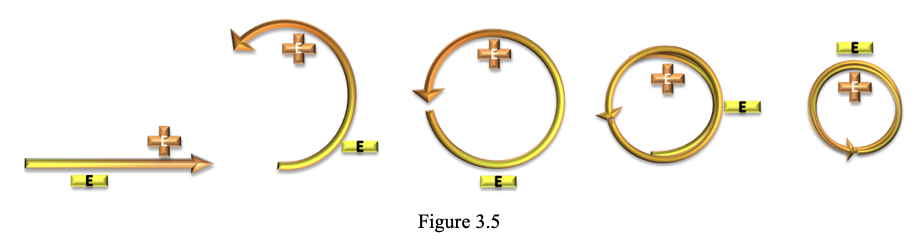Everything posted by Spring Theory
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
I'm saying the geodesic is a spiral path.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
When the photon collapses, the charge source is the dipole that is created. I stipulate that every electric field implies a charge source. By deterministic, I'm implying you can tabulate the momentum and position properties of a particle (at the same time) with plank's constant being a fundamental property of all particles. Lorentz's dilation equation can be made more precise from using the speed of the orbiting photons instead of the speed of a photon in free space as the correction factor. Autopsy is just the best we can do when a positron and electron is annihilated into photons. I'm inferring that what is left after the carnage is what makes up the bodies. Hope that helps. The intrinsic argument is a weak one to me. There is no actual physical spin but it has the properties of something spinning? How unsatisfying is that. Yes, because the radius times the mass also scales by the same factor. The orbital velocity is still c for both.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
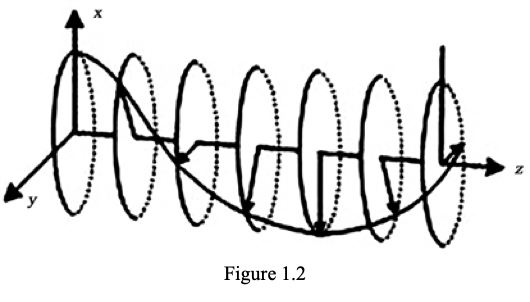
Defining Mass as overall curvature: Since the structure of a photon is described in quantum physics as a “particle” of spin “1” and +/-h angular momentum, this means it will rotate one revolution per wavelength. A potential candidate for a physical description would be a symmetric photon with a length of one wavelength and a circumference of one wavelength as in figure 1.2. This means it’s effective radius can be determined: circumference=λ=2πrc Solving for radius: [latex] r_c = \frac{\lambda}{2 \pi} [/latex] So now the photon has a propagation direction and physically defined radius. This radius is the curvature radius of the photon since it otherwise travels in a straight line. Since all particles are made of photons, then the curvature has to be somehow conveyed by the structure and properties of the photon to calculate mass. Without redefining what mass is, whether a convention selection or simply a property of a particle made up of photons, the standard idea across classical and quantum physics is the consistency of momentum. This means momentum is a conserved quantity which does not change over time or the rate of change is zero or its derivative with respect to time is zero. As stated previously, it is well accepted that photons have momentum. The classical momentum of a photon (usually described with greek letter gamma) is defined specifically in physics and quantum mechanics as follows: [latex] momentum_{\gamma} = p_{\gamma} =\frac{h}{\lambda} [/latex] Where h is Planck's constant and λ is the wavelength of the photon. By defining momentum as mass times velocity: p=mv We can derive a mass equation as: [latex] m_{\gamma} = \dfrac{p}{v} = \dfrac{h}{λv} [/latex] Where h is planks constant, λ is the wavelength of the photon and v is the velocity of the photon (typically the speed of light). Following this path of logic, the mass can be expressed in terms of the curvature radius and the velocity of the photon along that curvature: [latex] mass = m_{\gamma}= \frac{h}{λv_c} =\frac{h}{2πr_cv_c} = \frac{\hbar}{r_cv_c} [/latex] Where ħ is the reduced planks constant (h divided by 2π) as stated before. Since the curvature is geometrically a helix and effectively “open” (like a slinky), we will see that leads to the reason the photon appears to have no mass but still can have momentum. In fact, the mass would be just incredibly difficult to measure.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
I know you're busy but I would really like an good explanation of spin. Maxwell described the electromagnetic field "as the part of space which surrounds bodies of electric (charge) to magnetic conditions." (Maxwell, James Clerk (1865). "A dynamical theory of the electromagnetic field". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 459–512. page 460) I'm proposing an underlying structure to charge that does not conflict with Maxwell's equations. Positronium decay is a decay of both an electron and a positron into photons. You'll have to do an autopsy on the photons that are released. An electron won't decay by itself, but I do propose a positron will decay on it's own.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
It is common to refer the photon as having no charge. It is more complete to say the photon has no “net” charge. A relative observer sees the positive field, then the negative field as it passes by. This is an oscillating effect as with the magnetic fields. You could equate this as seeing a positive charge and then a negative charge with the total net effect zero. Please describe the correct way spin works. Positronium decays into two or three photons. This is an example of an electron being destroyed by a positron. ref: https://arxiv.org/pdf/hep-ph/9911410.pdf Testable prediction: The decay will be offset in trajectory. Picture (2) ball like photons in orbit held together by a piece of string between the photons. If the string is cut (particle decays), then the photons will fly off in opposite directions along lines that are tangent to the orbit diameter. The path is parallel but it is not collinear.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
