Everything posted by Luc Turpin
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
I stand to be corrected and yes what one can do is resist further overlap / intrusion where its not appropriate or pertinent - well said Agree, assertions that I will try and substantiate. I got vaccinated for covid and still caught it twice; possibly a lesser form, but who knows, like bias. 😊
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
Please substantiate?
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
Why not just follow the scientific process with objectivity in mind and not bring preconceived ideas into play. I may be naive, but why bring philosophy into science experimentation. A lawyer should be encouraged to be biased towards a legalistic worldview. The scientist should go where evidence goes, not where he thinks it should go. I admit being biased; can you? I question everything, but I am rarely right would be a better description of myself
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
The process is not immune to the people making use of the process. Actually, I made a mistake calling it an argument as it was my opening statement that I will now try to argument with evidence. However, a preliminary review of articles and documentation on the said statement showed limited information available. Notwithstanding, I will attempt to demonstrate that indeed science has been biased by this worldview. I admit that this will be a tall feat to accomplish.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
I will respond this evening
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
1- You can indirectly investigate NDE’s by asking those, through a questionnaire, to describe their experiences and then analyse the data, for example. 2- i think that I have answered this, but again our concept of the living comes essentially from biology, so changing its paradigm to a non-mechanistic point of view will impact biology and have a trickle down effect on other science disciplines. What would science become if it was determined that mind works through brain and that life cannot be created solely out of matter? 3-you are correct in your statement, so I should maybe be looking at philosophy for answers 4- at least for mankind, it is the case that we want to understand the nature of reality and science is at the service of mankind and not the other way around
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
I have established that there is bias in science in general, that bias is being mitigated, but net entirely. there is one type of bias that is of particular interest to me and that is the worldview bias tainting science, so I do not need to identify and mitigate other biases. I would like then to focus our discussion on this matter. The issue though here is that there is much less data on this topic More to come It will be difficult to find the information again, but I will try. The point was to show that there are things to scientifically study even for obscure subjective topics such as ghosts
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
Starting tomorrow, I will be away for the next ten days and will be responding.sporadically. 1- yes, there is mind again and that is why it is important to know if it is through or from brain, as it will drastically change the picture that we have of our world 2- Even your definition mentions “a "one substance" view of the nature of reality,” I think that science studies more than behavior 3- So, who does the subjective to understand the nature of reality, which is the ultimate goal of humanity.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
The doctrine of thinking that all there is in the universe is space, time, matter and energy is called physicalism.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
Physicalism= space, time, energy and matter.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
Mind and the living which involves most if not all science disciplines. Then I think that you are talking about materialism’s close cousin, physicalism, which is matter-energy. It is still matter, energy and the laws of nature that rule the world.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
Everything in the nature of reality is made up of only one substance, matter and that mind comes from matter
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
My argument is that science is biased towards a materialist view of the world, which is not necessary to conduct science and even hampers the full investigation of reality.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
1- I am aware of this because one lone scientist is trying to do research on this, while having to endure the backlash from the scientific community. He has no funds to pursue the investigation, cannot publish, let alone, have his research material peer reviewed. Black mold, parietal region and demographic factors need to be investigated as probable causes of "apparitions", but they are not, because..... 2- There is a growing body of evidence that is shouting out to be investigated on. It is data that does not entirely match up to the mind from brain theory. Again, we have been studying the brain for decades and still cannot figure out how flesh or chemicals or electrical pulses turn into consciousness. 3- There was no need for fairies and Tinkerbell in the discussion. Tell me how mind through brain is untestable? The body of knowledge is incomplete. It lacks a whole side of the story that is necessary to unlock the true nature of reality.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
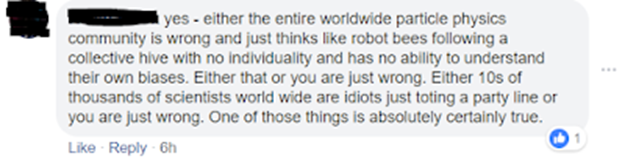
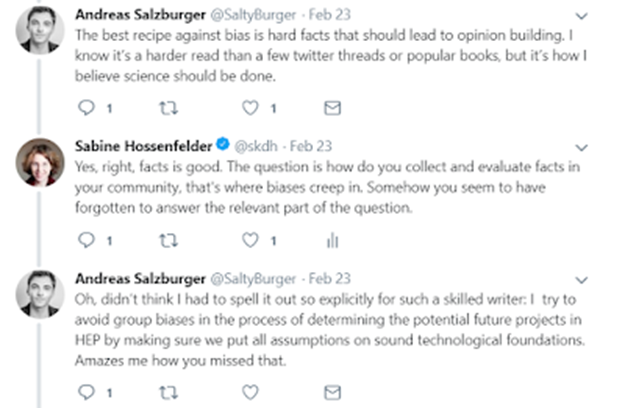
