phyti
Senior Members-
Posts
212 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by phyti
-
I didn't believe you could get free energy to accelerate toward a larger mass, and that a typical mass supplied the energy for a typical g-field. Is it possible to consider the newly captured mass as contributing energy to the BH g-field? (still thinking conservation of energy)
-
Does the g-field require energy to persist (after collapse), and if so, what is the source?
-
My brother asks me this question for which I have no answer. If gravitational effects are propagated as waves at light speed, and light cannot escape from a black hole, how do the g-waves escape?
-
Unless Fred is considering the acceleration time for anaut and two clocks as not uniform/not simultaneous,which would mean difference in speed from front to back, until reaching target speed. Just trying to see his pov.
-
What do you mean by "a speed-up of time dilation"?
-
An object in free fall receives a uniform acceleration for all it's components, thus there is no sensation of acceleration. Think of astronauts experiencing weightlessness in a plane flying a parabolic arc. The person on the ground experiences acceleration, which you can verify by standing on a scale. Gravity is always on.
-
Einstein worked with 'time' as distinct from space, and subjective or observer dependent. It was Minkowski who generalized the equations to mathematically treat 'time' as a dimension. He then derived the coordinate transformations,based on the the two postulates. For every speculation with positive results, there are hundreds without.
-
The mutual observations of clocks are symmetrical, but demonstrate doppler shifts, not aging or accumulated time. Aging can only be determined when the clocks are reunited. In the simple case, The cast is A(naut) and E(arth). E records: A leaves, moves inertially for t1, reverses direction (due to rocket) for t2, and returns in t3. A records: E leaves, moves inertially for t1', reverses direction (due to g-field) for t2', and returns in t3'. Note, each has an explanation for the non inertial part of the trip, and A senses it, using the equivalence principle, and E does not. The A times will be less, since his speed profile varies from the constant speed of E. This is the point where you have to avoid the road map interpretation of the Minkowski drawing. It's not necessarily a longer path. It's a different speed profile or path, and the relation is t = x/v, i.e., faster speed, less time. (At least one segment will be faster than that of E.) Consider acceleration as establishing the rate of time dilation. Acceleration is not fictitious, since it can be measured (every time you weigh yourself). What if A and B are both anauts in ships, and at max separation, each accelerates to rejoin, which one counts? This is an example showing acceleration is not a factor. twin clocks-no accel140402.doc
-
If you prove there are only a finite number of twin primes, then it implies a finite number of consecutive multiple prime pairs, 4, 6, etc. It seems you are just restating the tpc in a different way. Quartets depend on twins, but the reverse is not true.
-
The only asymmetry that matters is the difference in speed profiles, as drawn on a Minkowski diagram. The profile (path) that varies from the the constant speed (straight line) one, loses more time. It's permanent and results in a differnce in aging. In the common simple case, only one twin changes speed, thus the speed change has to be assigned to that profile. It's a coincidence, but not a cause. If both twins changed speed, the aging would be decided by the inertial portions of the profile. Doppler shift is nothing more than watching clocks.If both count ticks, the answer is only apparent IF they reunite. There is a paper in post 23 that explains this, if anyone is interested. Of course, if it's explained, there would be no debate.
-
Eliminating 2 and 3, all primes are of the form 6x-1 or 6x+1, i.e. twin primes. The twin prime conjecture has not been proven yet. If there are gaps in the twin primes, that implies bigger gaps. It would seem that solving the tpc is more fundamental than searching for other intervals, 4, 6, etc.
-
The motion is symmetrical, but the physics is not. When you reverse your course to return, you experince inertial forces. Via the equivalence principle, you can assume a pseudo rest frame in a gravitational field for the duration of your reversal. The earth reverses and moves toward you, as a result of that g-field (your perception by choice). If you ask them if they felt any forces, they will say no. No symmetry there. Even without acceleration, the case is asymmetrical, since the speed profiles are different, which results in differential aging.
-
Assume distance markers in the T1 frame. They agree to reverse at .6 ly. The expression t=x/v works in either frame. T2 calculates t=.6 ly/.6c=1y. Unable to detect his time dilation, he arrives at .6 ly when his clock reads .8 y, and concludes the universe has contracted by a factor of .8. By symmetry, his trip takes 1.6 y. The contracted T1 frame is his interpretation of his own time dilation, and the markers are now contracted distances. If T2 wants to reverse at .48 ly, his clock would read .64 y. Here is a geometric method for aging. Time dilation and aging for a pair of clocks.doc
-
The process of elimination still works! Thanks
-
JVNY initially questioned why the setup is considered an inertial frame. Isn't this because Einstein considered the rotating disk as an inertial frame with a g-field?
-
There is also the Hafele-Keating experiment with clocks moving with and against earth rotation, one gains, one loses.
-
Consider the loop as a circle and consider angular velocity relative to the center. The light moves independently of the setup, while the setup rotates.
