

SergUpstart
-
Posts
501 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
1
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Posts posted by SergUpstart
-
-
I briefly read the text that is indicated by the link in the first post of this topic. What I would like to note is that there is no mention of the costant alpha=1/137 in the text, and this is the most important physical constant.
0 -
1 hour ago, Aeromash said:
The main goal is to find a single equation that describes the entire Universe.
It was Hawking's dream.
From my point of view, the main formula of physics is not E=mc^2, but
1 -
2 hours ago, Markus Hanke said:
It’s very frustrating when something is being explained at length, and then goes ignored.
I'm sorry? But the main thing in this issue was the Mach principle, it was not discussed earlier.
0 -
On 9/8/2021 at 3:41 AM, iNow said:
One of the best ways to do so is to enforce tax laws and prosecute tax evasion.
I remembered how in 1998, a couple of weeks before Russia's default, Sergey Kiriyenko (then he was the prime minister of Russia) came to the Gazprom office and demanded to pay all taxes.
0 -
On this forum, they communicate in English, take the trouble to make a translation. With the help of Yandex-Translator, it will take a couple of minutes https://translate.yandex.ru
( На этом форуме общаются на английском языке, потрудитесь сделать перевод. С помощью Яндекс-Переводчика это займет пару минут https://translate.yandex.ru)
1 -
23 hours ago, Markus Hanke said:
In general spacetimes, the concept of gravitational potential is replaced by the metric
Does the metric reflect the Mach principle? The fact that the gravitational potential of the Universe is the sum of the gravitational potentials of all particles in the universe is essentially a mathematical formulation of the Mach principle.
-1 -
10 hours ago, Markus Hanke said:
There is no such thing as “gravitational potential” in general curved spacetimes - the concept only makes sense under some very special conditions, and certainly not for large regions of the universe. I seem to remember that this has been pointed out numerous times in past threads on here.
The gravitational redshift can be expressed as
where
is the gravitational redshift,
is the optical clock transition frequency,
is the difference in gravitational potential, and }
denotes the violation from general relativity.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitational_redshift
It is impossible to do without the gravitational potential.
If you look at the definition of the gravitational potential, then this is the energy that must be communicated to a resting body of a unit mass so that it flies to infinity. Probably, the fact that this energy is difficult to calculate from the GRT equation does not mean that this energy does not exist.
In addition, it follows from the definition of the gravitational potential that it is equal to the square of the escape velocity from a given point in space. Does the escape velocity exist?
10 hours ago, Markus Hanke said:I’m pretty sure he didn’t actually say this, since metric expansion is itself a gravitational phenomenon. Can you provide an exact reference, so we can see the context?
Metric expansion means simply that measurements of distances depend on when you make them - the results get bigger (on large enough scales) as you age into the future.
I can't give you a link. Hawking's books do not contain formulas, so it is convenient to listen to them in audio format, which I did. But here I found the link http://kosmos-x.net.ru/news/kuda_rasshirjaetsja_vselennaja/2018-08-09-5403 It is in Russian, but now this is not a problem, since many browsers automatically translate the text. Here is a quote from there, Space expands only where the gravity of matter and energy are limited. Therefore, space does not expand inside galaxies or complex galactic groups, but only between galactic clusters and superclusters.
0 -
53 minutes ago, swansont said:
Good. Now please explain what you mean by the fifth force, and why you phrased it as if this were mainstream physics.
Here's what you wrote "Frankly, this does not seem to be a difficult concept; the concepts of motion and force it evokes are Newtonian. If gravity in a region is strong enough to prevent expansion, that’s what happens. "
I just asked a counter question, the meaning of which is "Won't we need the fifth interaction to explain the nature of this Newtonian force ?"
0 -
5 minutes ago, swansont said:
Expansion of space is not a force.
Yes, the expansion of space is not a force. The expansion of space is a change in the scale of distances. In the first post of this topic, I offered my explanation for the fact that we observe a change in scale only in intergalactic space.
0 -
45 minutes ago, swansont said:
What leads you to this conjecture? There is no fifth interaction in mainstream physics.
Then which of the four interactions is this force associated with??
If with gravity, then it is necessary to introduce a negative mass, because this force, the force of repulsion.
0 -
2 hours ago, swansont said:
Frankly, this does not seem to be a difficult concept; the concepts of motion and force it evokes are Newtonian. If gravity in a region is strong enough to prevent expansion, that’s what happens.
Does this mean that there is an anti-gravitational force in the universe and is this force a manifestation of the fifth fundamental interaction ?????
0 -
25 minutes ago, beecee said:
My apologies...Off with my head on on goes a pumpkin!!😬 The title threw me actually, "Why does it seem to us that the universe is expanding where there is no gravity"
A correct remark, in the title it would be necessary to write " Why it seems to us that the Universe expands ONLY where there is no gravity"
0 -
46 minutes ago, beecee said:
Gravity actually decouples regions of high mass/energy density from the overall expansion rate.
