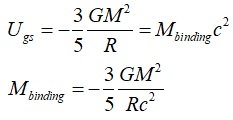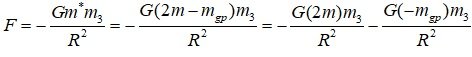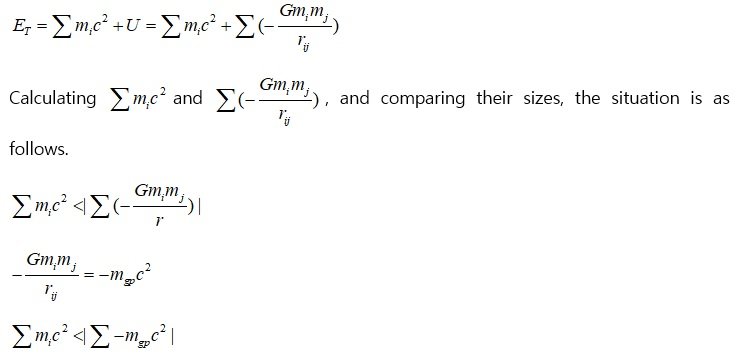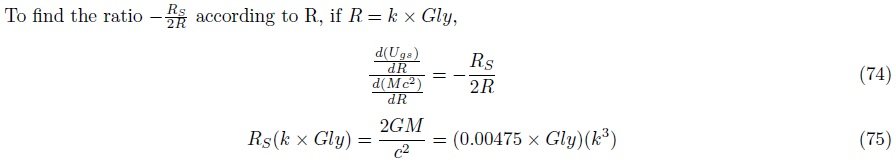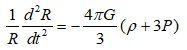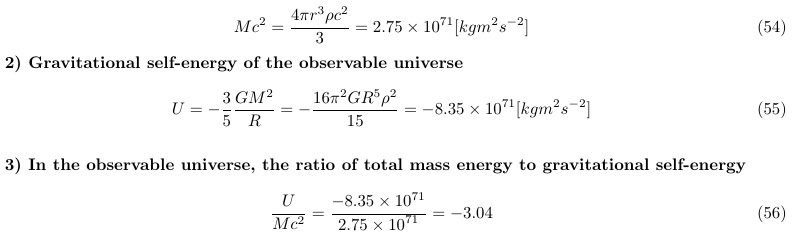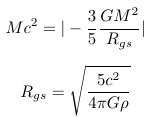The source of dark energy is gravitational self-energy.
1. The need for negative energy density
1) Negative energy (mass) density in standard cosmology
From the second Friedmann equation or acceleration equation,
In standard cosmology, it is explained by introducing an entity that has a positive mass density but exerts a negative pressure.
ρΛ + 3PΛ = ρΛ+3(-ρΛ) =- 2ρΛ
However, If we rearrange the dark energy term, the final result is a negative mass density of - 2ρΛ .
There are too many people who have an aversion to negative energy (mass). However, in the standard cosmology, accelerated expansion is impossible without negative mass density. It is just that the negative mass density term is called negative pressure, so it is not recognized.
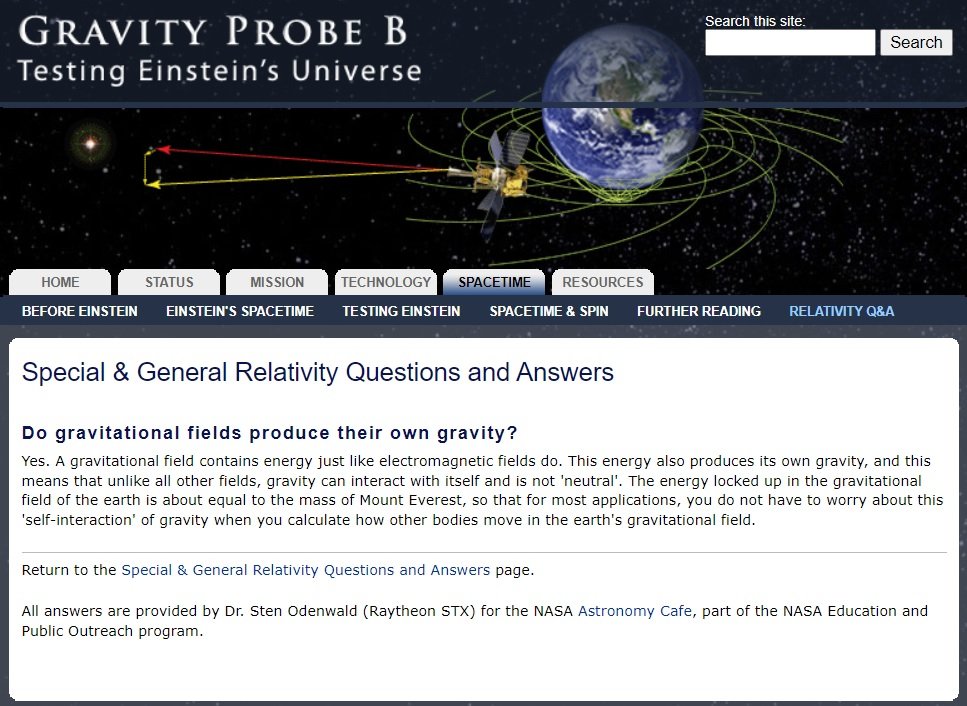
2) The energy of a gravitational field is negative
In his lecture, Alan Guth said:
Stephen Hawking also argued that zero energy state could be maintained when mass energy and gravitational potential energy were offset each other at the inflation period only.