1- My position is to use other methods along with the one already in use and my reasoning behind this is to capture the part of reality that is not currently being captured by the standardized methods. 2- Is physics science? Then see below 3- Its' not who does it, but if it is done right? 4- Is physics open to address bias? see below 5- Then I will respond _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Bias in Research Research bias results from any deviation from the truth, causing distorted results and wrong conclusions. Bias can occur at any phase of your research, including during data collection, data analysis, interpretation, or publication. Research bias can occur in both qualitative and quantitative research. Understanding research bias is important for several reasons. Bias exists in all research, across research designs, and is difficult to eliminate. Bias can occur at any stage of the research process. Bias impacts the validity and reliability of your findings, leading to misinterpretation of data. It is almost impossible to conduct a study without some degree of research bias. It’s crucial for you to be aware of the potential types of bias, so you can minimize them. https://www.scribbr.com/category/research-bias/ Bias in Physics 1- From “A selected history of expectation bias in physics by Monwhea Jeng (trying to obtain full text) “The beliefs of physicists can bias their results toward their expectations in a number of ways. We survey a variety of historical cases of expectation bias in observations, experiments, and calculations.” https://pubs.aip.org/aapt/ajp/article-abstract/74/7/578/1056232/A-selected-history-of-expectation-bias-in-physics?redirectedFrom=fulltext 2- From “Quantum Physics is Fine, Human Bias About Reality is the Real Problem by Ethan Siegel “The idea that there is a fundamental, objective, observer-independent reality is an assumption with no evidence behind it, just thousands upon thousands of years of our intuition telling us "it should be so."” “But science does not exist to show that reality conforms to our biases and prejudices and opinions; it seeks to uncover the nature of reality irrespective of our biases. If we really want to understand quantum mechanics, the goal should be more about letting go of our biases and embracing what the Universe tells us about itself.” https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2019/09/11/the-most-unpopular-interpretation-of-quantum-physics-may-make-all-the-others-irrelevant/ 3- From post ‘Check your Bases" from Sabine Hossennfelder Physics World recently interviewed the current director of CERN, Fabiola Gianotti. When asked how particle physicists address group-think, Gianotti explains instead why some research avenues require large communities. You would think that sufficiently much has been written about cognitive biases and logical fallacies that even particle physicists took note, but at least the ones I deal with have no clue. If I ask them what measures they take to avoid cognitive biases when evaluating the promise of a research direction, they will either mention techniques to prevent biased data-analysis (different thing entirely), or they will deny that they even have biases (thereby documenting the very problem whose existence they deny). Here is a response I got from a particle physicist when I pointed out that Gianotti did not answer the question about group think: (This person then launched an ad-hominem attack at me and eventually deleted their comment. In the hope that this deletion documents some sliver of self-insight, I decided to remove identifying information.) Here is another particle physicist commenting on the same topic, demonstrating just how much these scientists overrate their rationality: It is beyond me why scientists are still not required to have basic training in the sociology of science, cognitive biases, and decision making in groups. Such knowledge is necessary to properly evaluate information. Scientists cannot correctly judge the promise of research directions unless they are aware how their opinions are influenced by the groups they are part of. https://backreaction.blogspot.com/2019/03/check-your-biases.html 4- Another one by Sabine Hossenfelder, “Particle physicist: Science is suffering from “baked in” bias “For the past 15 years, I have worked in the foundations of physics, a field which has not seen progress for decades. What happened 40 years ago is that theorists in my discipline became convinced the laws of nature must be mathematically beautiful in specific ways. By these standards, which are still used today, a good theory should be simple, and have symmetries, and it should not have numbers that are much larger or smaller than one, the latter referred to as “naturalness.” Based on such arguments from beauty, they predicted that protons should be able to decay. Experiments have looked for this since the 1980s, but so far not a single proton has been caught in the act. This has ruled out many symmetry-based theories. But it is easy to amend these theories so that they evade experimental constraints, hence papers continue to be written about them. People said it was just the maturity of the field. But this doesn’t explain the stunning profusion of blundered predictions. It’s not like we predicted one particle that wasn’t there. We predicted hundreds of particles, and fields, and new symmetries, and tiny black holes, and extra-dimensions (in various shapes, and sizes, and widths), none of which were there. No, and crackpot cosmology around the non-evidence-based multiverse has begun to play too big a role in the science news cycle as a result.” “Of course I am not the first to figure beauty doesn’t equal truth. Indeed, most physicists would surely agree that using aesthetic criteria to select theories is not good scientific practice. They do it anyway. Because all their colleagues do it. And because they all do it, this research will get cited, will get published, and then it will be approved by review panels which take citations and publications as a measure of quality. The challenge is simpler than sometimes supposed. People must be willing to accept a truth they don’t like. If the universe is not as we would like it to be, imagining a different one is fun and maybe profitable, maybe aesthetically pleasing. But it is not science.” https://uncommondescent.com/philosophy/particle-physicist-science-is-suffering-from-baked-in-bias/ 5- From “Naïve Physics and Quantum Mechanics: The Cognitive Bias of Everett’s Many-Worlds Interpretation” by Andrew SID Lang and Caleb J Lutz “We discuss the role that intuitive theories of physics play in the interpretation of quantum mechanics. We compare and contrast naïve physics with quantum mechanics and argue that quantum mechanics is not just hard to understand but that it is difficult to believe, often appearing magical in nature. Quantum mechanics is often