-
Bohr hydrogen atom model revisited
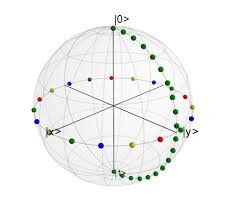
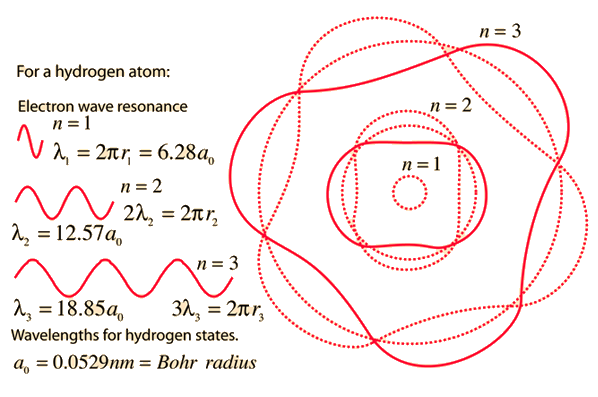
Bohr sees electron as a sphere traveling on Bohr radius around proton (folowing“equator “ trajectory- in the middle between top “north”and Bottom (south ) of proton . In this revisited hydrogen model ,we are going to apply probability of finding electron graph (electron cloud ) to Bohr original model. In this revisited model ,instead of one electron orbiting around proton There is N electrons traveling one at a time from top side (north) of proton to the bottom side (south) of proton . The direction of single electron is perpendicular to original Bohr orbit . The green spheres traveling north/ south (N/S) are trajectory of single electron traveling and “cutting “ the Bohr radius .Dots red ,blue ,green yellow are the pints where Bohr radius is “cut” by single electron . The N number of electrons move N/S and their motion is synchronized to create Bohr radius around proton. The trajectory of single electron traveling north/south will Follow probability function The N number of electrons “cutting “the Bohr radius is the Number of electrons inside the electron cloud. The radius of electron is Bohr circle Circumference divided with N. Let’s calculate number of electrons cutting the Bohr diameter in one second . Bohr radius Rb =5.29x10^-11m Number of revolutions of single electron around proton f=6.65x10^15/sec Circumference of Bohr or or C=5.44x10^-11m The electro static force between electron and proton is Fe=8.24x10^-8N Impulse of electrostatic force J=Fe x t Fe =J/t This force can be crated by a bunch of smaller J’ impulses . Fe=N x J’ x t Thus could be the reason for The time for single electron to travel Distance C/2- from in N/S direction is t’=0.15x10^-15 sec J’=Fe x t’ J’=8.24x10^-8x0.15x10^-15 J’=1.236x10^-23 N’ Is the number of electrons traveling North / South in t’ time. N’=J/J’ N’=8.24x20^-8/1.236x10^-23 N’=1.44x10^15 In one second N=1.44x10^15*************** Single electron travels from North to South perpendicular to Bohr radius and cuts it .The electrons are synchronized and cut Bohr diameter one at a time (in average mode). In real situation every single electron follows the spiral trajectory cording to probability graph. In Bohr model electron is sphere . The diameter of Bohr is cut by N diameters of electrons in one C in time t. The N is number of electrons inside the electron cloud. The dimeter of electron is De=C/N De=5.44x10^-11/1.44x10^15 De=3.73x10^-26m To check this results we are going to use the same procedure but we are going to use entirely different force. Fg=6.65x9.1x10^-31x 1.6x10^-27/26.98x10^-22 Fg=3.46x10^-47 Jg=Fg x t Jg’=Fgxt’ Jg’=3.46x10^-47x 0.15x10^-15 Jg=0.51x10^-62 Ng=Jg/Jg’ Ng=3.46x10^-47/0.519x10^-62 Ng=6.78x10^15************ Opinions ?
-
Calculation of mirror mass using sun gravitational lens formula
Let’s try this approach: The air duct is 1x1 m and 100 meter long . When straight air ,fluid and light travels through in straight line unchanged . If the air duct is straight for 90.5 m and than 9.5 meters at the and is bent - air,fluid and light will change direction . The sun gravitational lensing is “bent” part of time space “duct”. Anything traveling inside the “duct” or curved space time will change trayectory and follow the shape of “duct “.
