on? It has been argued that civilisation defined by cities, writing, and monumental architecture, came about as a consequence of the end of a glaciation. Civilisations in a narrower sense like, e.g., the Minoans, probably disappeared because of a volcanic eruption. Others, like the Egyptians, because of people from the seas invading lands that were essential to their trade; as to the Mayas, it's debatable, but climate change may have played a role. It could also be for internal reasons... Earthquakes, meteorites, you name it. I concur with @MigL that there are too many unknowns. Also, I know you pitched this topic for applied mathematics, but we should try to make these ideas falsifiable, because we're concerned with science. You cannot experiment with civilisations as a subject of study in real time. (My emphasis) This is funny, because --and I think it's happened before-- you've made a good argument, but it seems to me that it works against your idea. How can we surmise that probability distribution? On other threads I've argued that the word 'random' in itself doesn't mean much. You would have to make a statistical hypothesis => probability distribution. Equiprobability doesn't apply in general.
-
Could someone give me an appropriate criticism for this?
There you go. That doesn't mean Claudio must be wrong. It's mostly a problem of it being or not being enough for other scientists to drop what they're doing and focus their attention on the idea. I can guarantee you that if you're a scientist, and they present you with a theory that really cuts it, you'll be paying outmost attention to it. In the meantime, nice words to your friends --maybe a little over-the-top encouragement-- doesn't do much harm.
-
Could someone give me an appropriate criticism for this?
I have to confess I'm out of touch with this thread. The only thing I'm saying is that the last attachment is but a show of mutual affection between Arturo Tozzi and Claudio Messori. Nothing more. I see no scientific arguments displayed there. That's all I can say, honest. Now that I've reminded myself of what the whole thing is about, I stand by what I said. Even great scientists can be highly susceptible to ideas from the periphery that seem to strongly support theirs. Scientists are human, you know. I have serious doubts that QED can shed any light on cognitive processes in any far-reaching way. The most I can fathom, as it stands, is that renormalisation schemes have something (vaguely) to do with the fact that what we wish to know about a physical system deeply affects how the system responds. From that to a theory of mental processes, it takes a long stretch of the imagination, and is dangerous territory --as both theories stand. Again, that's all I can say.
-
Could someone give me an appropriate criticism for this?
About the dialog between Claudio Messori and Arturo Tozzi? That they should get a room.
-
James Webb Telescope and L2 Orbit Question
Just a couple of comments to add (and without getting into Hessian traces and eigenvalues .) The centrifugal term scales like v2, and the Coriolis term scales like vr(v). So it's, in principle, within our control to set that value (a low-enough orbiting speed) such that the line of instability can be controled by means of appropriately-gentle thrusts. At least that's what my physical intuition tells me. We must all learn to think in 3D!!! I spend hours on end on 1D. Happy New Year.
-
James Webb Telescope and L2 Orbit Question
Yeah it seems that L1, L2, L3 are all saddle points: Very interesting. There's a part of it I can follow; other parts, like the stability conditions on the Hessian, which make sense to me but go over my head too. This is quite advanced Newtonian mechanics, and I don't think all of it can be safely done without computers.
-
James Webb Telescope and L2 Orbit Question
Good call. I'm not sure. In the reference that @beecee provided, they say it requires relatively little thrust to keep it in orbit. If it's a very gentle saddle... What the technical reasons are, I don't know. Based on this, I'm assuming little fuel needs to be spent in order to keep it in orbit. The only thing I'm sure about at this point is that it's not going to be there forever.
-
James Webb Telescope and L2 Orbit Question
Maybe not a peak, but a saddle point. A saddle point would be unstable too. I studied this ages ago, and I don't remember. Wikipedia: It's as @beecee says. Apparently you need some thrust now and then to keep it in orbit.
-
Scientific establishments control over human evolution.
From 19.45 to 22.04: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r-L690pQhuo Here's a transcription of what Smolin says, *Does it matter that we let go of the attempt to pursue a concept of objective reality/objective truth. It's clear that's what Smolin is talking about if you rewind the video 30 seconds or so from where I've transcribed. It's very clear to me that Smolin is concerned that giving up on a concept of objective reality, when wielded by political minds, can turn into an excuse for 'everything goes'. It's nothing to do with elite scientists thwarting young, creative scientists when/if they're trying to push their ideas forward.