discussed in the context of "quantum weirdness" and quantum entanglement is known as "spooky action at a distance." This spookiness is more than just because quantum mechanics doesn't match everyday experience; it ruffles the feathers of our naïve physics cognitive module. In Everett's manyworlds interpretation of quantum mechanics, we preserve a form of deterministic thinking that can alleviate some of the perceived weirdness inherent in other interpretations of quantum mechanics, at the cost of having the universe split into parallel worlds at every quantum measurement. By examining the role cognitive modules play in interpreting quantum mechanics, we conclude that the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics involves a cognitive bias not seen in the Copenhagen interpretation.” https://arxiv.org/pdf/1602.06821 6- From “Is Physics Biased Against Alternative Possibilities? From the book New Approaches to Scientific Realism by Tomasz Placek The paper poses the question of whether physics contains some rules or interpretational principles that result in it being biased with regard to indeterminism (understood modally) and in favor of determinism. It identifies one rule of that sort with Hadamard-inspired principles of theory construction. It then describes four strategies that are used to guard determinism in the presence of non-unique solutions to a theory’s basic equations. https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9783110664737-014/html?lang=en 7- From article “See No Bias, Hear No Bias, Speak for No Change" and I postulate that this gender bias carries into research or at least shows the whole field to be blinded towards bias. “A study of the attitudes of progressive, white, male physicists suggests that their inaction in confronting biases contributes significantly to the problem of inequality in physics research.” Yes, philosophical bias has some responsibility in scientists steering clear of what you call fringe science and that I call phenomena part of reality that must be studied in order to have a fuller picture of reality. If I understand your question correctly, yes, this avoidance could be feasibly challenged. Are you aware that most "ghosts" apparitions are in houses with either a stream under the house of electrical towers close by; why is this? why could science not investigate this and get to the bottom of it? You can inquire into disembodied minds by untangling the part that is brain from the part that is mind. Some neuroscientists are doing this already (gave also names that were doing this in the past, but were ignored: Lashley, Persinger, Pietsch). Difficulties yes, but not obstacles. We built the Hadron collider for goodness’ sake to get at the core of matter-physics. Not true on observation, for example IANDS has thousands of reported NDE's ready for investigation. I will pass on fairies and Tinkerbell which were added to discredit not discuss the matter of bias in science.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
1- I have a few holistic studies in mind; will need time. 2- Never said that they were unsuccefful. 3 to 6 - So, does that change anything on reporting about bias? 7- Because they are more open to talk about bias than other science fields? Why turn to ridicule; you are much smarter than that. A last batch of studies for those still interested in the topic. From «Herding, social influences and behavioural bias in scientific research: Simple awareness of the hidden pressures and beliefs that influence our thinking can help to preserve objectivity (don’t accuse me of sampling bias as this one seems to have a simple remedy for it; from Michell Baddele “The mission of scientific research is to understand and to discover the cause or mechanism behind an observed phenomenon. The main tool employed by scientists is the scientific method: formulate a hypothesis that could explain an observation, develop testable predictions, gather data or design experiments to test these predictions and, based on the result, accept, reject or refine the hypothesis. In practice, however, the path to understanding is often not straightforward: uncertainty, insufficient information, unreliable data or flawed analysis can make it challenging to untangle good theories, hypotheses and evidence from bad, though these problems can be overcome with careful experimental design, objective data analysis and/or robust statistics. Yet, no matter how good the experiment or how clean the data, we still need to account for the human factor: researchers are subject to unconscious bias and might genuinely believe that their analysis is wholly objective when, in fact, it is not. Bias can distort the evolution of knowledge if scientists are reluctant to accept an alternative explanation for their observations, or even fudge data or their analysis to support their preconceived beliefs. This article highlights some of the biases that have the potential to mislead academic research. Among them, heuristics and biases generally and social influences in particular, can have profoundly negative consequences for the wider world, especially if misleading research findings are used to guide public policy or affect decision‐making in medicine and beyond. https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.15252/embr.201540637 From « Do Pressures to Publish Increases Scientists’ Bias? An Empirical Support for US States Data by Danielle Fanelli The growing competition and “publish or perish” culture in academia might conflict with the objectivity and integrity of research, because it forces scientists to produce “publishable” results at all costs. Papers are less likely to be published and to be cited if they report “negative” results (results that fail to support the tested hypothesis). Therefore, if publication pressures increase scientific bias, the frequency of “positive” results in the literature should be higher in the more competitive and “productive” academic environments. This study verified this hypothesis by measuring the frequency of positive results in a large random sample of papers with a corresponding author based in the US. Across all disciplines, papers were more likely to support a tested hypothesis if their corresponding authors were working in states that, according to