-
Posts
7715 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
26
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Posts posted by Sensei
-
-
why would smooth rubber create so much friction compared to other smooth objects
Who said rubber is smooth?
Did you look at it by microscope?
Good smooth surfaces have: specular highlights, and reflections like mirror..
0 -
I was wondering what friction was caused by and why rough textured create more friction then smooth ones.
Rough texture under microscope will look like mountains and valleys. While smooth will be pretty flat.
How to get smooth surface? by f.e.heating and melting material. Liquid material from mountains will fill valleys and they will reduce them self.
If we will send light beam to rough surface material, photons will bounce from mountains, bounce from valleys, perhaps many times, and photons will be going in the all random directions.
Rough material has many surface normal vectors.
Smooth material has quite uniform normal vector.
Normal vector of surface is used to calculate direction of reflected light.

Once one object mountains are attaching to other object mountains, while object is moving, or is under force, there is needed even more force to unlock them.
There can be also attraction between positive ions in one object and negative ions in other object.
0 -
So what is the correct direction of current if I replace your battery with the AC mains?
AC is swapping direction of electrons 50 Hz or 60 Hz, times per second, depending on country.
So for AC both answers are correct.
I would see the same (heating) effect in the external resistor.
Correct.
This can be even experimentally confirmed by plugging heating element to AC, and heating water (with mass m, and initial temperature T0), then through rectifying diodes DC (and heating it for the same period of time, same mass, same initial temperature).
~4.1855 J/K*g
m=250 g of H2O
T0=20 C
T1=100 C
~4.1855 * ( 100 - 20 ) * 250 = 83710 J
For U = 230 V, I = 2 A, time needed to increase temperature of water from 20 C to 100 C will be approximately 83710 / 460 = 182 seconds = 3 minutes 2 seconds..
And are there not actually more AC circuits than DC ones in this world?
But it's meaningless which one is more or less used. AC is used to transfer energy on large distances, while DC is what we use in f.e. electronic equipment. There is just a few devices that doesn't need DC, like light bulb, or heating element, that works regardless of direction of electrons/current. But diodes and transistors bother about it. LED won't shine light after plugging it reverse.
You won't make electromagnet with AC for instance. It needs DC. Constant flow of electrons in one direction.
Electromagnet that will be changing direction 50/60 times per second will not work.
Whether electromagnet is repelling or attracting magnets is quite substantial difference...
I can show you in couple minutes on video recorded by my phone how direction of current through my electromagnet is causing on compass array below it..
Electric motor will be spinning in opposite direction after applying to it current with opposite direction.
And that still did not answer the question what is the direction from + to - within the circle you have drawn?
The whole point is that most theory is independent of the direction of carrier flow.
If this become necessary it is simply covered by assigning the same sign as that of the charge to the flow.
Did you see my experiments with Cockcroft-Walton generator with 40000+ volts videos?
Electrons gather on one side of capacitors, while other side has excess of electrons.
We will see how on positive electrode will appear coronal discharge. Sometimes it looks like little violet thunderbolts. Positive electrode is stealing electrons of air medium, and medium is stealing electrons from surrounding it medium and it's going and going, like thunderbolt, with time. It takes even a few seconds when we can observe it growing. Once it reaches negative electrode, there is appearing electric arc between them, and electrons gathered on capacitors will flow freely to positive electrode, discharging. And then it can start from beginning.
Just by looking at electrodes I can tell you which has excess of electrons, and which one has abundance of them. It's clearly visible after a few seconds while capacitors are loading..
Negative electrode (that has abundance of electrons) cannot steal electrons from Nitrogen & Oxygen from air, it has too many of them.
Coronal discharges differ (visible by naked eye) between positive & negative electrodes.
Surely you cannot be suggesting that electrons simply move around your path through the resistor from - to plus and stay there at the + sign, building up an excess of negative charge, which would repel further electrons arriving?
Of course they stop flowing, when there is no more abundance electrons, and no more "holes".
The same is with charged capacitor. Electrons can flow from - side of it, to +, only to moment of ~full discharge...
And that still did not answer the question what is the direction from + to - within the circle you have drawn?
Actually I didn't draw it. These are images from wikipedia.