All these are addressed in the paper.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
Page 5 shows a particularly good candidate for the photon propagating in space as a slinky like structure. Reference: https://www.scirp.org/pdf/oalibj_2019112114183125.pdf An electric charge is presented by the formation of the dipole. Not sure if this is too pedantic, but maybe you can say an electric field is presented. Since electric fields are created by electric charge I don't see how you get around having a field without the charge present. I consider the photon having zero net charge in free space. How does spin work? I'm familiar with the a geometric description and the angular momentum description: 1/2 ħ There are numerous testable predictions.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
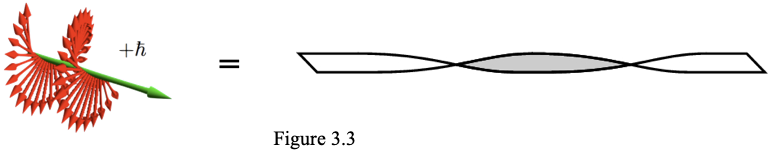
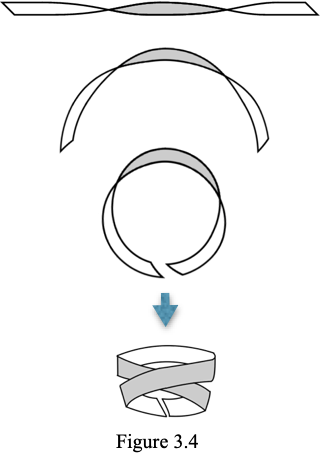
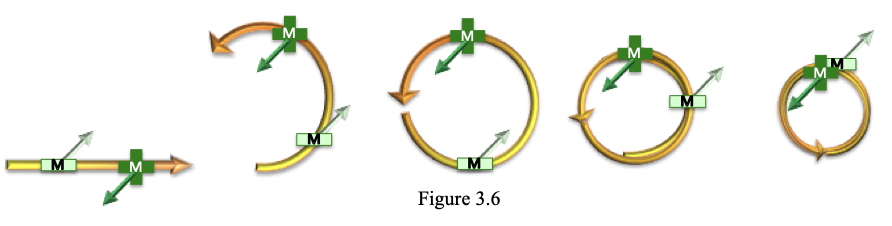
The electron is actually (2) photons, but looking at (1) photon is easier to envision. The topology of the photon is such that it has (1) spin or twist per photon wavelength (per quantum mechanics). This can be modeled as a flat ribbon as shown in Figure 3.3: The flat ribbon with a single twist can have the gray side representing negative charge and the white side representing positive charge side. If this topology is projected around a circumference, it will collapse into (2) flat circular obits (no twist) with the photon’s opposing electric fields aligned radially in an out as shown in figure 3.4. The net effect is a double orbit of the photon in on itself. The Electric fields also line up opposite of each other creating an electric dipole point. A simplified depiction of a single photon collapsing into a double orbit, ignoring the spiral structure, is shown in figure 3.5. Likewise the magnetic field alignment will be similar but perpendicular as in figure 3.6. All three depictions help to describe the ring structure. The topology figure shows how the twist results in the flat portions of the ribbon to align radially. This flattens the twisted electrical fields to a purely radial direction after the collapse effect. Positive charge is shielded completely inside and negative charge is presented outwardly. Included for free is a 1/2 spin property. It takes (2) rotations to get back to where you geometrically start.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
It is a combination of photons in orbit. The ring structure is stationary, but the photons are traveling in orbit to give properties such as mass and charge.
-
The Deterministic Ring Theory of Particles
Hello world...I'm a mechanical engineer (oh no!) and appreciate some feedback. I have updated my theory of everything which explains the following: The nature of spacetime Quantum gravity and unification with electromagnetic force The reason for antimatter scarcity A physical description for the Wave Function and therefore a solution to the measurement problem A definition of mass and force An explanation of dark Matter A more precise Lorentz dilation equation The reason for the electron’s anomalous magnetic moment A physical description of the Fine Structure Constant Many others My first papers abstract: Current quantum theory is based on probability and includes a myriad of fields, forces and force carrying particles. The principle cornerstone of physics is to determine observable values from experiments that match quantum calculations. There are several particles classified as fundamental such as the electron, the quark and the photon. The cloud of uncertainty (principle) around quantum physics has kept any deterministic explanation from been accepted in the physics community. This paper sets the groundwork to connect quantum physics with classical physics concepts. First principles define the photon as the single fundamental particle that all other particles are made from. A geometric analysis of the photon and its measured properties are used to derive a mass equation. Mass is defined as a function of curvature and the velocity along that curvature. This mass equation is used to derive the equations of motion based on the principle of least action. The semi complete Lagrangian of the photon presented leads to Euler-Lagrange equations that agree with its measured properties. The kinetic energy of the presented Lagrangian also directly leads to the Einstein Planck relation. Taking these first principles and applying various thought experiments, explanations are revealed including the double slit experiment, vacuum energy, the Casimir effect and a potential contributor to Dark Matter. A testable prediction resulting from the Ring Theory hypothesis is that the photons resulting from decaying particles have an offset in trajectory. The trajectory is based on the geometry of the ring based particle. The final takeaway is that Ring Theory lays the foundation for the photon to geometrically present positive charges, negative charges, positive masses and magnetic moments that appear in particles previously considered to be fundamental. Here is the full paper: https://acct89456.app.netsuite.com/core/media/media.nl?id=11245&c=ACCT89456&h=QJmsw4-9zydXKSC5cKdu4TMeVg3heptvZM8n4z3fYZOeuA4q&_xt=.pdf Thanks for reading this and let me know what you think. Paper 1 - On the Structure of the Photon 2023 R39.pdf