Isn't that what I'm talking about? Where there is gravity, more precisely, where gravity is stronger, the change in the distance scale is slower than where gravity is weaker. And we see only a relative change in scale.
0 -
Hawking wrote in his book "A Brief History of Time" (or in "M-Theory" ) that it is a big mystery that the universe expands where there is no gravity. That the expansion of the universe cannot be explained by a simple change in the scale of distances. After all, if all the sizes and distances, from the size of atoms, the radius of the Earth, the distance from the Earth to the Sun, the diameter of the galaxy and further to the distances to distant galaxies, would change in the same number of times, then we would simply not notice it.
This is indeed the case. Thus, the distance standard changes more strongly in intergalactic space than in galaxies where there is gravity.
And it's easy to explain it. The distance standard decreases in proportion to the gravitational potential. Let's assume that in intergalactic space the gravitational potential is equal to Phio , and we are inside the galaxy, where the total gravitational potential is equal to Phio+Phig, where Phig is the gravitational potential of the galaxy .
Now let's assume that after some time the gravitational potential of the Universe between the galaxies will decrease and become Phi1.
Then the total gravitational potential inside the galaxy will become Phi1+Phig.
It is easy to see that the gravitational potential between galaxies will decrease by a large relative amount, because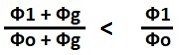
For example, if Phio is taken as 100%, Phig as 2%, and Pfi1 as 98%,
then the gravitational potential inside the galaxy will become 0.98039% of the initial one, and between galaxies it will become 98%.
The distance scales will also change accordingly, but we will not notice that our distance scale has become 0.98039% of the previous one, we will only notice that the distances between the
galaxies have increased by 0.00039% .
That's why it seems to us that the universe is expanding where there is no gravity.0 -
Russian President Vladimir Putin, in an interview with schoolchildren, called the war that Peter I waged with the Swedes a seven-year war, instead of a Northern one. The schoolboy pointed out the mistake to Putin. Some political scientists have already said that Putin made this mistake deliberately to make the student feel smart.
0 -
11 minutes ago, beecee said:
If you call gravity a force, you are essentially in the Newtonian domain and the most well known and used domain with everyday run of the mill calculations.
If you call gravity as geometry, specifically spacetime geometry, then you are in the GR domain, and essentially when high accuracy is the goal.
The author of this article points to 17 unresolved problems in GRT http://sergf.ru/litgen.htm
He believes that these problems can be solved within the framework of the LITG but using the GRT metric. In LITG, gravity is a force.
The above features of general relativity show that most of problems of theory of gravitation may be removed by use of LITG with the idea of using a metric similar to metric of general relativity, as a first approximation to a more accurate theory of gravitational field. In this case, general relativity becomes an extension of special relativity and has its function in the case when the results of spacetime measurements are dependent on existing in a system of electromagnetic and gravitational fields produced by sources of charge and mass. If there were not of influence of gravitation on propagation of light, similar to effects of deflection of electromagnetic waves from the initial direction, changing the wavelength and speed of its propagation, instead of general relativity would continue to operate special relativity and would be valid LITG. As well as special relativity is not a substitute of electrodynamics then general relativity can not be instead of LITG or electrodynamics, which have arisen and exist independently of general relativity. From the point of view of LITG, Einstein-Hilbert equations for metric are needed to determine the metric tensor that defines effective properties of spacetime for a given energy-momentum distribution, and changes metric tensor of flat Minkowski space. After finding the metric tensor from the equations for the metric, electrodynamics and LITG are not just Lorentz covariant (it is a special case of covariance that take place only in special relativity), but covariant for all the possible systems of reference in which the metric can be found. It follows from the possibility of writing the equations of these theories in the vector and tensor form. Then LITG becomes the
0 -
Every year, the warm summer period increases by an average of 10-15 days, respectively, the winter period decreases. Thus, it is impossible to exclude the fact that winter in Ukraine will not be at all soon.
This was warned by the director of the Ukrainian Hydrometeorological Center Mykola Kulbida. According to him, this may happen in 20-25 years,
0 -
2 hours ago, Muster Mark said:Light from distant objects is being stretched by the expansion of the universe, such that light that was ie blue (short wavelength) gets shifted to red (long wavelength). As short wavelength light has inherently more energy than long wavelength light, and as energy cannot be destroyed, where does the lost energy go when light is redshifted?TY!
Look at the model of the universe with zero energy. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zero-energy_universe The energy of photons in the Universe decreases and at the same time its gravitational energy decreases.
0 -
2 hours ago, swansont said:
Light doesn't leave or enter the universe. We are inside forever.
Are we living inside a black hole???
0 -
12 hours ago, Airbrush said:
What is "all-over inflation"?
Inflation in the economy is the depreciation of the dollar, and inflation in the universe is the depreciation of the meter.