1 -
More informations about electromagnetic radiation:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bremsstrahlung
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synchrotron_radiation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclotron_radiation
So a direction was chosen a couple of centuries ago ... (...)
Studiot, but centuries ago they picked up wrong direction of current I..

You see arrow of I is going from + to - in battery, while electrons are flowing in exactly opposite direction:
 0
0 -
Again, the best acceptable answer to any of my postings gets a free ebook of mine, your choice. You can look my 32 published ebooks over at
Good scientist is sharing his knowledge for free, doesn't sell it.
0 -
How are they closer or further?
You know - apogee, and perigee..
Similar like between Earth and Sun, we have perihelion, and aphelion.
According to this website:
https://www.fourmilab.ch/earthview/pacalc.html
Max perigee is 356921 km
and
max apogee is 406568 km
406568/356921 = ~ 14% (~ -7... +7% from average)
More info about perigee and apogee
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apsis
And how big of an effect will that be?
Interesting question.
If tidal forces are caused by only distance between our two (or more) massive objects, the strongest tidal should be at perigee or in perihelion.
Yeah. Only problem is it is happening so slowly that the Sun will have expanded prior to the process reaching completion.
Tidal is not Earth-Moon phenomena.
Between Jupiter and Io it also happens.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Io_(moon) (second paragraph).
We can easily imagine 2 planets system in outer space, var away from any living stars, orbiting around elliptical orbits.
0 -
The tidal interaction with the moon is slowing the earth's rotation. That's ultimately the source of the energy. (it's also making the moon recede; angular momentum must be conserved)
If that's truly the only source, then when Earth will be spinning at the same rate as Moon orbit around Earth (so they're facing always the same side), tidal should vanish.
But I don't think so- we can easily imagine situation when both objects are facing always the same side to each other, but once they're closer, other time they're further from each other. And in such case also there should be tidal.
0 -
If you don't want insulation to dissolve, and contaminate solution, do the same as in Hofmann's voltameter
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hofmann_voltameter
Place electrodes up-side-down in bottom of container.
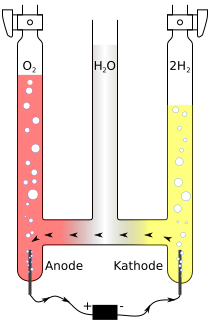
You can buy ready device for 50 ukp, see f.e.
http://www.sci-mart.com/Chemistry/Stands/hoffman-voltmeter
0 -
hi,guys,
how can i connect my iphone5c to my PC to get data exchange ?
thanks.

I don't have iPhone, but Samsung.
Typically I am simply connecting USB cable (it's part of phone package) between them and phone asks in which mode it should run.
One of modes is to work as disk storage. (Other mode is f.e. use phone as modem to connect computer to Internet, people use it very often in hospitals. Needs phone & laptop, but pricey as hell. People usually disable images & flash in browser to not bankrupt)
After that computer see my phone as yet another disk with the first free letter.
f.e. H:\
You can then use Windows explorer to visit that location, and copy paste files like you would do with any other remote flash USB memory stick f.e.
Another option is using FTP and/or HTTP.
If your computer has public IP, you can set up FTP server, HTTP server,
and use phone web browser you visit your own computer's server.
Better to have wifi local connection than use phone Internet transmission which is pricey.
If you don't have public IP, you can still use external FTP/HTTP servers though. But that would be even slower (have to upload file to external server, and then download it using phone browser).
0 -
-
Emphasis added: that's a key caveat. Light absorbed from a non-thermal source could heat an object to an arbitrary temperature, dependent only on the power. There's a higher power in blue light vs red light if the photon count is the same. But 1 W of absorbed light from each would have the same heating effect.
Exactly.