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
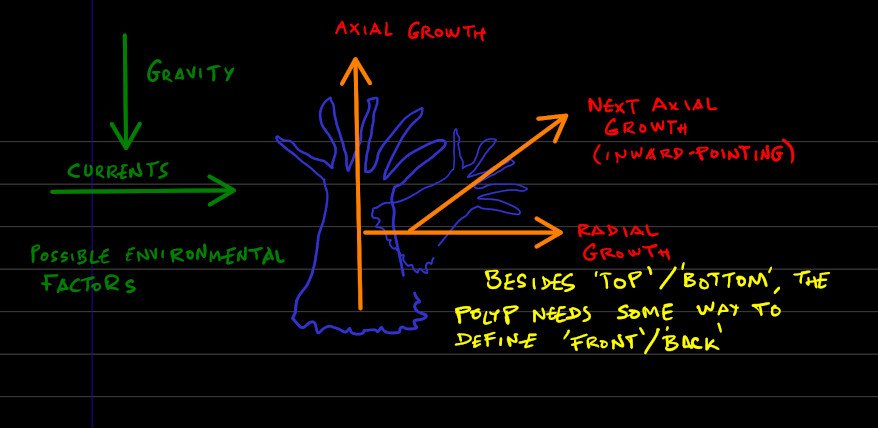
But I did answer that part, I think, although implicitly. The key words are 'inward pointing' in my drawing. The new polyp would grow 'radially apart' from the parent one and continue describing an ever opening helix, because with every new 'generation', the plane shifts, as well as the radial distance with respect to the first 'ancestor'. The radius of that definite-chirality helix would increase more and more or less depending at a rate that depends on the ratio between the radius at which the offshoot buds and the angles (both with respect to that radius, and to the drawing's plane). I don't know if coral polyps can be grown in laboratory conditions. I suspect not. But if that could be done, it would be very interesting to set up a laboratory assay to test what environmental factors affect the growth pattern (by the way, I forgot prevalent direction of light, as corals are heavily dependent on it). I think it's a very interesting observation you made. I've scanned for different similar corals of the same family, and it seems to me that they all are right-handed helices. Edit: Sorry for the abundance of quotation marks, but I think you understand what I mean.
-
E.O. Wilson
Sorry, I looked for that in 'News' only. I should have done a look-up in the forums.
-
E.O. Wilson
https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/dec/27/edward-o-wilson-naturalist-modern-day-darwin-dies May a path of ants lead you to wherever there is light.
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
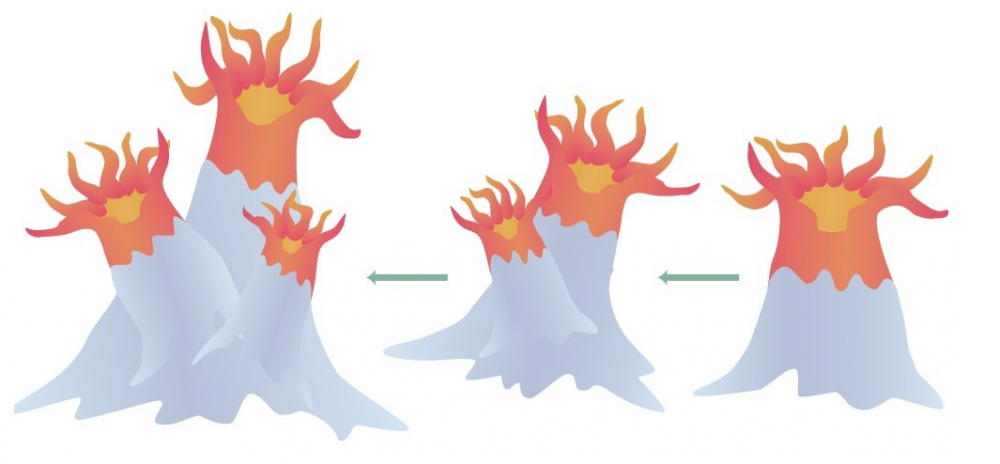
Replacing 'left' by 'tangential' doesn't exactly clinch the case, IMO. There is a clockwise tangential, and an anti-clockwise tangential. But I think you touched a very important point that for some reason you don't recognise as having a molecular basis (homeobox genes, which are what determines developmental hormones, which in turn determine relative placement of organs, cells, etc.): It's the pattern with which the next polyp buds out of the progenitor polyp. As far as I can see, you need another plane of assymmetry to complement the axis defined by the growth, and always keep it 'doing the same thing', so to speak. The simplest hypothesis that would explain the appearance of this plane of 'slight asymmetry' is how growth hormones flow away from one side of that plane and onto the other. Environmental factors cannot be excluded, of course (See image below.) Plants always grow their stems towards the Sun and their roots towards the ground due to combination of growth hormones + light, gravity, etc. Consider a spherically symmetric phase of the embryo previous to the blastocyst (the first 'axial' phase.) There's no up, no down, no front, no back, no left, no right. After that stage, a migration of subsequent-generation stem cells has to decide what's up and what's down (blastocyst). 'Up' and 'down' don't mean anything in themselves. It's cellular development that decides that. And who decides these placements? Hormones do. You've got an equivalent to your polyps here, because the organism is cilindrically symmetric. Next, stem cells of another generation have to decide what's front and rear. A second axis, perpendicular to the first, defines this, forming a plane with the previous one. Migration is induced with respect to this plane. Now the fact that you've defined two perpendicular directions, in 3-dimensional space, automatically determines the third. This is a peculiarity of 3 dimensions. What is right and what is left is only possible because we've agreed first what's up and down, front and rear. The curious aspect of these corals seems to be that chirality is minimally and elegantly defined, not having to do with migration of specialised tissue, and resembling very much the (minimal) mathematical definition. Why it's fixed once an ancestor organism evolved it that way I think boils down to macromolecules, the very same reason why our liver is on the right, and our children's liver is also on the right. These orientation factors rarely ever change once they've been decided.
