phyti
Senior Members-
Posts
212 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by phyti
-
As Supernerd, why do you ask, you should know. Did you find an error in the paper?
-
Chemistry teaches us that matter exists in lumps and can be deformed. Measure a metal rod, heat it and remeasure it. There are no rigid objects. The attached file explains why length contraction is necessary to resolve the MMX. reflecting circle.pdf
-
You are right, there is nothing to discuss here. From the feedback; lacking clarity and too much detail.
-
You gave the correct word (red). The ellipsis was invented for just that reason. Since there is no largest integer, no one can write it. Sequences are not laid down instantaneously, so it's a real question as to how long to form one that has no end. . If you read below the tree, it says each sequence corresponds to a unique path.
-
In the real world, how long would it take him to write any infinite sequence? Given 0 precedes 1, the tree begins with a repeating zero and ends with a repeating 1, so all sequences will be included between those two. How can p (green) be in the tree, when Cantor says it isn't in L?
-
You begin at L, toss a coin, which selects 0 or 1, move 1 segment/branch, repeat... The choice is always the same, and it's always from L! Repeating 10101... would continue along the lower portion of the tree. The acceleration is just a description for his task, he has more to change than what he has changed. Cantor's list has no end, thus he can't reach it by any means, just as he can't write the greatest integer. I'm just using HIS method to show where it doesn't lead.
-
The paper has been revised many times, and the one linked was not the latest. After reducing it to the bare essentials, it's up for criticism. https://drive.google.com/file/d/0ByCTeSH4WyfPSXRtdUR6OC04RjQ/view?usp=sharing
- 24 replies
-
-3
-
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0ByCTeSH4WyfPTWtMWEtGQjVPQ3c/view?usp=sharing
-
wikipedia tests of special relativity time dilation and length contraction Direct confirmation of length contraction is hard to achieve in practice since the dimensions of the observed particles are vanishingly small. However, there are indirect confirmations; for example, the behavior of colliding heavy ions can only be explained if their increased density due to Lorentz contraction is considered. Contraction also leads to an increase of the intensity of the Coulomb field perpendicular to the direction of motion, whose effects already have been observed. Consequently, both time dilation and length contraction must be considered when conducting experiments in particle accelerators. Don't be ignorant.
-
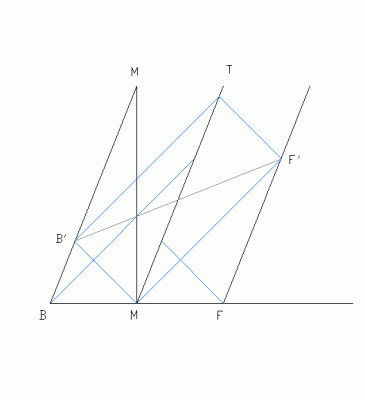
In the M frame, the train is moving to the right, with the viewer T at center, and B and F back and front emitter/detectors. B and F emit simultaneous signals in the M frame, which are simultaneous with the ends of the train, but will not arrive simultaneously for T. In the process of accelerating to a constant speed, the T frame has an altered symmetry. If T polls the F and B clocks, B’ and F’, they show different values. This is a consequence of light propagation speed being constant in space. If T synchs the clocks to his center clock, according to the SR convention, then he has “relative simultaneity”, and perceives B’ and F’ as simultaneous. Notice the path lengths are equal, but out of synch, depending on their origin. Simultaneity is a function of speed, not a property of the frame.
-
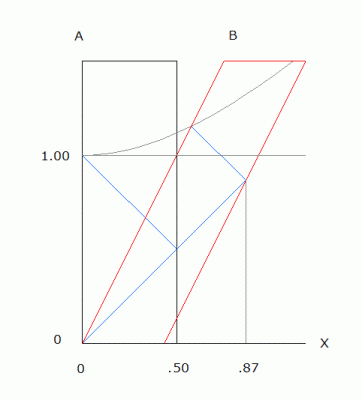
The hyperbola is a constant time t=1, wherever it intersects the path of a moving object. In the A frame (black) light requires 1 unit of time to reflect from the end of a stick .5 units long. If the same measurement is expected in the B frame (red), the same stick requires a physical length contraction. The space between 2 sticks in tandem would increase, not contract. The volume of space remains unchanged.
-
It's a question of simultaneity. Maybe I wasn't clear in #14. The clocks are synchronized in the ship/train at rest, which is equivalent to ground time. When the ship is moving relative to the ground, its axis of simultaneity is skewed (at an angle in a spacetime graphic). If the viewer on the ship polls the end clocks with light, the clocks will return different readings. Per SR the viewer must establish a relative synchronization of of the end clocks using light signals. The procedure is described in the beginning of the 1905 paper.
-
The end clocks are synchronized to the center clock while the ship*is at rest. When the ship reaches high speed, the axis of simultaneity is different from the ground aos. The signals will not arrive at the center simultaneously. If the end clocks are synchronized upon reaching the target speed, then they will emit signals at a preset time, and arrive simultaneously. * A train moving at relativistic speed would be too risky!
-
1. The objects are independent of each other. 2. If they moved at different speeds, that would require space to contract at two different rates simultaneously! 3. There is no known substance to space that can contract. 4. The contraction involves em fields. 5. The solution to the Bell spaceship problem is decided on the basis of the gap increasing as the ships contract, which stresses the connecting "rope". 6. The separation of the objects contracting along with the objects would be perceived by a viewer moving past them at high speed. 7. In the launch frame U, assume the objects contract from the front, while the back ends maintain a constant separation. The gap increases. To maintain a constant gap, the rear object would have to increase speed, or the front object would have to decrease speed. I.e. they could not follow the same speed profile.
- 24 replies
-
-1
-