-
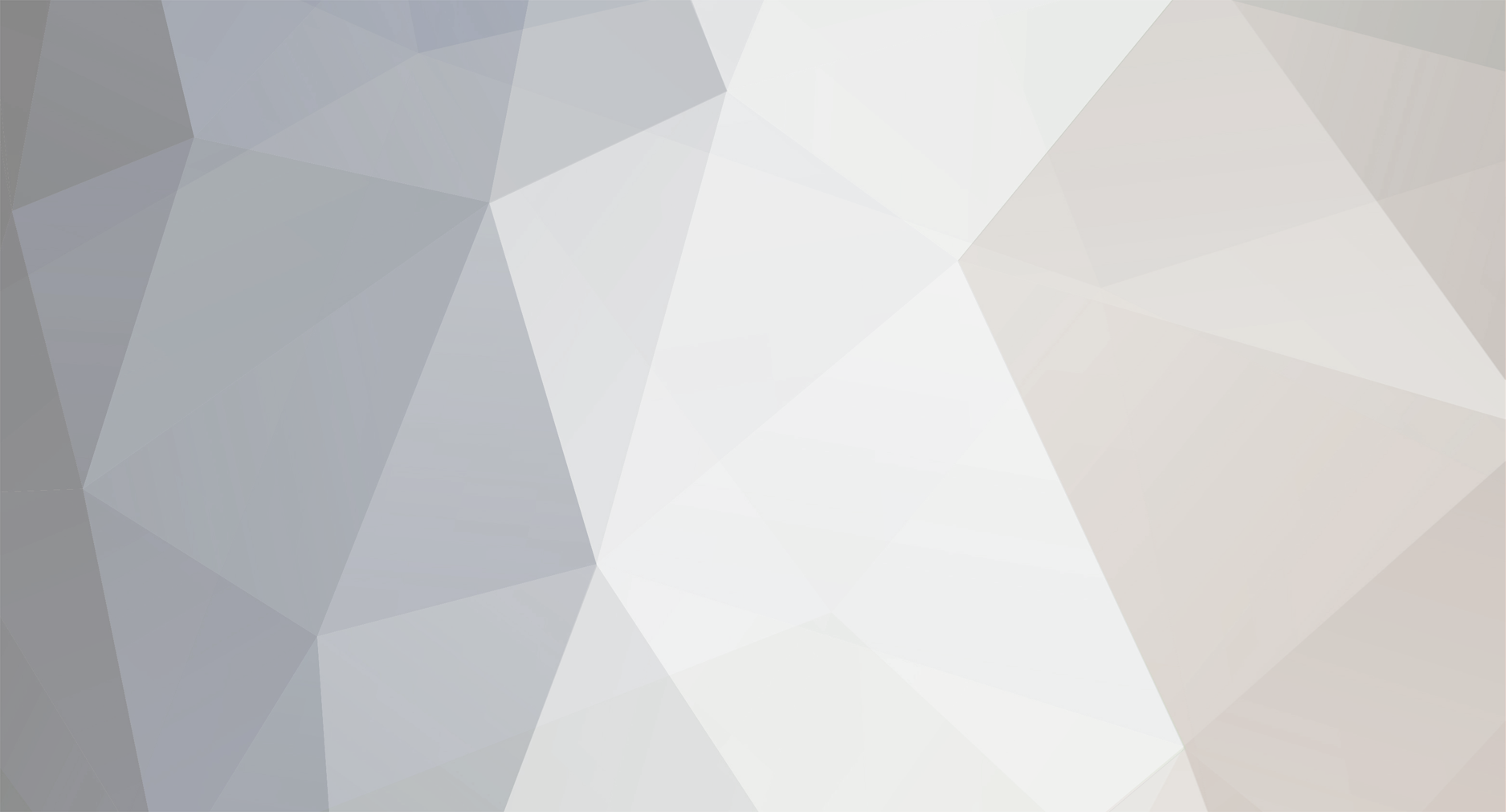
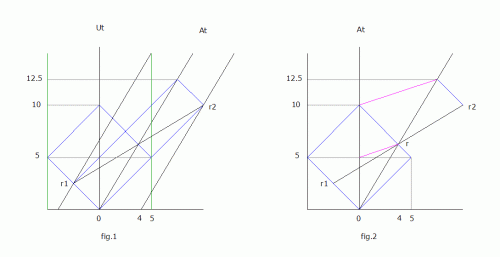
If we generalize that all observers are moving, a reasonable assumption in a dynamic universe, then all simultaneity is apparent/relative, as indicated in fig.1 of my previous post. It’s the perception (in the mind) of simultaneous events. The moving observer always measures the ‘rest’ length for his spacecraft no matter what his speed and effects of length contraction. The observer in the center of a reflective ring perceives simultaneous reflections from all points on the circumference no matter what his speed, and in contrast to all other observers with a different velocity, who see the same reflections over an interval of space and time. My point is, it’s altered perception. The observer is not exempt from the effects of time dilation and length contraction. Unless a way is discovered to measure the speed of the observer to that of light, there is no way to assign observer independent coordinates to an event. If you consider r1 and r2 in fig.1, notice a forward event r2 occurs after the halfway point for the light path, and a rearward event r1 occurs before the halfway point. The SR convention including the synchronization of clocks if located at r1 and r2, is just to maintain the appearance of a pseudo rest frame for the moving observer. It has no significance beyond this (in agreement with the previous quote by A.E.
