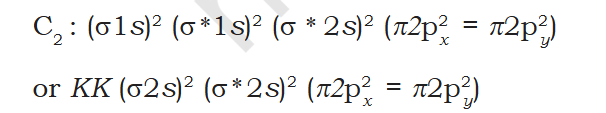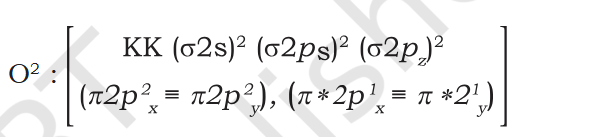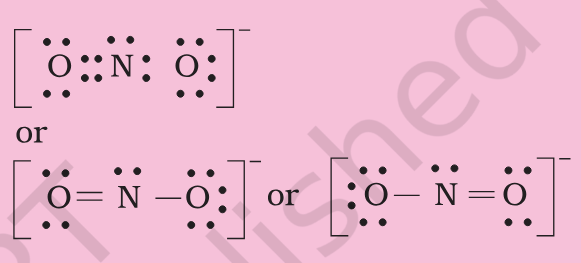Everything posted by HbWhi5F
-
Molecular Orbital: Need help conceptualizing.
@studiot I think you meant atoms. Yes I understand s p d are 3d spaces where electron are like to be found (ie wave function).
-
Molecular Orbital: Need help conceptualizing.
@exchemist Please recommend resources to learn molecular orbitals
-
Molecular Orbitals: What is with and without 2s-2p mixing ?
- Molecular Orbital: Need help conceptualizing.
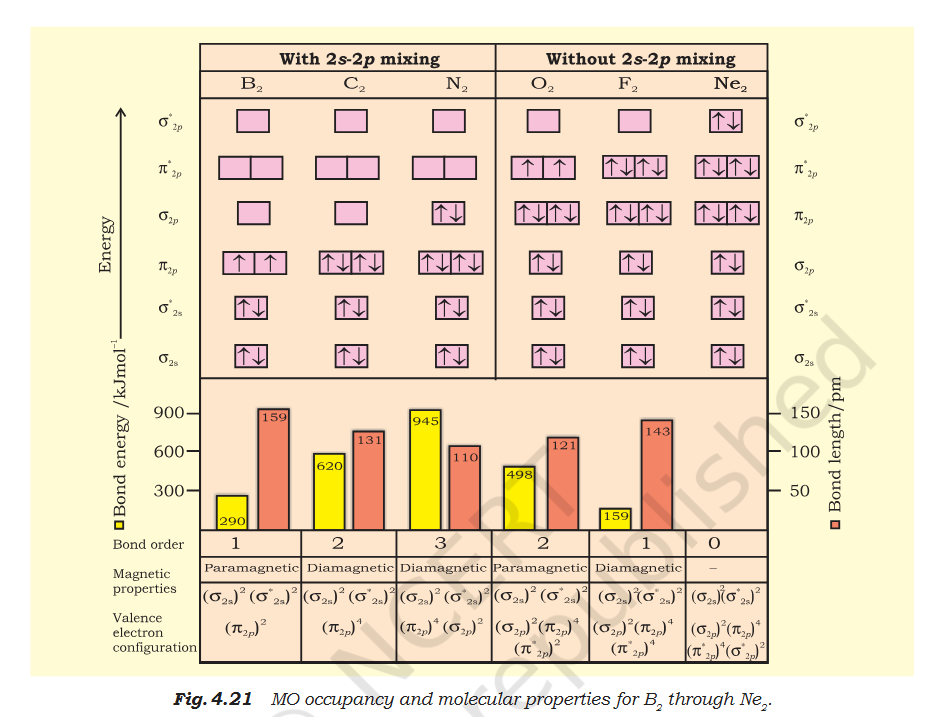
Book "4. Carbon molecule (C 2 ): The electronic configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2. There are 12 electrons in C2. The electronic configuration of C2 molecule, therefore, is The bond order of C2 is ½ (8 – 4) = 2 and C 2 should be diamagnetic. Diamagnetic C2 molecules have indeed been detected in vapour phase. It is important to note that double bond in C 2 consists of both pi bonds because of the presence of four electrons in two pi molecular orbitals. In most of the other molecules a double bond is made up of a sigma bond and a pi bond. In a similar fashion the bonding in N2 molecule can be discussed. O2 5. Oxygen molecule (O 2 ): The electronic configuration of oxygen atom is 1s2 2s2 2p4. Each oxygen atom has 8 electrons, hence, in O 2 molecule there are 16 electrons. The electronic configuration of O 2 molecule, therefore, is From the electronic configuration of O2 molecule it is clear that ten electrons are present in bonding molecular orbitals and six electrons are present in antibonding molecular orbitals. Its bond order, therefore, is Bond order = [Nb – Na] = [10 – 6] =2. So in oxygen molecule, atoms are held by a double bond. Moreover, it may be noted that it contains two unpaired electrons in π ∗2px and π ∗2py molecular orbitals, therefore, O 2 molecule should be Paramagnetic, a p r e d i c t i o n t h a t c o r r e s p o n d s t o experimental observation. In this way, the theory successfully explains the paramagnetic nature of oxygen. Similarly, the electronic configurations of other homonuclear diatomic molecules of the second row of the periodic table can be written. In Fig. 4.21 are given the molecular orbital occupancy and molecular properties for B2 through Ne2. The sequence of MOs and their electron population are shown. The bond energy, bond length, bond order, magnetic properties and valence electron configuration appear below the orbital diagrams. " Question Seeing it in atomic orbital perspective the molecules electronic config should be KK 2s2 2p4 ie 1 filled and 2 single filled orbitals. But according to the book there is no single filled molecular bond or anti-bond so the molecule is diamagnetic. Is the atomic bonding and molecular orbitals totally unrelated ? When Pie bond is formed doesn't both atoms' orbitals needs to be acting i.e. Px of Atmos A acts with Px of Atom B ? There Px of 1 Atom and Py of other Atmos forms 1 molecular bond each ? O2 Question Why does O2 form 1 bond and 1 antibond ? O2 form a double bond and complete the valance but the book shows 3 bonds but says double.. Explain "Moreover, it may be noted that it contains two unpaired electrons in π ∗2px and π ∗2py molecular orbitals"- is x-y = |y-x| ?