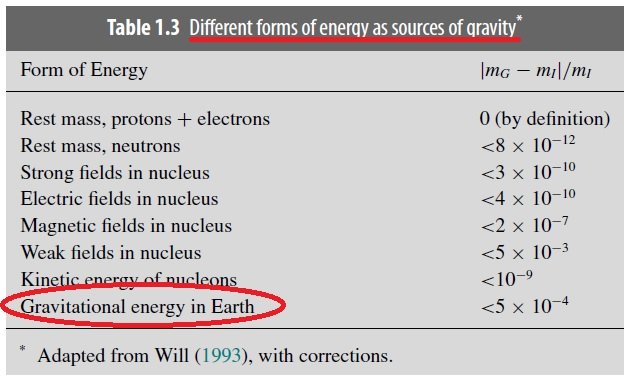
3) Earth's and Moon's Gravitational self-energy
4) Our common sense was wrong long ago
Our conventional wisdom is already wrong about the accelerated expansion of the universe and the rotation curve of galaxies. So, instead of thinking about whether negative energy exists, we should focus on whether the universe is explained by the introduced physical quantity. For those of you who are still reluctant to negative energy, first assume that gravitational potential energy is negative energy, and then look at the following logic.
2. Comparison of magnitudes of mass energy and gravitational self-energy in the observable universe
1)Total mass energy (include radiation energy) of the observable universe (particle horizon)
Simply put, the particle horizon is important because it means the range of the interaction. The critical density value p_c = 8.50 x 10-27[kgm-3 ] was used. Observable universe (particle horizon) radius : 46.5Gly.
Since the universe is almost flat spacetime, the total mass energy in the particle horizon is
The repulsive force component is approximately 3.04 times the attractive force component. The universe is accelerating expansion.
For reference, assuming the current average density, in the cosmic horizon 16.7Gly, U/Mc2 = -0.39 is obtained.
At the cosmic horizon 16.7Gly,the repulsive force component is smaller than the attractive force component, suggesting that it is a period of decelerated expansion.
3. Find the inflection point where the attractive and repulsive components are equal
I searched for the point at which the universe transitions from decelerated expansion to accelerated expansion.
I do not know the magnitude Rgs at which the positive mass energy and the negative gravitational potential energy are equal, since I do not have the data of the density. We only need to understand the general flow and possibility, so let's get ? by putting in the current critical density value.
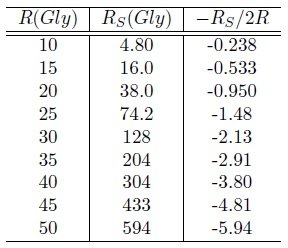
Rgs = 26.2Gly
Assuming that the average density is approximately 1.25 times the current average density, we get Rgs = 23.7Gly.
Assuming that the average density is approximately 2 times the current average density, we get Rgs = 18.7Gly.
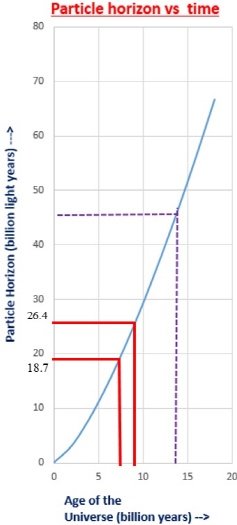
Comparing the data from the existing particle horizon graph, it is estimated that it is approximately 5 to 7 billion years ago from the present. It is necessary to review this model because it includes the transition of the universe to the period of decelerated expansion, the inflection point, and the period of accelerated expansion.
Particle horizon vs time. We need to know the average density to get an accurate value. However, as a rough estimate, according to this model, it is estimated that the transition to accelerated expansion was approximately 5-7 billion years ago.
4. The ratio of increase in gravitational self-energy to increase in mass energy
If the particle horizon increases and a positive mass is produced by M, the equivalent mass of negative gravitational potential energy is produced by -5.14 M.
