

SergUpstart
-
Posts
501 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
1
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Posts posted by SergUpstart
-
-
On 12/5/2021 at 8:40 AM, iNow said:
Intelligence suggests Russia is planning to invade Ukraine in January apparently with the intent to take it over. Likewise, China has been stepping up plans to seize Taiwan. Have been talking about it for years, but seem to sense more opportunity in todays global political climate.
Should US respond if/when either of those two things happen? If so, how and for how long? Does your answer change if both events happen at the same time?
And if Aliyev and Erdogan also seize Armenia
Earlier, Aliyev had already stated that Yerevan belongs to Azerbaijan
0 -
On 12/4/2021 at 10:05 PM, joigus said:
Another thing is that ε0 is not really a constant of Nature. Rather, just an artifice in the choice of units for electric charge. Stick to Heaviside-Lorentz units and there's no ε0 . It disappears!
It seems to me that a more important physical constant is 4 *Pi*G*epsilon0, which shows how many times stronger bodies with masses of 1 kg interact gravitationally stronger than two charges of 1 Coulomb at the same distance. The dimension of this constant is Сoulomb^2/kg^2 that is, it does not depend on the distance scale.
0 -
2 hours ago, TheVat said:
Ukraine, with its central location, and having major NG and mineral resources, and being one of the planet's major grain exporters, and having received some serious commitments from the US and European allies, and being headed towards NATO membership, might be a more significant bone of contention, and maybe even rise above our domestic catnip issues. It will be ugly when it heats up. But I'm not scanning the real estate ads in Auckland yet. Maybe I should.
In 2014, Putin could have seized the whole of Ukraine, but limited himself to Crimea. Putin only needs the opportunity to export gas to Europe. He can send troops into Ukraine only in response to Ukraine's actions, which may be the offensive of Ukrainian troops on Donetsk or the blockade of Tiraspol.
0 -
41 minutes ago, A_curious_Homosapien said:
I heard about fly wheel battery systems and after reading a bunch of articles and watching some videos about it I have an Idea. Basically the fly wheel looses it's rotational energy only due to friction(or am i wrong?), so if I we are able to eliminate all the friction forces by taking it to space where it won't take much energy to elevate it with magnets and also by creating vacuum, will I be able to create unlimited energy since the wheel will keep spinning for ever(or at least for drastically longer period than the current ones)?
Even an ideal flywheel will lose energy if you take it away from it. So you won't get unlimited energy. And if you mean storing energy for an unlimited time, then a superconducting ring with a current or a vacuum capacitor is better.
1 -
On 11/15/2021 at 3:11 AM, StringJunky said:
Putting it all together: the US was heading towards authoritarianism.
The movement towards authoritarianism is a global trend. Xi Jinping, Putin, Lukashenko, Erdogan, Aliyev, Maduro...
0 -
3 hours ago, exchemist said:
Entanglement isn't a process, it's a state.
And the collapse of the wave function is just a process. And instantaneous.
0 -
On 11/10/2021 at 10:00 AM, bangstrom said:
Can you give us some examples where interactions between light and matter can't be explained as a wave. The photoelectric effect has been discussed and the discrete nature of photon termination can also be explained as a wave without recourse to the simplistic analogy of particle impact. I don't find either of these as convincing evidence for the particle nature of light or am I missing something?
The sensitivity of the human eye allows detecting a stream of 100 photons, but the frog's eye can detect even single photons. Therefore, if you move away from the glowing flashlight in the void and darkness, a person at some distance will stop seeing the flashlight. But the frog will always see the flashlight, but from a certain distance the light of the flashlight will blink and the frequency of blinking will decrease with increasing distance.
0 -
6 hours ago, MigL said:
Yet some people still claim quantum particles MUST be either a particle or a wave.
While the particle is spreading, it is a wave, but at the moment of absorption it becomes a corpuscle. Isn't it?
0 -
37 minutes ago, swansont said:
Can you re-phrase the question?
Actually, the question was asked to the author of the previous topic, who was trying to find a classical explanation for the results of the experiment with electron diffraction at two slits. And it was set to show that it is impossible to find classical explanations for quantum effects.
0 -
And can you explain the results of the Stern Gerlach experiment, which showed that the spin of a charged particle can have only two values, plus or minus 1/2????
0 -
1 hour ago, amshion said:
The big bang theory is very vague, it doesn't explain how the matter was created to cause the big bang you would need energy but where did the energy come from. lets say this universe is a simulation, the universe that created our universe how was that universe created or is their a god but what created the god? in science matter cant be created by nothing it requires energy.
Matter and energy arise and disappear constantly in accordance with the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. So the origin of the universe is most likely a quantum effect. God is not needed for this.
0 -
7 hours ago, bangstrom said:
I understand the evolution of the universe as a several billion year emergence from a gravity well with the BB at the very bottom
Yes, and after BB, the universe rises in a gravitational well. This means that the red shift in the spectra of galaxies has not only a Doppler component, but also a gravitational one.
0 -
As Hawking said, God is not needed to explain the origin of the Universe, God is superfluous.
0 -
19 hours ago, Markus Hanke said:
Scalar curvature (I presume you mean the Ricci scalar) only measures one particular aspect of curvature; it can’t account for all necessary degrees of freedom.
Sure. If we take the above formula g=C^2/r, then it gives only the module g, but g is a vector.
0 -
Although I see an error in the above quote, near a more massive body, r will be smaller, not larger.
0 -
17 hours ago, Markus Hanke said:
What do you mean exactly by ‘radius of curvature of spacetime’?