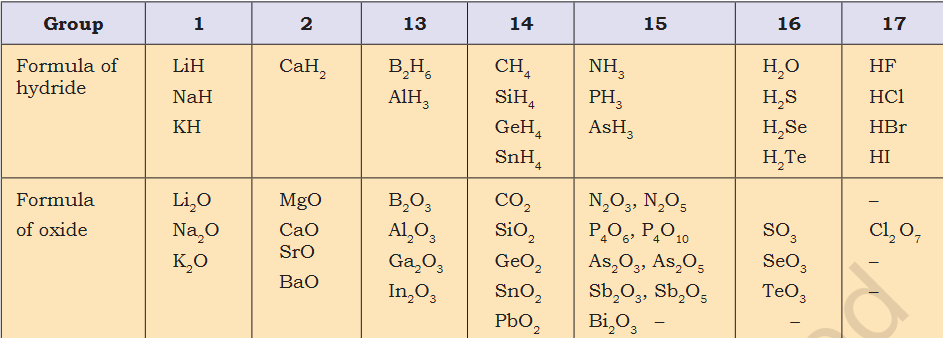
It is not homework. I was thinking about it and can't seem to find a situation there it is incorrect. This equation surely tells interesting things when graphed. @MigL When X>Y 10-4 = 6 |Y-X| =| -6| = 6 When Y>X 4-10 = -6 |10-4|=6 Ok lets modify, when Y>X, |X-Y| =|Y-X|- How are 2 types of oxides possible ? N2 O3 , N2 O5
Question is how multiple molecules are possible with different atom ratio ? Do they leave lone electrons ? I don't get the math is it some other phenomenon ?- Explain 03 CO3 -2?
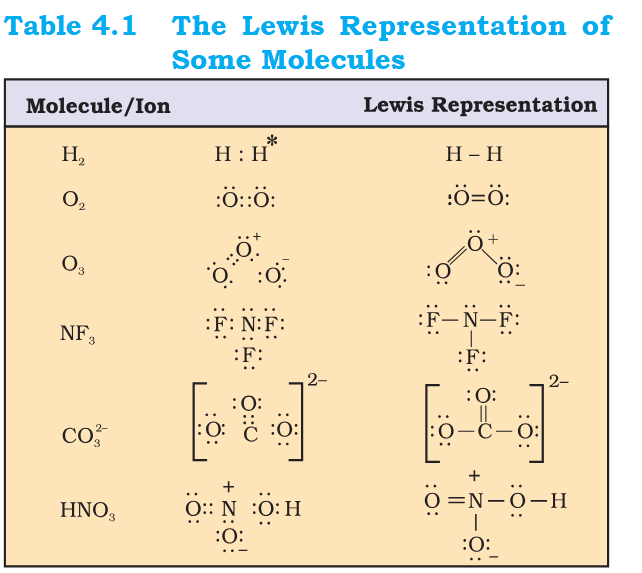
CO3 (-1) charges - C -2 O +2 on top and x2 O -2 ? NF3 should also have charges indicated ? x3 F has -1 each and N has -3. In HNO3 left O doesn't have charge it should be +2. N has +4. RIght O should be +2. H should be +1 In O2 they both share 2 eletrons to become noble but that also makes each O, -2 charged right ?- Explain 03 CO3 -2?
- Explain 03 CO3 -2?
This O3 Lewis Diagram looks weird - why does atom with 8 electrons positive, why is atom with 4 electrons neutral, why is atom with 6 electrons negative In CO3 -2 Why there is a -2 charge ? What is happening in HNO3 ? N is positive that means it is 5 electrons short of Nobel config. Why there is a negative charge on bottom oxygen ? Are these Lewis Diagram possible or covalent and electrovalent bonds ? [NO2]- is there 1 electron extra on oxygen ? [NO2]-- How to manage Anger as a ghost from past when Studying ?
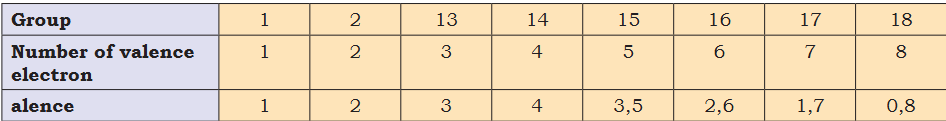
I get grudgeful though when studying wasting my energy and time. Intrusive when studying and day-to-day tasks they are not that bad.- How does group 15 has valance of 3 or 5? Group16- 2,6. Group17- 1,7. Group18- 0,8
Periodicity in valence - among representative elements, the valence is either equal to the number of electrons in the outermost orbitals or 8 - minus this number What is 8 ? There can be a max of 6 electroins untill p shell and 3 in s shell- is x-y = |y-x| ?
If not, when it is ? Can the make it a function to understand the nature of the formula ?- How are 2 types of oxides possible ? N2 O3 , N2 O5
- Molecular Orbital: Need help conceptualizing.
Important Information
We have placed cookies on your device to help make this website better. You can adjust your cookie settings, otherwise we'll assume you're okay to continue.