-
Posts
358 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Posts posted by elementcollector1
-
-
Spotted this playing one of my old Pokemon games under the Pokedex entry for Magneton:
"It is actually three Magnemite linked by magnetism. It generates powerful radio waves that raise temperatures by 3.6 degrees F within a 3,300-foot radius."
That got me wondering how much power that would actually need, and whether it would be feasible for Magneton to actually output it via microwave radiation. Best equation I could find was the heat capacity equation (altered for power instead of energy):
P = mcΔT/t
(P = power in watts, m = mass in kg, c = heat capacity in J/kg.K, ΔT = temperature change in Kelvin, and t = time in seconds)We know ΔT is 2 K, and I'm assuming c is the value for water vapor (steam) at 1996 J/kg.K.
m is a bit trickier - I assumed an average relative humidity of 30%, which gives 0.0066 kg water vapor per cubic meter air. In non-Imperial games, that 3300 feet is replaced with 1000 meters, so I'll use a sphere of 1000 meter radius for Magneton's maximum influence, which has a volume of 4.1887902 x 109 m3, giving a total water content of 27646015.3 kg.
t is also tricky - I assumed Magneton takes one hour (or 3600 seconds) to achieve this temperature rise. No real reason behind the assumption other than giving it plenty of time.
From all this, I get a value of 3.0656359.2 x 107 W, which seems pretty realistic given the sheer mass of water being heated (and pretty terrifying for a lone Pokemon to be outputting somewhere in the wilderness). However, I want to take into account more complex factors, such as attenuation of the radiation, the frequency of the microwave (which I'm assuming is 2.45 GHz, since that's the one commonly used in commercial microwave ovens). I found this graph for attenuation of a range of EM frequencies from oxygen and water:
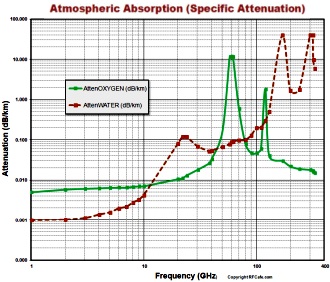
However, I'm not quite sure how to factor all this stuff in. Plus, assuming the number doesn't drop too much, what would be the temperature one meter from Magneton? What would be some other consequences of that much microwave radiation in the atmosphere?
1 -
A Raspberry Pi or Arduino?
0 -
I recently read about an interesting and potentially relevant housing development: Installing packets of paraffin wax in the walls. These absorb the heat during the day, and release it at night, lowering the change of temperature in rooms.
Found here: http://www.wpi.edu/Images/CMS/News/Apelian_JOM.pdf
0 -
Sn's valency is 4, not 6 - the Na+ ions take care of the rest.
As for separation, I would suggest mixing with an acid to change the pH - hydrous Sn(OH)2 or Sn(OH)4 (can't remember which) should precipitate in a certain pH range.
0 -
Not sure what you mean, Enthalpy - I've been doing calculations this whole time.
Anyway, if there's no way to "cheat" the work equation (W = Fd) into thinking there's more distance than there really is, I think I'll have to settle for a system with a lower tolerance for falls - better than what a human could manage, but not perfect.
0 -
Hmm. But shouldn't the plane be heavy enough that the reduced vertical momentum (from the action of the wings) is still greater than the vertical momentum of a person at terminal velocity?
The latter figure comes from FAA certification requirements, which require that a landing gear be designed to handle a hard landing with a sink rate of 10 feet/second (or 600 FPM). A simple calculation shows that for a main landing gear strut with a typical maximum throw length of 12 inches, the required deceleration from such a landing is about 3g. Thus, the strut needs to be able to dissipate a worst-case landing force equivalent to about three times the aircraft's normal static weight.Source: http://www.avweb.com/news/savvyaviator/192153-1.html?redirected=1
3g might not be much acceleration, but considering the plane that's a whole lot of force.
Then again, if deceleration's the issue, wouldn't there still be a problem even if all the force of landing was absorbed?
Back to your earlier calculations on deceleration, the minimum distance to get the deceleration within "safe" (relatively speaking) limits would be 12 m. Is there any way to make this length less - as in, could it be coiled up or otherwise rendered shorter while still acting as if it were the full length?