This value is not a fixed value, it depends on the density and the size of the particle horizon.
5. Increase in dark energy (gravitational self-energy) due to increase in particle horizon
1)Particles and galaxies spread almost uniformly throughout the universe through the inflation process.
2)Galaxies move according to the Hubble-Lemaitre law.
3)On the other hand, the propagation speed of the field, the range of interaction (particle horizon), has the fastest speed, the speed of light in expanding space.
4)Thus, over time, many new substances (matters and galaxies) enter the particle horizon. In other words, the newly entering materials undergo gravitational interaction, resulting in an increase in mass energy and an increase in gravitational potential energy in the region within the particle horizon.
5)By the way, while mass energy is proportional to M, total gravitational potential energy (gravitational self-energy) is proportional to - M2/R. As M increases, the gravitational potential energy increases faster. Accordingly, the repulsive force component increases faster than the attractive force component.
6)The increase in gravitational potential energy due to the newly incorporated matter into the particle horizon is causing the dark energy. The same principle is applicable to the birth of energy within a particle horizon. That is, when the mass energy increases by M, the gravitational self-energy increases by - M2/R.
7)In the present universe, it is predicted that the dark energy effect (repulsive effect) surpassed the gravitational effect of matter and dark matter about 5 billion years ago. According to this model, it is the point at which the positive mass energy and the negative gravitational self-energy are equal. Knowing the average density function, we can get the exact value.
8)Gravitational potential energy is a concept that already exists and is negative energy that can create repulsive force. This model produces similar results to the phenomenon of applying negative pressure while having positive (inertial) mass density. As the particle horizon expands, the positive mass increases(New influx or birth of matter), but the negative gravitational potential energy created by these positive masses is greater. While having a positive inertial mass, it is creating a negative gravitational mass that is larger than the positive inertial mass. Because of this factor, this model should be reviewed.
6. How to validate the dark energy model that gravitational self-energy is the source of dark energy
1)Find the expressions of p(t) and Rph(t)
p(t) is the average density inside the particle horizon. Rph(t) is the particle horizon.
2)At each time, within the particle horizon
Find E = M(t)c2 and Ugs = - (3/5)(GM(t)2/R
E = M(t)c2 is the attractive energy component and Ugs is the repulsive energy component.
3)Compare Ugs/E with the observations
Anyone familiar with particle horizons and density functions can verify this model.
*The potential of this model
1. Description of the current accelerated expansion
R = 46.5Gly, the ratio of the attractive component to the repulsive force component, U/Mc2= - 3.04, and the negative energy component and the repulsive force component are larger, explaining the accelerated expansion.
2. Numerically, it represents the change from decelerated expansion to accelerated expansion, and by calculating the inflection point, it can be compared with the observed value. The roughly calculated inflection point is 5 to 7 billion years ago, So this model has potential.
3. In standard cosmology, dark energy is an object that has a positive energy density and exerts a negative pressure. The gravitational self-energy provides an explanation for this bizarre property.
1) Characteristics: It has a positive mass (energy) density and acts as a negative gravitational mass.
2) Size: Produces a negative gravitational mass density that is greater than the positive inertial mass density. The repulsive component is greater than the attractive component.
The gravitational self-energy accounts for both of these properties.
Mass energy is positive energy and is attractive, whereas gravitational self-energy is negative energy and has repulsive properties.
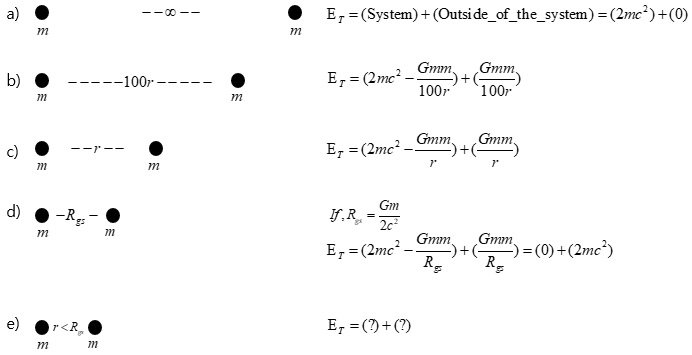
Mass energy is proportional to M. On the other hand, gravitational self-energy is proportional to -M2/R. At a size smaller than Rgs (The magnitude at which the positive mass energy and the negative gravitational self-energy are equal.), the mass energy is greater than the gravitational self-energy created by positive masses, and at a size larger than Rgs , the gravitational self-energy created by positive masses is greater than the mass energy.
4. Since gravitational self-energy is pointed out as the source of dark energy, verification is possible.
#On the solution of the strong gravitational field the solution of the Singularity problem the origin of Dark energy and Dark matter
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/359329109