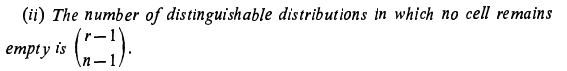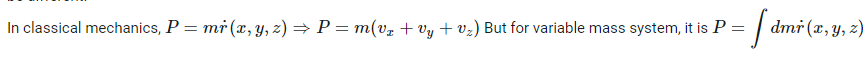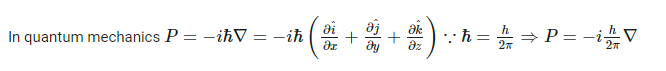Everything posted by Dhamnekar Win,odd
-
Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
I did those computations for case(1) r=2, n=2 and case(2)r=2 and n=3. For case(1) The number of distinguishable distributions of 2 indistinguishable objects putting into 2 cells is 1 (equation or formula 1) and the numbers of distinguishable distributions of 2 distinguishable objects putting into 2 cells are 2(equation or formula 2) For case(2) The number of distinguishable distributions of 2 indistinguishable objects putting into 3 cells is -1 (equation or formula 1) and the number of distinguishable distributions of 2 distinguishable putting into 3 cells is 0(equation or formula 2) So, now how can we change the order of summation and use the binomial formula to express A(r, n+1) or in our case A(2,3) as the difference of two simple sums?
-
Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
Assuming equation(2) to hold, how to express A(r-k, n) in equation (1) accordingly? How to change the order of summation and use the binomial formula to express A(r, n+1) as the difference of two simple sums as feller suggested? How to replace in the second sum v+1 by a new index of summation and use the following important property of binomial theorem [math]\binom{x}{r-1} + \binom{x}{r} = \binom{x+1}{r}[/math]?
-
Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
-
Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
- Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
Did you go through the corrected equation (2) in my last post? v and k are the same variable i-e we are to select v or k cells from the n cells. That's it.- Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
Please read my post under the heading "Elements of Combinatorial Analysis". Source " An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications" by W.Feller, Chapter 2 and 4.- Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
If I am not wrong, both formulas are meant for the computation of number of distinguishable distributions of indistinguishable r objects putting into n cells so that none of the n cells remains empty.- Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
- Elements of Combinatorial Analysis
Corrected equation (1) [math] A(r, n+1)= \displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{r} \binom{r}{k} A(r-k, n)[/math] Corrected equation (2) [math] A(r, n) = \displaystyle\sum_{v=0}^{n} (-1)^v\binom{n}{v}(n-v)^r[/math] Then the author W. Feller says to replace in the second sum v + 1 by a new index of summation and use important property of binomial theorem which I wrote in my original question- Elements of Combinatorial Analysis
Some more information : This problem refers to the classical occupancy problem (Boltzmann-Maxwell statistics): that is, r balls are distributed among n cells and each of the [math] n^{r} [/math] possible distributions has probability [math]n^{-r}[/math]- Elements of Combinatorial Analysis
- Combinatorial Analysis (Investments)
I have made mistakes in the computations of answers to question (a) and (b). Corrected answer:(a) [math]\binom{n + r -1}{r}= \binom{12}{9}= 220 [/math] where n=9 and r = 4 Corrected answer:(b) [math]220 + \binom{15}{13} + \binom{14}{12} + 2 \times \binom{13}{11} =220 +105 +91 + 156 =572[/math] Hence, author's answers are correct.- Combinatorial Analysis (Investments)
- Electron transfer reactions question (ElectroChemistry)
How to answer all these following questions? I am working on all these questions. Any chemistry help, or even correct answers to all these questions will be accepted.- Momentum in Classical mechanics and Quantum mechanics
In the above second question, [math] \nabla r , \hbar [/math] means gradient r (position vector) and reduced Plank's constant respectively.- Momentum in Classical mechanics and Quantum mechanics