0 -
I don't get it - if the strut can stop an airplane, why wouldn't it stop a human (ignoring practicality)?
0 -
Well, unless time travel is involved, I don't think I'll be applying the second method.
After some thought, I wondered why we could survive airplanes landing (after all, that's quite some momentum!), and looked it up - apparently something called an 'oleo strut' absorbs most of the shock, apparently by damping with compressed air or nitrogen and oil.
An oleo strut consists of an inner metal tube or piston, which is attached to the wheel axle, and which moves up and down in an outer (or upper) metal tube, or cylinder, that is attached to the airframe. The cavity within the strut and piston is filled with gas (usually nitrogen, sometimes air – especially on light aircraft) and oil(usually hydraulic fluid), and is divided into two chambers that communicate through a small orifice. When the aircraft is stationary on the ground, its weight is supported by the compressed gas in the cylinder.[1] During landing, or when the aircraft taxis over bumps, the piston slides up and down. It compresses the gas, which acts as a spring, and forces oil through the orifice, which acts as a damper. A tapered rod may be used to change the size of the orifice as the piston moves, and a check valve may be used to uncover additional orifices so that damping during compression is less than during rebound.
-WikipediaHypothetically, what if a human pogo-sticked one of these off of a 1200-meter cliff (or some similar setup where the strut would take the brunt of the impact), in keeping with the earlier numbers - would they still be injured from deceleration? I would think they wouldn't if a few of these things could stop the vertical momentum of a passenger plane, but maybe I'm missing something more subtle.
0 -
So if the acceleration is directly proportional to the stopping distance, what is the upper limit on deceleration for a human?
Also, would it be possible to 'transfer' the acceleration somewhere else - as in, direct the shock somewhere it can be less harmful? Not sure on how shock 'moves', at any rate.
0 -
So why is an airbag able to decelerate a person safely? After all, it's not all that big compared to a person, yet it stops collisions very well and allows the driver to survive mostly intact.
0 -
What would be an appropriate "soft" substance? Foam, or maybe a type of rubber?
0 -
Huh. So energy and shock absorption do nothing in this case, because the deceleration itself is enough to damage the human body?
1 -
Okay, so assuming two pads, one on each of the person's feet, the contact area for the body would be about 20 cm by 10 cm, or 200 cm2. How would the force exerted on this area be calculated, then?
0 -
It's mentioned on the webpage (http://www.sorbothane.com/) that it can be used for both "shock" and vibration applications.
0 -
I've recently been considering buying a material titled "sorbothane", a very soft and energy-absorbent derivative of polyurethane. The product list can be found here: http://www.sorbothane.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/11-26-12-Sorbothane_SPG_11.2012_v4.pdf
My question is, when one examines the 4"-by-4"-by-1/2" square pad of durometer 70(product 0204025-70-10), it claims to be able to withstand a load of up to 7400 pounds, or about 33 kN. Now, this already seems kind of ridiculous, but maybe that's just how good it is. Maybe. But how does that translate to impact force?
I've been trying to calculate, as a rough example, how much force a person would experience if they dropped from freefall at terminal velocity and hit the ground with one of these pads on each of their shoes. However, calculating impulse seems to be useless, as the amount of time the person takes to hit the ground is essentially zero. Attempting to derive from I = delta(p) where p is momentum, I arrived at something like 1600 kg*m/s impulse given a person who weighs approximately 600 N, but I don't know if that's correct, or even what to do with it if it is.
Not only that, wouldn't the person experience some sort of force based on all the potential energy - turned - kinetic energy from the distance they fell?
0 -
Is there any way to create a focused beam of sound - either a flat wave or a phaser - with a simple setup?
0 -
I believe NurdRage has a few videos you may want to peruse. Failing that, oxalic acid complexing with iron(II) might do the trick.
0 -
Huh, I wonder how that works.
According to Wikipedia, most acoustic levitation setups nowadays can only manage a few kilograms, though there is no known limit.
Guess I'll have to experiment when I get the chance, then.