NSF data, produced more academic papers per capita. The size of this effect increased when controlling for state's per capita R&D expenditure and for study characteristics that previous research showed to correlate with the frequency of positive results, including discipline and methodology. Although the confounding effect of institutions' prestige could not be excluded (researchers in the more productive universities could be the most clever and successful in their experiments), these results support the hypothesis that competitive academic environments increase not only scientists' productivity but also their bias. The same phenomenon might be observed in other countries where academic competition and pressures to publish are high. From the abstract of “The Bias Blind Spot: Perceptions of Bias in Self Versus Others by Emily Pronin, Daniel Y. Lin and Lee RossView Three studies suggest that individuals see the existence and operation of cognitive and motivational biases much more in others than in themselves. Study 1 provides evidence from three surveys that people rate themselves as less subject to various biases than the “average American,” classmates in a seminar, and fellow airport travelers. Data from the third survey further suggest that such claims arise from the interplay among availability biases and self-enhancement motives. Participants in one follow-up study who showed the better-than-average bias insisted that their self-assessments were accurate and objective even after reading a description of how they could have been affected by the relevant bias. Participants in a final study reported their peer’s self-serving attributions regarding test performance to be biased but their own similarly self-serving attributions to be free of bias. The relevance of these phenomena to naïve realism and to conflict, misunderstanding, and dispute resolution is discussed. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0146167202286008 From abstract of “Assessment of potential bias in research grant peer review in Canada by Robyn Tamblyn, Nadyne Girard, Christina J. Qian and James Hanley. This also provides solutions to funding bias. BACKGROUND: Peer review is used to determine what research is funded and published, yet little is known about its effectiveness, and it is suspected that there may be biases. We investigated the variability of peer review and factors influencing ratings of grant applications. METHODS: We evaluated all grant applications submitted to the Canadian Institutes of Health Research between 2012 and 2014. The contribution of application, principal applicant and reviewer characteristics to overall application score was assessed after adjusting for the applicant’s scientific productivity. RESULTS: Among 11 624 applications, 66.2% of principal applicants were male and 64.1% were in a basic science domain. We found a significant nonlinear association between scientific productivity and final application score that differed by applicant gender and scientific domain, with higher scores associated with past funding success and h-index and lower scores associated with female applicants and those in the applied sciences. Significantly lower application scores were also associated with applicants who were older, evaluated by female reviewers only (v. male reviewers only, −0.05 points, 95% confidence interval [CI] −0.08 to −0.02) or reviewers in scientific domains different from the applicant’s (−0.07 points, 95% CI −0.11 to −0.03). Significantly higher application scores were also associated with reviewer agreement in application score (0.23 points, 95% CI 0.20 to 0.26), the existence of reviewer conflicts (0.09 points, 95% CI 0.07 to 0.11), larger budget requests (0.01 points per $100 000, 95% CI 0.007 to 0.02), and resubmissions (0.15 points, 95% CI 0.14 to 0.17). In addition, reviewers with high expertise were more likely than those with less expertise to provide higher scores to applicants with higher past success rates (0.18 points, 95% CI 0.08 to 0.28). INTERPRETATION: There is evidence of bias in peer review of operating grants that is of sufficient magnitude to change application scores from fundable to nonfundable. This should be addressed by training and policy changes in research funding https://www.cmaj.ca/content/190/16/E489
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
I am not the one saying that this topic is circling back to the beginning. What I said is that I did not understand why folks were saying that we were running around in circle. I feel that some progress is being made, at least in the comprehension of the subject matter. Bias is not "rampant" nor "running amok" in science, it's just there because you have people involved in science and they bring their values and beliefs with them and the process tries to eliminate it. This is better said by Fredrik Andersen, Reni Lill Anjum and Elena Rocca in" Philosophy of Biology: Philosophical bias is the one bias that science cannot avoid." Here is the excerpt "....all scientists also make assumptions of a non-empirical nature about topics such as causality, determinism and reductionism when conducting research". I would add to the list materialism and physicalism. What I am saying is even with bias, science is conducted in a progressing manner with very important and relevant findings being made all the time. That is good. However, my contention is that with those biases always in play, science is going in a single direction and forced to ignore other possible avenues of scientific investigation. It "biasly" (inventing a word here) leaves out things that should be included. Finally, it is incorrect to say that I have not given examples of the pervasive and permanent nature of bias. From the abstract of "Bias and Values in Scientific Research by Torsten Wilholt - "But as a result of the debate on science and values, the idea that all ‘extra-scientific’ influences on research could be singled out and separated from pure science is now widely believed to be an illusion.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