Momentum is used to sense the amount of force applied to a moving object. With the help of Momentum, you can know the nature of the applied force on an object. Momentum is usually represented by the product of the mass and velocity of a moving object. But in this case of quantum mechanics, the equation of momentum will be different. How is this computed? How is this momentum computed in Quantum mechanics?- Computation of longest wavelength emission from [math]Ca^{19+}[/math]
There is typographical error in the above question. Please read ' Is [math]Ca^{19+}[/math] one electron atom? '- Computation of longest wavelength emission from [math]Ca^{19+}[/math]
Was the above question correctly stated and correctly answered? In [math]Ca^{19+}[/math], how many electron shells are there? answer is n=1,2,3,4 Then in ground state how can we found its valence electron in 6th shell or n=6? Is [math]Ca^{19+}[/math] one lectron atom?- Question on structure of Atom
Answers: REMOVED BY MODERATOR- Question on structure of Atom
An x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy experiment with an unidentified element, X, displays an emission spectrum with four distinct kinetic energies: [math] 5.9 \times 10^{-17} J, 2.53 \times 10^{-18} J,[/math] [math]2.59 \times 10^{-20} J, 2.67 \times 10^{-20} J [/math] (Assume the incident light has sufficient energy to eject any electron in the atom.) (a)Name all of the possible ground state atoms that could yield this spectrum. (b)Calculate the binding energy of an electron in the 2p orbital of element X if the x-rays used for the spectroscopy experiment had an energy of [math] 2.68 \times 10^{-16} J[/math] (c)Consider both the filled and unfilled orbitals of element X. Determine the number of: (1) total nodes in a 4d orbital (2)angular nodes in the [math]2p_y[/math] orbital (3)degenerate 5p orbitals How to answer all these questions?- How to prove the normal distribution tail inequality for large x?
How to prove (7.1)? How can we use the following two expansion formulas of CDF of normal distribution to prove (7.1) lemma?- Can I ask here statistics question?
Can I ask here statistics question? If yes, under which forum?- In Daniell cell, anode has higher reduction potential and cathode has lower reduction potential
For additional information, refer to the following table:- In Daniell cell, anode has higher reduction potential and cathode has lower reduction potential
- Rates of reactions [math] N_2O_4 \rightarrow 2 NO_2[/math]
Answer to d) 1)∆H = 17.4 kJ/mol 2)∆H = 8.7 kJ/mol 3)∆H= 4.35 kJ/mol Answer to e) Mechanism for this reaction is [math]1)N_2 + 2 O_2 \rightarrow 2 NO_2 \Delta H^\circ_f = 66.4 kJ/mol [/math] [math]2) N_2O_4 \rightarrow N_2 + 2 O_2 \Delta H^\circ_f = -9.16 kJ/mol [/math] - Why are two answers different using the two equivalent formulas in combinatorics ?
Important Information
We have placed cookies on your device to help make this website better. You can adjust your cookie settings, otherwise we'll assume you're okay to continue.
Account
Navigation
Search
Configure browser push notifications
Chrome (Android)
- Tap the lock icon next to the address bar.
- Tap Permissions → Notifications.
- Adjust your preference.
Chrome (Desktop)
- Click the padlock icon in the address bar.
- Select Site settings.
- Find Notifications and adjust your preference.
Safari (iOS 16.4+)
- Ensure the site is installed via Add to Home Screen.
- Open Settings App → Notifications.
- Find your app name and adjust your preference.
Safari (macOS)
- Go to Safari → Preferences.
- Click the Websites tab.
- Select Notifications in the sidebar.
- Find this website and adjust your preference.
Edge (Android)
- Tap the lock icon next to the address bar.
- Tap Permissions.
- Find Notifications and adjust your preference.
Edge (Desktop)
- Click the padlock icon in the address bar.
- Click Permissions for this site.
- Find Notifications and adjust your preference.
Firefox (Android)
- Go to Settings → Site permissions.
- Tap Notifications.
- Find this site in the list and adjust your preference.
Firefox (Desktop)
- Open Firefox Settings.
- Search for Notifications.
- Find this site in the list and adjust your preference.