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
It's the mirror image of the picture you attached... Picture a human as a perfect cilinder. Now picture an arm growing from somewhere. The human says: 'This is my right arm' Well she may say so, but something's not right. And yes, I'm right.
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
The problem is: In other words, you said the polyps are cilindrically-symmetric. In that case, whatever you call the left, turn around 180 degrees and, voila, it's the right.
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
The problem I see with crowding effects is that one way or the other (one chirality or the other) makes no difference to the effects of getting tangled, as long as all the individuals (colonies or whatever) become helical in the same way. If that were the case, we would see left-handed colonies as often as right-handed ones. Also with eddies and currents playing a role, I would expect to see regional differences. All this, of course, taking at face value: The effect you propose is not to be ignored in many cases. There are mossy plants in New Zealand that grow to exactly the same height, so as to form a collaborative pad that's useful to protect the whole community against frost. Any plant that grows above that is penalised, because it losses protection. With chirality though, it's either this way or the other, --a binary menu of possibilities, shall we say-- which suggests to me a developmental mechanism based on molecular grounds. I'm not sure though, and I wish this OP gets the contribution of experts ASAP. x-posted with @Genady That's interesting. I can't find this information on the web. Can you give me a pointer to that, please?
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
Your assumption No. 1 is a must; otherwise there's no way you can correlate internal chirality with overall growth pattern that displays chirality. It stands to reason. Your assumption No. 2 I don't see as necessary. If you can tell your head from your feet, and your liver-side from your non-liver-side, it's child's play to write an instruction (internal) in your memory that says: If your neighbour is to your left, hold hands and bend this way. Minimize interference is not necessary. In fact, you must interact and correlate. The important thing is to correlate how you bend, how your neighbour bends, and what side you face to them --I think. You can 'amplify' chirality any way you want with these prescriptions --I think.
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
Whether something is a colony or not is not a clearcut biologycal category in my opinion. Endosymbiosis* changed that picture, and while we still talk about "organisms", the distinction is blurry at best. Kelp is a multicellular protist. Eukaryotes have plastids (genetically-independent inclusions). I consider myself a colony that includes intestinal bacteria, my mom's mitocondria, etc. Yet my liver is on the right because my homeobox genes ordered developmental hormones that made my stem cells put it there. *Among other things. 'My liver is on the right' is chirality, not of such sublime beauty as an helical coral. But chirality it is, and monitored by homeobox genes.
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
Take some time to read about homeobox genes and your difficulties will ease considerably. As I said, I'm not an expert, but I do remember development of organism spatial patterns is heavily monitored by homeobox genes and decides what's up, and down, left, or right, where your liver is, and such. Symmetry is also determined by this package of genes, AFAIR.
-
Wire Black Coral helix ?
Thank you. Yes it does apply to tartaric acid and a bunch of sugars, including glucose. Google for "stereoisomers of" and whatever compound you're interested in and you'll get the physico-chemical information. As to the relevance in biology, I don't know. I hope some experts can illuminate aspects of it at least. I'm not one. Whether it's an effect due to the currents, it could be for all I know, if eddies tend to form with a particular chirality, which they do. A Coriolis effect, as you suggest, is possible. Maybe @Genady is also a traveller, and can provide more information. I somehow find it hard to believe that the calcium carbonate scheletons of corals could be shaped by local eddies, but let's see what others think. Interestingly enough, I've googled for "chirality and corals" and I've found that some calcium carbonate coral scheletons are affected by chirality: https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms15066 Corals and chirality seems to be an active field of research, judging by Google Scholar's search results. Most of what I've seen is targeted at a molecular level.