Anyway it is visible from equations:
[latex]E = \frac{h*c}{\lambda} = \frac{6.62607*10^{-34} * 299792458}{650*10^{-9}} = 3.056*10^{-19} J[/latex]
[latex]E = \frac{h*c}{\lambda} = \frac{6.62607*10^{-34} * 299792458}{525*10^{-9}} = 3.784*10^{-19} J[/latex]
[latex]E = \frac{h*c}{\lambda} = \frac{6.62607*10^{-34} * 299792458}{405*10^{-9}} = 4.9*10^{-19} J[/latex]
quantity of red photons in [latex]1 W = 1 \frac{J}{s}[/latex] is [latex]\frac{1 J}{3.056*10^{-19} J} = 3.27*10^{18}[/latex] photons per second.
quantity of green photons in [latex]1 W = 1 \frac{J}{s}[/latex] is [latex]\frac{1 J}{3.784*10^{-19} J} = 2.64*10^{18}[/latex] photons per second.
quantity of blue photons in [latex]1 W = 1 \frac{J}{s}[/latex] is [latex]\frac{1 J}{4.9*10^{-19} J} = 2.04*10^{18}[/latex] photons per second.
1 -
Light, colours as we see it, is reflected light. If white light falls on an object, which in its turn sends out light in that colour that we accept is the colour of the object, then it must absorb the rest of the white light - the negative of the reflected colourful light.
In most cases it's correct.
There is yet another explanation:
white light is falling on object, then reflected photons are reacting us, but other also reflected photons with different frequencies, or at different angles, are not reaching us (instead of absorption).
It's called Iridescence.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iridescence
Also instead of absorption there can happen refraction.
E.g.
I have in front of me a computer mouse which appears black to me (let's assume it's pure black - not very realistic, but hey, we're reasoning theoretically here). Black (or 'no light') is being reflected from it. No light is reflected, so all light must be absorbed, making this mouse in fact white.
Majority of black body objects are emitting light at frequencies invisible to human eye. For instance infra red, or microwave. You can see them emitting light (especially when they're really hot) using IR camera.
This can be used to detect fire, before flame really appeared.
Photon with frequency f, has energy E=h*f
f = c/wavelength
and
wavelength = c/frequency
so
wavelength = h*c/E
My red photon laser has wavelength 650 nm,
green photon laser has wavelength 525 nm (24% more energy than red),
blue/violet photon laser has wavelength 405 nm (30% more energy than green, and 60% more than red).
So it's not just matter of "color", it's matter of energy.
Energy can be used to heat substances.
Red photons will heat substances to lower temperature, than green, than blue (if we send them in the same quantity) (assuming they will be all absorbed).
Photons with certain frequencies (energies) trigger (or not) chemical reactions.
1 -
In the case of electron pairs and positronium (which has the size of an atom), the size of the wave would fit perfectly.
But it wouldn't fit to idea of annihilation of electron and positron that happens later.
To do so, there is needed that they're more or less point particles, that meet together and finally annihilate.
Until they don't annihilate, they're existing as e+ and e-.
If you can keep them separate (like in magnetic trap), they won't annihilate.
When electron accelerated to relativistic velocity collides with positron, there are created other particles.
"There are also many examples of conversion of relativistic kinetic energy into rest energy. In 1974, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory accelerated electrons and positrons up to relativistic velocities, so that their relativistic energy \gamma mc^{2} (i.e. the sum of their rest energy and kinetic energy) is significantly increased to about 1500 MeV each. When those particles collide, other particles such as the J/? meson of rest energy of about 3000 MeV were produced.[30] Much higher energies were employed at the Large ElectronPositron Collider in 1989, where electrons and positrons were accelerated up to 45 GeV each, in order to produce W and Z bosons of rest energies between 80 and 91 GeV. Later, the energies were considerably increased to 200 GeV to generate pairs of W bosons"
Quote from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tests_of_relativistic_energy_and_momentum
A trace in a cloud chamber is wide, hugely wider than an atom.
It's result of cascade ionization I mentioned before.
Similar ionization happens when charged particle is passing through liquid Hydrogen in f.e. Bubble Chamber.
But that's not the point. If electron would be as "wide" as orbital of let's say Hydrogen, it's path in chamber should looks like zig-zag constantly changing directions after hitting nucleus of medium.
Alpha particle has a few femtometers and is occasionally hitting medium nucleus and changing directions, like here:
It doesn't need an electron smaller than an orbital.
Free electron is not limited to any orbital...
One might ask, which atom orbital, and with what quantity of electrons.
If you have f.e. Gold nucleus with 79 protons, and 1 electron,
ionization energy is approximately 13.6*Z^2 = 13.6*79^2 = 84.8776 keV
In other words you must send photon with ~85 keV to remove the last electron from ion 79Au78+
Such molecule is "Hydrogen-like", all charge concentrated in nucleus (+79e), and single electron outside (-1e).