The radius of curvature of spacetime is a quantity inversely proportional to the scalar curvature of spacetime. It has the dimension of length. For weak gravity there is an approximate formula r=c^2/g
The graphic shows a projection of the path followed by a falling object in four-dimensional spacetime into three-dimensional space. Objects fall because they follow geodesics in this spacetime. They are of maximal length, maximizing proper time. For all trajectories, the initial angle or speed does not matter and the curvature is the same,
 . Near a very massive object such as a black hole, this value is considerably greater. https://demonstrations.wolfram.com/SpacetimeCurvatureForAFallingObjectNearTheEarthsSurface/
0
. Near a very massive object such as a black hole, this value is considerably greater. https://demonstrations.wolfram.com/SpacetimeCurvatureForAFallingObjectNearTheEarthsSurface/
0 -
@Marcus Hanke said "So visual appearance in curved spacetime does depend on the observer, because different events are linked by different sets of null geodesics."
Exactly. The acceleration of gravity is related to the radius of curvature of spacetime by the approximate formula
r = c^2/g or g=c^2/r
In the reference frame of a remote observer, the radius of curvature of spacetime increases by k times, as do all distances, and, accordingly, the acceleration of gravity decreases by k times, as mentioned above.
0 -
5 hours ago, Markus Hanke said:
What do you mean by “observe”? You mean visually?
Yes
0 -
There are not one equivalence principle, but two, strong and weak.
It is necessary to distinguish between "weak equivalence principle" and "strong equivalence principle"[13]. A strong equivalence principle can be formulated as follows: at each point of space-time in an arbitrary gravitational field, one can choose a "locally inertial coordinate system", such that in a sufficiently small neighborhood of the point under consideration, the laws of nature will have the same form as in non-accelerated Cartesian coordinate systems of SRT, where "laws of nature" mean all laws of nature[14].
The weak principle differs in that the words "laws of nature" are replaced in it by the words "laws of motion of freely falling particles"[13]. The weak principle is nothing but another formulation of the observed equality of gravitational and inert masses, while the strong principle is a generalization of observations of the influence of gravity on any physical objects. https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Принцип_эквивалентности_сил_гравитации_и_инерцииI believe that these equivalence principles should be applied depending on the situation.
If the same system is observed by several observers in different places of the gravity well, they should all observe the same picture only at different time scales. There is a strong equivalence principle at work here.
If one observer observes several identical systems but located in different places of the gravity well, then only a weak equivalence principle should work here.
0 -
12 minutes ago, swansont said:
We have requirements in speculations, demanding a certain level of rigor. We also require discussions stay on topic, and this thread was about G, not h
If you have more than conjecture(i.e. more than what you have presented here), open up a new thread
12 minutes ago, swansont said:!Moderator Note
We have requirements in speculations, demanding a certain level of rigor. We also require discussions stay on topic, and this thread was about G, not h
If you have more than conjecture(i.e. more than what you have presented here), open up a new thread
Initially, the topic was broader. Here is a quote from the first post of the topicThus, this thought experiment with an oscillatory circuit shows that in the reference frame of a remote observer, the dielectric and magnetic constants must change in different directions in accordance with the change in the time/distance scale. Then it is not difficult to show
that the Planck constant will also change in the reference frame of the remote observer, since it is equal to0 -
1 hour ago, Ghideon said:
Is the above a speculation of yours or by the authors of the article? I did a quick read of the Astrophysical Journal Letters:
Of mine
0 -
12 hours ago, MigL said:
You would then, have G evolve with the evolution of the universe such that earlier eras of the universe would have differing values of G.
Examining far-away ( and therefore, much earlier ) parts of the universe has yielded no variation in the value of G.
And observational evidence, not pretty mathematics, is the final arbiter.A very difficult, I would say practically unsolvable task. If we observe two objects that revolve around each other, then in order to measure G we must measure their masses and the distances between them. Any deviation in the period of rotation can be explained by both the deviation of G and the deviation in the masses of objects. How to distinguish a change in the masses of objects from a change in G??
In addition, in the first post of this topic, I showed on a thought experiment with an oscillatory circuit that in the reference frame of a remote observer, ε0 and µ0, and therefore h, should change.
And here is the news on this topic. An international team of astronomers has discovered a giant dead galaxy that existed 12 billion years ago, when the age of the universe was 1.8 billion years. This is reported in a press release on Phys.org.
The team conducted spectroscopic observations using the MOSFIRE spectrograph (Multi-Object Spectrograph for Infrared Exploration) located at the Keck Observatory (Hawaii).
The galaxy, which was designated as XMM-2599, was characterized by a high rate of star formation (one thousand solar masses per year), but then this process completely stopped. Scientists do not yet know what the cause of death of XMM-2599 is.
This may mean that in the early universe h was much smaller, which is why the stars did not light up.
0 -
If you want to write your own program for reading QR codes, for example in C#, you can use the ZXing library
0 -
9 hours ago, Markus Hanke said:
Besides, if you allow G to vary, the overall equation is no longer covariant, and will have completely different solutions.
Of course, the solutions will be different and the event horizon and singularity will not appear in them.
0

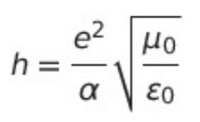
War Games: Russia Takes Ukraine, China Takes Taiwan. US Response?
in Politics
Posted
Russia has approved the defense budget for 2021-2023 — it was reduced by 10%. Despite this, it guarantees the combat readiness and development of the country's Armed Forces.
Deputy Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation Tatyana Shevtsova told the newspaper Krasnaya Zvezda about this.
https://360tv.ru/news/army/rossija-sokratila-bjudzhet/
At the same time, military salaries have been increased in Russia, so the cost of purchasing weapons will be reduced even more.