0 -
15 minutes ago, swansont said:
Bottom of what? Ascent of what? You are saying things without giving context.
Bottom - the lower point from which the photon rises to the height h
17 minutes ago, swansont said:I don’t see how this means anything. We’re talking about atoms. Fine structure and hyperfine structure refers to energy level splitting. There is no such thing as ultra-thin structure.
I'm sorry, naturally an hyperfine structure. I use an online translator for communication and such incidents happen.
0 -
23 minutes ago, swansont said:
Why do clocks that don't rely on photons (e.g. quartz oscillators) feel the same effects?
Have they been detected? Does the accuracy of a quartz watch allow you to detect these effects?
24 minutes ago, swansont said:non-medzhu? What is that?
A typo, it was meant that a transition is used that does not change the main quantum number
28 minutes ago, swansont said:You mean the redshift that you have yet to calculate for the conjecture you are championing? Why is there no calculation?
How do you get from your formulas to 4gh/c^2?
I wrote above that According to Yanchilin's theory, the atom at the bottom emits a photon at a frequency with a violet shift of 2gh/c^2, but going up it experiences a shift to the red side by 3gh/c^2. If, during the transition without changing n at the bottom, a photon is emitted with a shift to the red side gh/c^2 and there is another shift by 3gh/c^2 during the ascent, then the total shift will be 4gh/c^2.
35 minutes ago, swansont said:Spin-orbit is the fine structure. The clock transition is in the hyperfine structure.
e.g. in hydrogen, it's the fine structure is splitting of the excited P state. The hyperfine structure is seen in the ground state
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/quantum/hydfin.html
The spin-orbit interaction is not involved in the atomic clock operation.
Ok, I will deal with an ultra-thin structure.
0 -
I found an explanation in the framework of V. Yanchilin's quantum theory of gravity that when approaching a massive body, the course of the atomic clock on caesium slows down.
V. Yanchilin explained the increase in the frequency of photons emitted by an atom when approaching a massive body, relying on the Niels Bohr model of the atom. According to this model, an electron in an atom can only be at strictly defined energy levels, each level corresponds to its own
the radius of the orbit.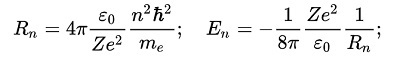
According to the quantum theory of gravity, when approaching a massive body, the square of Planck's constant decreases inversely
according to the absolute value of the gravitational potential, this means that all the radii of the orbits in the Bohr atom model also decrease
inversely proportional to the absolute value of the gravitational potential. In the formula for the energies corresponding to the orbits of
the radius of the corresponding orbit is in the denominator, which means that the electron energy for each energy level
increases, and therefore increases the energy that is transferred to the photon that is emitted during the electron transition
from a higher energy level to a lower one. The frequency of the photon increases accordingly.And now let's look at how the cesium atomic clock works. In them, the frequency is set by the electron transition with non-medzhu energy
the levels of the model of the Bohr atom, and the transition of an electron between sublevels, which are formed by the splitting of one of the levels due to spin-orbit interaction of the electron's magnetic moments. For the energy of such a transition, there is the following formula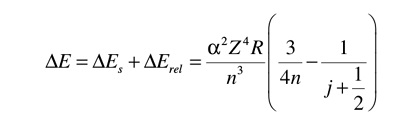
In this formula, the radius of the orbit is not in the denominator and in the numerator, which means that when approaching a massive object
the energy of the photons emitted in the transition between sublevels, not increases and decreases, thus decreasing their frequency and
therefore, the course of a cesium atomic clock.
It follows from the above that the deceleration of the current of the atomic clock does not occur in spite of, but in full accordance with the quantum theory of gravity.
To finally decide which theory is correct, the quantum theory of gravity or the general theory of relativity,
we need an experiment with a clock whose frequency is set by the transition of electrons between the allowed energy levels of the Bohr model.
But, unfortunately, there are no such watches yet.
In addition to the above, it should be added that another effect can be detected here. For an external observer, the photons are located at the top,
the photons emitted during the transition between such sublevels should experience a stronger redshift, 4gH/C^2, instead of gH/c^2 for photons emitted at
normal transitions.
From this point of view, you should pay attention to the wavelength of 21 cm, because it is emitted by hydrogen during the transition between sublevels.
If it is possible to measure the red shift at a wavelength of 21 cm for a distant galaxy, and it turns out to be relatively large,
than the red shift of the spectral lines of other chemical elements, this will testify in favor of the quantum theory of gravity.0 -
I have an idea how to make long-range trucks more efficient. They must have combined wheels that will allow them to move both on rails and on highways. For the transfer between remote cities, trucks are linked and the locomotive takes them from one city to another, upon arrival at the place, they are uncoupled and each goes to its destination.
1



Доказательство гипотезы Больших Чисел Дирака. Proof of the Hypothesis of Large Dirac Numbers.
in Speculations
Posted
What do you think is the smallest particle and what is its radius???