1- You brought Big Foot into the discussion and I tried to turn it into a metaphor, but I agree with you that it was not my best attempt at a metaphor. 2- It's not Charlie, Phil and Louise that think so, its scientists investigating their relevant field of study. So all of them including me are "totally" wrong about it? Those that say never are most always wrong. They are more blind than others to bias. Although, I believe that in physics, there is much less opportunity of being so. 3- I gave seven examples outside of the field of cognitive sciences (see my response to INow), with some researching the topic and finding bias. What else is required? As I indicated, its through reading many scientific articles, research results and papers over the years, that I was convinced by them that there is most probably bias in science. All 24 articles that I could find currently were introduced to this forum as examples of what is out there presently on the topic. They did not affect nor even reinforce my impression that there is bias in science. It is regretful that I did not keep all of the articles and research that I encountered over the years that convinced me of such bias, but I did not. I agree also that physics is much more impermeable to bias than other scientific disciplines. And reiterate, there must be research out there that shows no bias in science, but personally, over the years and during my brief research for this forum, I have not encountered even a single one (though I encountered many that said there was bias and offered mitigation strategies without finding out if those measures were effective). I even typed science isn't biased to see what would come about and got bias avoidance measures or titles like Science is not biased, we are! Which is what I have been saying all along. To me, someone who says he is not biased is only fooling himself, and this personal biasness is brought into play in the act and art of science.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
There is a significant number of observational articles on bias in science and the materialism dogma. I have not encourntered any observational articles saying that the is no bias nor materialism dogma in science. I have come to the conclusion that there is a materialism bias in science after reading a significant amount of scientific papers, publications and studies over decades. I have not come to this forum saying this and then finding a few articles to back my claim. At the very least, you must acknowledge that I am not the only holding up this view. And it is an easy form of an extreme selective reading. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 1- From the abstract and introduction of “Bias and Values in Scientific Research” by Torsten Wilholt. “When interests and preferences of researchers or their sponsors cause bias in experimental design, data interpretation or dissemination of research results, we normally think of it as an epistemic shortcoming. But as a result of the debate on science and values, the idea that all ‘extra-scientific’ influences on research could be singled out and separated from pure science is now widely believed to be an illusion. I argue that nonetheless, there are cases in which research is rightfully regarded as epistemologically deficient due to the influence of preferences on its outcomes. I present examples from biomedical research and offer an analysis in terms of social epistemology.” “Bias is becoming increasingly recognized as a serious problem in many areas of scientific research. Of particular concern are cases in which research results seem directly to reflect the preferences and interests of certain actors involved in the research process. Troubling examples of this have been identified, especially in privately funded research and in policy-related areas.” “Intuitively (and traditionally) it seems clear that the suggested kind of bias constitutes outright epistemic failure. But philosophers of science have begun to realize that the ideal of pure and value-free science is at best just that—an ideal—and that all scientific practice involves all kinds of value-judgments. While some philosophers have sought to distinguish acceptable from unacceptable influences of values on science, efforts to draw this distinction in a principled way have proven immensely difficult (see Sect. 6). So why should not some values that inform scientific research be, for example, shareholder values?” https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0039368108001155 2- From “Philosophy of Biology: Philosophical bias is the one bias that science cannot avoid” by Fredrik Andersen, Reni Lill Anjum and Elena Rocca Scientists seek to eliminate all forms of bias from their research. However, all scientists also make assumptions of a non-empirical nature about topics such as causality, determinism and reductionism when conducting research. Here, we argue that since these 'philosophical biases' cannot be avoided, they need to be debated critically by scientists and philosophers of science. https://elifesciences.org/articles/44929 3- From the abstract of “Heuristics and biases: The science of decision-making by Steve Dale A heuristic is a word from the Greek meaning ‘to discover’. It is an approach to problem-solving that takes one’s personal experience into account. Heuristics provide strategies to scrutinize a limited number of signals and/or alternative choices in decision-making. Heuristics diminish the work of retrieving and storing information in memory and of streamlining the decision-making process by reducing the amount of integrated information necessary in making the choice or passing judgement. However, whilst heuristics can speed up our problem-solving and decision-making processes, they can introduce errors and bias judgements. This article looks at commonly used heuristics and their human psychology origins. Understanding how heuristics work can give us better insight into our personal biases and influences and (perhaps) lead to better problem-solving and decision-making. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0266382115592536 4- From “Molecular Bias” by John P. A. Loannidis Bias is ubiquitous in research. The advent of the molecular era provides a unique opportunity to study the consequences of bias with large-scale empirical evidence accumulated in the massive data produced by the current discovery-oriented scientific effort, rather than just with theoretical speculations and constructs. Here I discuss some empirical evidence about manifestations of bias in molecular epidemiology. Bias may manifest as either heterogeneity or as deviation from the true estimates. The failure to translate molecular knowledge and the failure to replicate information are some typical hallmarks of bias at action. The acquired knowledge about the behaviour and manifestations of bias in molecular fields can be transferred back also to more traditional fields of epidemiology and medical research. Getting rid of false claims of the past is at least as important as producing new scientific discoveries. In many fields, the observed effects sizes that circulate as established knowledge are practically estimating only the net bias that has operated in the field all along. Issues of plausibility (in particular biological plausibility), replication, and credibility that form the theoretical basis of epidemiology and etiological inference can now be approached with large-scale empirical data. 5- From “Cognitive Bias and Blindness: A Global Survey of Forensic Science Examiners by Jeff Kukucka, Saul M. Kassin, Patricia A. Zapf Exposure to irrelevant contextual information prompts confirmation-biased judgments of forensic science evidence (Kassin, Dror, & Kukucka, 2013). Nevertheless, some forensic examiners appear to believe that blind testing is unnecessary. To assess forensic examiners’ beliefs about the scope and nature of cognitive bias, we surveyed 403 experienced examiners from 21 countries. Overall, examiners regarded their judgments as nearly infallible and showed only a limited understanding and appreciation of cognitive bias. Most examiners believed they are immune to bias or can reduce bias through mere willpower, and fewer than half supported blind testing. Furthermore, many examiners showed a bias blind spot (Pronin, Lin, & Ross, 2002), acknowledging bias in other domains but not their own, and in other examiners but not themselves. These findings underscore the necessity of procedural reforms that blind forensic examiners to potentially biasing information, as is commonplace in other branches of science. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2211368117300323 6- From the results and conclusion sections of “Science mapping analysis characterizes 235 biases in biomedical research by John P.A. loannidis Forty bias terms were used in the title or abstract of more than 100 articles each. Pseudo-inclusion clustering identified 252 clusters of terms. The clusters were organized into macroscopic maps that cover a continuum of research fields. The resulting maps highlight which types of biases tend to co-occur and may need to be considered together and what biases are commonly encountered and discussed in specific fields. Most of the common bias terms have had continuous use over time since their introduction, and some (in particular confounding, selection bias, response bias, and publication bias) show increased usage through time. This systematic mapping offers a dynamic classification of biases in biomedical investigation and related fields and can offer insights for the multifaceted aspects of bias. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0895435610000223 7- From the abstract of “Peer Review Bias: A Critical Review by Samir Haffar MD, Fateh Bazerbachi MD, Hassan Murad MD, MPH Various types of bias and confounding have been described in the biomedical literature that can affect a study before, during, or after the intervention has been delivered. The peer review process can also introduce bias. A compelling ethical and moral rationale necessitates improving the peer review process. A double-blind peer review system is supported on equipoise and fair-play principles. Triple- and quadruple-blind systems have also been described but are not commonly used. The open peer review system introduces “Skin in the Game” heuristic principles for both authors and reviewers and has a small favorable effect on the quality of published reports. In this exposition, we present, on the basis of a comprehensive literature search of PubMed from its inception until October 20, 2017, various possible mechanisms by which the peer review process can distort research results, and we discuss the evidence supporting different strategies that may mitigate this bias. It is time to improve the quality, transparency, and accountability of the peer review system.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
1- Agree that it is mostly cognitive science, not science in general. I will pursue my search. 2- Big foot was used as a metaphor to demonstrate that I am not the only one thinking about bias in science. 3- Again, big foot does not exist and bias towards materialism does leave physical evidence. 4- Good,I need to think before giving an answer. As a preliminary answer, I would say that a the core of altered stats of consciousness, there is oneness in everything and purpose to all of this, two attributes that may have given more social cohesion and a will to survive. Also, I would like to obtain your opinion from you and other physicists on this passage (e.g. is there a possibility that this could even be remotely true): and they should be consistent with the most accurate theories of physical manifestation, such as relativistic quantum field theories. Speculating within a quantum-theoretic context, consciousness could be inserted as a primitive element into reality by providing a role for intention in the selection process of observables, the collapse of the state vector, or the ordering of quantum fluctuations. But consciousness could be more fundamental, in the sense of a deep consciousness coinciding with a pre-physical substrate, from which intention shapes both mental experience and physical manifestation. If any significance can be attached to the mathematical formalism of relativistic quantum field theories, perhaps creation and annihilation operators, which determine the fluctuations of a quantum field, can metaphorically be regarded as the avenue through which intention acts. Morphic fields within the pre-physical substrate could hold in place patterns that shape the reality that we experience. Among such morphic fields could be ones that correspond to the world view of scientism. By becoming authentic, one could break from such constraints and consider alternative possibilities that can include various forms of radical transformation.” More so in cognitive science than psychology, but even so, what is wrong with psychology? Is this not a form of bias at play? Could not be an extreme form of selective reading as I found not even one article saying that there was no bias in science or that materialism was not a dogma in science. As for wild extrapolations, are you not at least a bit surprised that even others share my cockamamie views of consciousness ? Agree that a bend in the qm river might be wrong.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