0 -
Yes, I'm already aware of the microscale experiments, but they work a bit differently. I'm talking macroscale - upwards of a pound, if at all possible. I found this upon further research:
http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.174302
Hopefully, with the cone of sound, this is possible with non-triangular objects.
0 -
Hear me out here, because I feel like this shouldn't work but I don't know why.
Here are the two pieces of knowledge I base this off of:
-The concept of acoustic levitation is that a standing wave of sound produces enough force to lift an object in midair and hold it.
-If one takes a sufficiently thick piece of paper or thin sheet metal, folds it in half, places an object between the two parts of the fold and attempts to make the angle of the fold more acute, the object is drawn back toward them until it pops out of the wedge.
Therefore, if one was to make a cone of sound sufficiently powerful (whether that entails higher frequency, volume, or both), point it at an object so the object is just barely within the confines of the cone, and narrow the angle, wouldn't the object move towards them?
0 -
Could always make elemental antimony. What worries me more is the jars of thermite - are they premixed? Thermite's not exactly a ticking time bomb, and in fact usually requires a lot of energy to get going, but I still wouldn't feel too happy about having those lying around.
0 -
Among other things, recently added arsenic to my collection - made, not bought.
0 -
Then experiment for weeks/months. If time is your concern, that's not scientific: Some experiments last longer than lifetimes.
0 -
So, it's less like a true railgun and more akin to a multi-stage coilgun? Confusing.
The Wiki page for plasma railguns states that they can "produce controlled jets of given densities and velocities ranging from 5 to 200 km/s".
So, this is not a suitable method for "pushing" a given object without touching it, due to damage of the target. Does anyone know other means of accomplishing this? I'd rather not resort to electromagnetism, as that only affects magnets, and ferromagnetic and diamagnetic materials.
0



Fictional physics validity - Radio waves raising temperature?
in Physics
Posted
I ended up trying this again, this time using radiation physics for a different approach. This time, I assumed Magneton and its surroundings had reached thermal equilibrium, so time is no longer a factor (but is presumed to be quite a while).
I started by getting the solid angle of an area 1km from Magneton, assuming Magneton could be expressed as a 1.0m diameter sphere. This got me an angle of 3.1415 x 10-6 steradians.
From here, I (maybe correctly?) asserted that because Magneton and its surroundings both started at the same ambient temperature, the temperature added by radiation could be estimated via the following equation (taken from here) and used to solve for Magneton's surface temperature (again added to the ambient temperature):
ΔT = +2 K = ((ΔTMagneton)4 (3.1415 x 10-6) / (4pi))1/4
=> ΔTMagneton = 89.45 K
I then went back and altered the solid angle's distance to get the temperatures at 750, 500, 250 and 1 m from Magneton using this same ΔTMagneton, and graphed these to find the following equation:
ΔT = 63.251d-1/2
Where d is the distance from Magneton in meters. Integrating this from d=1 to d=1000 to find the area and then dividing it by the distance of 999 m between the two points, I found the 'global' temperature increase within the 1 km sphere to be an average of 4.004 K, which seems pretty reasonable.
Lastly, we can add this temperature increase to the average global temperature (I picked 1998's value of 58 oF or 287.594 K because this was when the game came out) and use the Stefan-Boltzmann Law to calculate the energy density in Joules/cubic meter of the 1 km sphere Magneton is inside, followed by the total energy in Joules to maintain this temperature inside the 1 km sphere.
pE = (287.594 + 4.004)4 (5.6625 x 10-8) (4/(3 x 108)) = 5.459 x 10-6 J/m3
E = (5.459 x 10-6 J/m3) (4/3)(pi)(10003) = 22,866 J
This is a surprisingly small amount, which I think makes sense at thermal equilibrium, but why is it so much different than the one calculated previously?
Also, would I be right in saying 23 kJ/s or 23 kW is needed for Magneton to maintain this temperature increase every second? So not only is it hot enough to boil water on contact, Magneton is also pumping 23 kW of microwave radiation into its surroundings. Anything nearby is going to get cooked pretty quickly (temperature at 1 m under these assumptions was +63.25 K, meaning a nearby Trainer or Pokemon is in a lot of trouble unless they have RF shielding...)