Nor does electron emission or capture by a nucleus need an electron smaller than the nucleus. It needs the ability for an electron to concentrate to this size; this is the probability that we compute with |Ψ|2, and call it "collapse" when the wave shrinks to fit the interacting particle.
Simply: finding where was our point particle..
This ability to change the size wouldn't alone need the particle to be a point.
You completely forgot that whole thread is your own hypothesis/speculation that electron is point particle, and now you're defending opposite...
0 -
I thought you wanted free discussion ("Your thoughts please?"), but unfortunately it seems I was wrong..
0 -
See the way electrons are created in pair production:
y + y -> e+ + e-
Each photon with E >= 510999 eV, which is wavelength equal to Compton wavelength = 2.426*10^-12 m = 2.426 pico meters.
or with single photon and nucleus:
y -> e+ + e-
E = 1.022 MeV, wavelength half of Compton wavelength.
After pair production we will have electron with half energy of such photon, and positron with another half of that initial energy.
Electron particle "bigger" than this wavelength, wouldn't make sense to me..
Another argument for small size of electron is positronium:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Positronium
Electron and positron are orbiting together making exotic atom.
You're thinking too much (and overestimating) orbitals.
While you should concentrate on free electrons, not bound to any atom IMHO.
See electron's trace which it's making in Cloud Chamber:
Electron had to be in the center of that trace. Electron accelerated to significant speed of light, with tremendous amount of kinetic energy (see decay energy calculations to find out it's possible maximum kinetic energy for given unstable isotope (that nucleus had mass-energy concentrated in couple femtometers *)).
Passing through medium, it gave part of its kinetic energy to medium, ionized it, and accelerated atom (or its electrons) of medium hit other medium atom - cascade effect happened (and repeat it along path for billions of billions of medium particles). After giving all its kinetic energy, it's stopping moving.
What happened at quantum, picometer or femtometer scale, is therefor visible in our scale by naked eye.
It would be worth to record it in slow motion 1000+ FPS camera, to see how trace is growing with time.
*) According to http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Femtometre "radius of a proton is approximately 0.84 - 0.87 femtometres"
Now imagine proton (in nucleus) decaying via beta decay+, to positron
p+ -> n0 + e+ + Ve
or neutron decaying via beta decay-, to electron
n0 -> p+ + e- + Ve
IMHO electron radius should be even smaller than nucleus that decayed (and while before decay was "containing" our electron/positron).0 -
As the videos Sensei posted show, the effect is quite dramatic.
I have personally performed test with 2 meter long Aluminum straight pipe, 1 cm diameter.
And couple (quantity does matter!) neodymium cylindrical magnets, 8 mm diameter, 4 mm height each.
With 5-6 such magnets, I was receiving steady 12-13 seconds time spend on moving to the other side of pipe (pipe vertically of course). That's 19-20 times longer than free fall.
Free fall 2 meters takes ~0.64 seconds normally (and that's delay when we pass anything but these magnets through my pipe).
I will make video when will buy new Full HD camera..
Results (today performed again to be sure):
1 magnet: ~16 seconds
2 magnets: ~21 seconds
5 magnets: ~12 seconds
0 -
Have you seen such home experiment?
0 -
I'm really not sure , if its correct this way , please help me out.
No.
I don't think so, if you meant "nuclear binding energy".
You should calculate decay energy of the all isotopes of the all mentioned elements for the all possible case of decay (or at least for proton, neutron and alpha decay).
For stable isotope, decay energy is negative value. And that's energy you need to spend to separate nucleus to smaller parts.
Then you can sort them in right order.
f.e. binding energy for isotope Carbon-12 is different than for isotope Carbon-13. Either one are stable.
But it's awful lot of work.
Tin for example has 10 stable isotopes
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isotopes_of_tin
You should ask your teacher whether he meant "average nuclear binding energy per nucleon".
If so, you should calculate energy of the all free protons and free neutrons in isotope with Z protons and A-Z neutrons. Subtract from it nucleus energy (isotope mass * c^2 - mass-energy of the all electrons).