-
md65536; In fig.1 A is at the center of his black ship 10 units long and moving at .6c past U at the center of his green ship of 10 units long. When A and U are at x = 0, a flash occurs sending light in opposite directions along the x axis. Signals reflect from the ends of the U ship at t = 5, and return to U at t = 10. Signals reflect from the ends of the A ship at t= r1 and t = r2, and return to A at t = 12.5. For U the signals from the ends of his ship are simultaneous, and those for A are not. For A in fig.2, r1 and r2 form a relative axis of simultaneity, with both events assigned to event r on A's timeline. The magenta line transforms U time to A time (12.5*.8 = 10), i.e. equal round trip times for A and U. The magenta line from r to (5, 0) confirms this. Events as perceived in a pseudo rest frame are perceived the same as in an absolute rest frame. Notice how the relative axis of simultaneity (r1-r2) is a true representation of the coordinates (x, t) of the events. Now enter the problem always lurking in the background, the inability to measure v/c, and therefore using reflected signals. If we stop here with the 2-way time, we have the most information to be gained since to continue is speculation. Also neither the actual coordinates (per this example) or those assigned via the SR convention can be verified, due to the v/c issue. The simultaneity convention gets a plus for consistency and a minus for relocating events (events can't move). To quote A. Einstein: "That light requires the same time to traverse the same path A to M as for the path B to M is in reality neither a supposition nor a hypothesis about the physical nature of light, but a stipulation which I can make of my own freewill in order to arrive at a definition of simultaneity."[1] I would agree with you, it is superfluous. Hope this might help you in your consideration of alternate ideas. 1. Relativity The Special and the General Theory Albert Einstein 1961 Crown Publishers Inc. pg 23
-
There is confusion here between the event and the perception/detection of the event. SR is also a theory of perception. If you wonder if a star 10 ly distant is still there, while looking at it, you will have to check every night for 10 yrs or until it disappears, whichever comes first. Since the speed of an object relative to light cannot be determined,relative simultaneity is the next best thing. Synchronizing the fore and aft clocks maintains the appearance of a pseudo rest frame.
-

Question about relation acceleration en special relativity
phyti replied to Rettich's topic in Relativity
The B clock will have ticked 10 yr while your clock ticked less, depending on your speed. As a result of this you will interpret the distance as less than 10 ly. You will see an increase in frequency of B signals. All this per SR. -
I think p.googol is considering the dilated (stretched) interval, not the proper (local) time. I.e. the tick is never completed.
-
Awareness/detection of an event is always historical or after the fact. Thus it is impossible for an event and its detection/awareness to be simultaneous.
-

Maintaining the appearance of fixed distance in spite of length contraction?
phyti replied to md65536's topic in Relativity
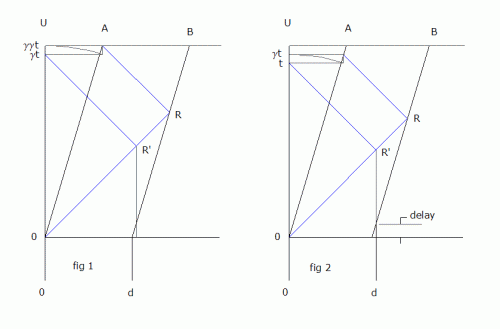
Try this. In fig.1 A and B are separated by a distance d in frame U with synchronized clocks. At t=0 A and B accelerate to a target speed v. A measures the distance to B with light, which returns at Ut =2γγt, and t = d/c. Time dilation transforms (via the arc) Ut to At=2γt, which per SR convention, places the reflection R at R' relative to A. The gap has increased by a factor of γ. If A and B were connected as a rigid body via em fields, d would have contracted, removing one order of γ, as required in the MMX. In this case, A and B move independently, so length contraction must be done by another method, such as delaying the acceleration for B. In fig.2 after B delays acceleration, the A measurement places R at R' relative to A, with a gap=d. Since each have the same velocity, the results are reciprocal. Note that the A clock will be slightly behind the B clock as a result of the delay. With a = v/c, the delay t1 = d/a(1-1/ γ) The acceleration was instantaneous for the purpose of simplification. -
md65536 I could not follow your reasoning on the subject. It seemed too complicated for such a simple idea. I lose interest in any logical arguments with a high content of 'lemons', and cannot offer an opinion.