This is the additional information that I was able to gather as there is not much available on bias in science and the scientific materialistic dogma. It is mostly observational, but how many need to see Big Foot before it gets embarrassing to say that he absolutely does not exist. 1- A postmodern criticism of P.S. Churchland’s claims regarding materialism. The abstract of the article Modern Manifestations of Materialism: A Legacy of the Enlightenment Discourse states that: “Neurobiological explanations of behavior are used increasingly in the place of psychological explanations. This trend is indicative of the rise in popularity of materialism. " In order for Churchland to maintain her materialist position, she must assume a transparency in scientific method, an assumption which is a legacy of Enlightenment philosophy. However, many postmodern philosophers including M. Heidegger (1962, and 1977) and H. G. Gadamer (1995) have questioned this assumed transparency of method”. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2020 APA, all rights reserved https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1997-05471-004 2- From the abstract “Materialism and Selection Bias: Political Psychology from a Radical Constructivist Perspective” “Political psychology rests on the assumption of the existence of a world outside and independent of consciousness. This ontological materialism is hardly spoken of within the field, as it is an unchallenged assumption among most psychologists and social scientists, including political scientists. However, the materialist paradigm frames research designs, the interpretation of data and theory building.” “……the choice of a certain approach to answer a research question rests on the deeply ingrained beliefs of researchers” “These beliefs are usually not part of research presentations even though they have tremendous influence on the results of the whole research process. Recipients use these necessarily biased research results as building blocks for the construction of their own realities.” “….instead of coming closer to any kind of an “objective” understanding of political attitudes, in political psychology we cannot help but invent new stories about the (political) world as long as our beliefs consciously or unconsciously influence our decision making in theorizing and research practice.” “The article is a description of how a researcher’s subjective perception and construction of the (social) world has consequences for the complete research process. https://constructivist.info/16/3/327 3- Jon Mills on page 5 of a document titled “Five Dangers of Materialism” states the following: “Contemporary theories in cognitive science and the philosophy of mind lend burgeoning support to the materialist position regarding the mind-body problem. That is, naturalism, physicalism, and material monism are the preferred theories that explain the relationship between mental processes and physical brain states. Although dualist and spiritualist approaches offer counter arguments to materialism (Vender, 1994; Warner, 1994), the preponderance of current research in the philosophical, natural, and social sciences concludes that mental states are nothing but physical states (Armstrong, 1968; Bickle, 1998; Churchland, 1981, Dennet,1991; Dretske, 1995; Searle, 1994). From these accounts, mind is brain.” https://static1.squarespace.com/static/6077171f228eb219180f62e9/t/60a47c900f22b814725f6d73/1621392530260/Five+Dangers+of+Materialism.pdf 4- In “Beyond Scientific Materialism: Toward a Transcendent Theory of Consciousness”, author Barus Imants describes some of the pathways that may lead us beyond a materialistic worldview. I think that this will be cause for a lively debate with the physicists participating in our forum. “Analysis of the social-cognitive substrate of scientific activity reveals that much of science functions in an inauthentic mode whereby a materialist world view constrains the authentic practice of science. But materialism cannot explain matter, as evidenced by empirical data concerning the nature of physical manifestation. Nor, then, should materialism be the basis for our interpretation of consciousness. It is time to move beyond scientific materialism and develop transcendent theories of consciousness. Such theories should minimally meet the following criteria: they should be based on all of the usual empirical data concerning consciousness, including altered states of consciousness; they should take into account data about anomalous phenomena and transcendent states of consciousness; they should address the issue of existential meaning and provide soteriological guidance; and they should be consistent with the most accurate theories of physical manifestation, such as relativistic quantum field theories. Speculating within a quantum-theoretic context, consciousness could be inserted as a primitive element into reality by providing a role for intention in the selection process of observables, the collapse of the state vector, or the ordering of quantum fluctuations. But consciousness could be more fundamental, in the sense of a deep consciousness coinciding with a pre-physical substrate, from which intention shapes both mental experience and physical manifestation. If any significance can be attached to the mathematical formalism of relativistic quantum field theories, perhaps creation and annihilation operators, which determine the fluctuations of a quantum field, can metaphorically be regarded as the avenue through which intention acts. Morphic fields within the pre-physical substrate could hold in place patterns that shape the reality that we