(after dividing it by A, you have average binding energy per nucleon).
0 -
It is a common misinterpretation of the uncertainty principle to assume we can never know what the momentum and position of a particle was.
The same can be said about any moving macroscopic object like f.e. airplane.
If we know position of airplane, it must be on land, not flying anymore.
If it's flying in air, its position is constantly changing, and while we're seeing it, it's not there anymore, we just see photons reflected from it after some time. And our recorded position is more or less not actual.
If the electron has been detected, then we can easily deduce its position and the momentum it needed to get there.
You're talking about electron in electronic circuit.
Double slit experiment for electrons is done in vacuum with free electrons, emitted by electron gun.
Detection of electron means it has hit detector. And perhaps created photon, which has been seen, and counted.
Electron slowed down, gave detector it's kinetic energy, or part of it. And it no longer poses that kinetic energy.
Act of "observation", measurement, caused change in object we're measuring.
0 -
IMHO it's good to visualize where are electrons, where they go, and which path they will be flowing.
Electric current I is going in opposite direction to flow of electrons (because XIX century scientists developed it up-side-down).
Take for example Faraday's disc
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homopolar_generator
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Faraday_wheel
Close to metal wheel there is placed magnet (but not touching it), wheel is spinning, and electrons in metal are repelled by magnets.
It happens regardless of whether circuit is closed or not.
Electrons gather in part of wheel not affected by magnets.
We can place there wire f.e. a few cm from outside of wheel, electrons will ionize air gap creating spark and will be going through wire, then where ever we want.
It might be used during electrolysis, which needs large current, with low voltage.
Four electrons, each with E = 1.23 eV will be able to split two water molecules, and produce 2 H2 and O2
0 -
values of physical constants like gravitational constant G , permittivity etc depends on dimensions of length, mass , time etc
Who said so.. ?
0 -
Really? If there is a particular pattern, then let's see it proven.
Nobody is saying about pattern.
I just said "pattern is completely not needed".
If this is so easy, let's see some supported results.
bool IsPrime( unsigned long long value )
{
if( value < 2 ) return( false );
unsigned long long max = (unsigned long long) sqrt( (double) value );
for( unsigned long long i = 2; i <= max; i++ )
{
if( ( value % i ) == 0 )
{
return( false );
}
}
return( true );
}
If prime would be random, chance to return true or false for given input value, would be 50/50.
Instead there is returned true, if value is prime,
or false, if it's not.
If we would be interested about even numbers, it'd be also returning true or false,
but inside there would be:
return( ( value % 2 ) == 0 );
0 -
Without that, the word random is a completely valid and accurate description of our knowledge today.
Nonsense.
Primes don't fulfill definition of random f.e.
http://www.macmillandictionary.com/us/thesaurus/american/random
"chosen or happening without any particular method, pattern, or purpose"
Probability of that 2,3,5,7,11,13 etc etc. is prime number is 100%.
Pattern to predict next prime is completely not needed. You don't ask for next even number while examining f.e. 10.
There is route to check whether some number is prime or not, by dividing it by all lower numbers.
Definition of even is that it's dividable by 2. 10 is dividable by 2, so it's even. We're not interested about any lower, or higher numbers at all.
0 -
Where do you have source of sound at such frequencies?
Do you have equipment generating such sound?
Do you have equipment detecting such sound?
If you do so, then start placing different materials between emitter and receiver, to see which one will be working..
Do you know how sound is generated by speaker?
By moving membrane in and out, in and out, as many times as frequency you have in sound.
If membrane would be moving 3 GHz for 1 cm it's 3*10^9 * 2 * 1 cm = 60 mln m/s = 20% speed of light.
For 1 mm distance movement, it's 2% speed of light.
At 16 kHz membrane moving 1 cm in & out, is reaching nearly speed of sound in air.
0






The McCaustland Theory
in Speculations
Posted
Obviously.
Obviously.
Only people without PhD have here any theory..
The problem is that there is known 118 atoms, and nearly 3143 isotopes. Which one do you have in mind? Each of them have different mass, different energy, and different binding energy (I don't believe you know what is binding energy)..
Yet another problem is that not only atoms are attracted by black hole, but also light-photons.
(cut there rest of crap)