Why isn't length contraction permanent even though time dilation is?
phyti replied to Ganesh Ujwal's topic in Relativity
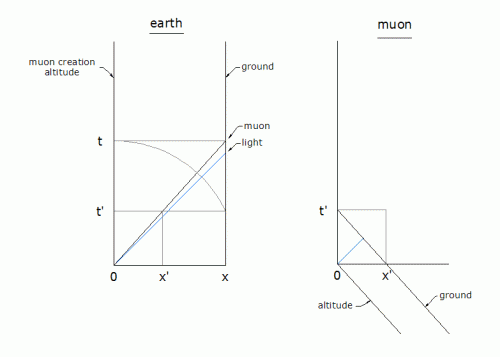
The perception of an observer on earth: muons are created at (x,t)=(0, 0), and move at .9c until decaying at ground level at (x, t). Time dilation slows the muon clock to read t' at x. The perception of an observer moving with the muons: the ground arrives at t', and x'=x(t'/t). Thus the ground is literally closer, as if the universe contracted in the direction of motion. Knowing that the muon motion cannot alter the dimensions of the universe, the effect is from the altered perception of the observer via time dilation. He cannot fault his clock or his biological sense of time, and concludes the universe has contracted as it passes him. This satisfies the reciprocity of the principal of relativity. 1. A clock produces, counts, and accumulates ticks (an arbitrary interval of activity). If clock A separates from an identical clock B, and later rejoins B, it will have ticked less. While in relative motion, each will appear to run slower than the other, via doppler effects, since clocks can be treated as frequencies. This supports the principle of relativity, in that observations are reciprocal, thus observers with the clocks see the same physical phenomenon. Because light speed is constant, any device requiring light interactions will occur slower, the faster the device moves relative to light. Since all objects are in motion, all clocks are losing time to various degrees. Any age difference between A and B requires a comparison of both at the same location before and after the excursion by A. In the simplest case, the one that changes speed to rejoin, will have aged less for the excursion. In SR there is no speed whereby the clock can regain lost time. If A rejoins B, its rate will change to match that of B. 2. Length contraction occurs when object motion affects the em fields that determine the separation of particles. This also results from constant light speed, and the calculations involve the same function of speed, the gamma factor, as used for time dilation. When the object slows to its original speed it regains the original length, i.e. it doesn't loose length. -

Michel's Q.s about time co-ords - Split from "what is time?"
phyti replied to michel123456's topic in Relativity
It’s misleading when misinterpreted as a 2D roadmap, and viewing the longer world line as the x=vt relation, when it should be the t=x/v (inverse) relation. Even without relativistic effects, and all other factors equal, the faster clock will reach the target showing LESS time. -

Michel's Q.s about time co-ords - Split from "what is time?"
phyti replied to michel123456's topic in Relativity
If they separate and later rejoin, both could not have maintained the same speed for the trip.If you use a Minkowski drawing, which shows the speed profile or history of each, it demonstrates why the shape of each profile determines the elapsed time. -
You can't travel into the future. The future is what will happen later. If you want to slow your rate of aging, that's another subject.
-
What about the cycles?
-
Motion is the behavior of multiple objects. It’s observing the change of positions relative to one of the objects selected as a reference. Obviously it is not an object property but a group property. If an object wanders into the vicinity of Earth, it acquired its velocity at some time in the past, if we accept cause and effect. It could be a relic from planetary formation thousands of light years distant, but we have no way of knowing its history. Yes, the propagation speed of light in space (ideal vacuum) is constant and independent of its source. It serves as an absolute reference for speed, as in the expression v/c used in SR. If we could set a marker at the spatial location of emission, we would have a fixed point of reference for subsequent calculations. Imagine finding a productive fishing spot and leaving a buoy (no anchor) at the site. The next day you return to the buoy. How do you know it’s the same spot? That’s the problem since light emission leaves no residue for the CSI. If you analyze the physical phenomena in a moving test frame relative to a theoretical absolute static frame of reference, you discover the phenomena occur as if the test frame is not moving. Fascinating to discover but greatly simplifying analysis and application of rules of science. Eg., NASA can calculate an orbit without knowing the center of mass of our galaxy.
-
Maybe this will help. Time dilation and aging for a pair of clocks.doc
-

Does the single speed of light mean an absolute frame of reference?
phyti replied to robinpike's topic in Relativity
Why does the absolute fixed frame keep coming up? Not because people can’t think. There are many creative minds in the world, but all aren’t interested in physics. It could be because given the fact of constant light speed in space, the inquiring mind expects a constant feature in space itself. If we begin with the obvious, events don’t move, then it’s simple to form a hypothetical fixed frame of events. An analogy would be watching fireflies at night in your yard. If you are a forming a theory involving light and object motion, you would require such a frame when expressing relative light motion using terms like (c±v). After developing the theory, you find that the moving frames behave like the fixed frame, with respect to the rules of physics. The fixed frame served a purpose, but because it is not observable does not imply it is non existent. -
Space contains many photons moving in random directions from random sources. Considering the earth intercepts only a small pencil of light from any source, the major portion moves past us. In this sense space is ‘full’ of light. Questioning what portion of the sun’s radiation is intercepted by the earth, consider the earth a disc projected onto a spherical surface with a radius of 93 million mi. Assuming no errors, if the surface was scaled to the radius of the earth, the disc has the diameter of a nickel. Imagining the amount of heat received on one hemisphere on a cloudless day, the total output of the sun has a high boggle factor.
-
Don't forget father time!
-
Thanks for all responses. I'll have to read suggested sources to learn more.