experience. Among such morphic fields could be ones that correspond to the world view of scientism. By becoming authentic, one could break from such constraints and consider alternative possibilities that can include various forms of radical transformation.” Author: Baruss, Imants Source: Journal of Consciousness Studies, Volume 17, Numbers 7-8, 2010, pp. 213-231(19) Publisher: Imprint Academic https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/imp/jcs/2010/00000017/f0020007/art00012 5- On my contention that life cannot be reduced purely to the physical, Jesse M. Mulder in the abstract of “A Vital Challenge to Materialism” states that: “Life poses a threat to materialism. To understand the phenomena of animate nature, we make use of a teleological form of explanation that is peculiar to biology, of explanations in terms of what I call the ‘vital categories’ – and this holds even for accounts of underlying physico-chemical ‘mechanisms’. The materialist claims that this teleological form of explanation does not capture what is metaphysically fundamental, whereas her preferred physical form of explanation does. In this essay, I do three things. (1) I argue that the ‘vital categories’, such as life form and life-process, do not reduce to the ‘physical categories’ and show that there are no grounds for the materialist's metaphysically limiting claim; (2) I sketch a positive view on how vital and physical explanations can both apply to a given phenomenon, and on how they interrelate; and (3) I show that this view meshes nicely with evolutionary theory, despite being committed to a form of ‘biological essentialism’. Philosophy , Volume 91 , Issue 2 , April 2016 , pp. 153 - 18 https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/philosophy/article/abs/vital-challenge-to-materialism/42296441632B6DC3FC77B61E5268E70C 6- A book preview of “A Skeptic’s Faith, Why Scientific Materialism Cannot be the Whole Truth” by Charles Siegel https://books.google.ca/books?hl=en&lr=&id=62ywEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT5&dq=bias+science+materialism&ots=epLVizXaRC&sig=-fJXBYxQUkVgwqN_OhwDguUWtE4#v=onepage&q=bias%20science%20materialism&f=false 7-In “Notes Toward Stamping on the Corpse of Scientific Materialism” by Gary Allen states that: Science and its aura constitute the pervasive, unavoidable view and methodology of modernity. We cannot understand our era without considering its dominant presence. How we receive and convey information, transport our bodies, nourish ourselves, heal, fight our wars, the objects we possess and the clothes we wear, indeed, much of what we think bears its seal. We live within a paradigm that science--consciously or not--has generated. Accordingly, the accreted ideology of “scientific materialism” bounds and determines what is real and what is not, and shapes our perceptual universe. Science is a series of methods aimed at exploring the natural world and inventing useful tools. It generates a changing fabric of theories about the origin, nature, and functions of that world. It’s often animated by an open-ended spirit of inquisitiveness and delight in discovery. Unfortunately, science as the study of the natural world--sometimes for scientists and very much for modern global society--easily slips into scientific materialism, a theory that only the natural world truly exists. Rather than simply being “truth:’ it’s instead a dogma fabricated out of scientific data by its proponents that stands as the modern paradigm for reality. Insidiously, this view filters our perceptual world and obstructs the mind’s potential. Hence “scientific materialism” describes a body of beliefs that determines how we think and what we value; how we regard our bodies, our relationships, our planet; what makes for a valid therapeutic response or an invalid one; even what kind of information we allow in and what we block out. It’s a theory of reality that constructs our universe. Scientific materialism begins with scientists themselves, some of whom have proclaimed the material world as the sole reality and view science as the only reliable source of knowledge about it. While it isn’t a ‘school,’ exactly, it has been advanced by some scientists as an encompassing way to view reality and been absorbed into modern philosophical schools like 20th century French deconstructionism. Scientific materialists can be quite definitive in their rejection of any kind of validity especially to religious views of reality. While we certainly can=t label all scientists as materialists because they individually reflect a range of philosophical positions and beliefs, a life in science doesn’t seem to correlate well with religious belief. Virtually none of the Nobel Prize winners in science, the majority of them American and European, have identified themselves as Christian. A 1998 survey of the most accomplished American scientists, those elected to the National Academy of Sciences, found only 7% ‘believe in a personal God,’ though 40% of American scientists generally would say they do. Biologists are apparently more likely to be atheists than physical scientists. Evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins remarks how ‘American scientists are less religious than the American public generally, and that the most distinguished scientists are the least religious of all.’5 https://garyallenantarabhavapress.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/NOTES-TOWARD-STAMPING-ON-THE-CORPSE-OF-SCIENTIFIC-MATERIALISM-for-website.pdf
-
OT by some six-year olds from Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
You know Dim that the monkey is still on my back with myself giving it no respect whatsoever and the empire is not even replaced, bot lost forever 😊
-
OT by some six-year olds from Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
yo dude, if people stop posting me, then I will stop posting. a parrot cunning trol apart from that😊
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
I suspected that this was the case.
-
Bias in science (split from Evolution of religiosity)
When I read msc,I see bias all over science and when I read yours i see no bias at play; I am now totally confused 1- got it and yes, the only issue is biased people 2-yes, looking at the right places and asking the right questions