-
Calculation of mirror mass using sun gravitational lens formula
The distance 0.4AU(69x10^8m) is the closest distance to the sun achieved by satellite. Satellite is positioned on 12:00 o’clock position on the first picture above .(distance b). The mirror is positioned between satellite and sun . The signal from Jupiter comes from “left hand side “perpendicular to the sun /satellite axis. That is marked source on the posture above. The mirror falls of of satellite and only for 9.5m(or 3x10^-5s)travels in curved trajectory mimicking the trajectory of light from Jupiter in that same spot(when mirror is not there ). In this time/distance radiation pressure from sun hits the bottom start of mirror which is A1=1x10^-21m^2) The intensity of sun radiation is about 8500w/m2 The Sun radiation pressure force acting on the bottom of mirror will be in magnitude of 10^-26N This force is not going to affect the gravitational pull on mirror(10^-18N). After 9.5 meter the mirror will be blown away and travel with solar wind away from satellite. The light from Jupiter will continue to travel to observer at 550AU. About 9.5 m: The “chunk “ of curved time space has dimensions 1x1x9.5m. It is the volume where light bending is happening . The mirror is pushed for 9.5 m horizontally by Jupiter radiation pressure force . The gravity is pulling mirror “down” towards the sun . The mass of mirror is calculated to make trajectories of mirror and bent light signal from Jupiter identical. The reflected Jupiter light hits 9.5m x1 m area on the top of volume at Alfa (10^-5 degrees ) and acts on curved time space” hard surface” exchange momentum - creating mechanical (Newtonian force) And gets “pushed down”towards the sun . We see this motion as a consequence of gravitational force Fg (10^-18N) . That is force created as a component of radiation pressure force F rp(10^-8)in the text above . Lower 9.5 x1 m area of volume is bent downwards for the same angle Alfa(a) and deflected light continue to travel towards observer .(at 550Au) Momentum transfer between massless wave and Unknown time space curvature - that is mechanical push of force (radiation pressure force) exerted on the wall(curved time space )- is this description of mechanical force ?
-
Calculation of mirror mass using sun gravitational lens formula
The Jupiter is very well known and data about Jupiter is easily found . The mirror traveling for 9.5m will mimic the trajectory of light beam being bent . The massless deflected light wave coming from Jupiter has area of 1 m^2(square 1mx1m) is going to be bent for angle a(10^-5 degrees ) for a distance Of 9.5m The Sun is curving time space and this curvature of time space is bending light . The mirror traveling inside this Jupiter wave is been pushed “horizontally “by radiation pressure force And “pulled “ down by gravitational force - the trajectory of mirror is identical to trajectory of light wave . The mirror has mass and curvature of space time caused by gravitation of sun is not enough to mimic curved trajectory. It takes horizontal force (Jupiter light radiation pressure force ) and curvature of time space (gravitational force) to mimic curved trajectory of massless wave . Sun gravitational lensing is curving the space time and bending the light (massless wave )in 95 m distance . Compared to: The same space time curvature is mimicked by using two Newtonian forces acting on mirror (baryonic matter with mass). The first force is explained as massless wave transferring momentum to the surface . The second force is explained as a curvature of space time .
-
Calculation of mirror mass using sun gravitational lens formula
Calculation of mirror mass from light radiation pressure force and gravitational force acting on mirror inside the sun gravitational lens The formula for angle of bent light inside the sun gravitational lens. a=4GM/C^2xr r= 69.7x10^8m this is the distance from center of sun to mirror.Two forces are acting on mirror: Pressure radiation force from light reflected from Jupiter surface and gravitational force of Sun. The formula for angle of bent light is a=4GM/C^2xr r= 69.7x10^8m this is the distance from center of sun to mirror Mirror has area A=1 m^2 m=? mass of mirror is not known a=4x6.6x10^-11 x 1.9x10^30/9x10^18x69.7x10^8 a=7.9x10^-7 The intensity of radiation of light reflected from Jupiter is I=1.8w/m2 The radiation pressure acting on surface of mirror is P=I/C=1.8/3x10^8=0.6x10^-8 The force acting on mirror is Frp =6x10^-9N The gravitational force pulling on the mirror is Fg=Frp x tan a And Fg=m x g tan a=1.37x10^-9 Fg=1.37x10^-9x 6x10^-9 Fg=8.22x10^-18N The gravitational acceleration of Sun g=GM/r^2 g=6.6x10^-11 x 1.9x10^30/4.8x10^19 g=2.69m/s mass of mirror m=Fg/g m=8.2x10^-18/2.67 m = 3.0712×10⁻¹⁸kg The length of curvature of light path is L=tg a x r L=1.37x10^-9x69.7x10^8 L = 9.549m Work made by resultant force is Ft x L=E- work Ft^2=Frp^2 + Fg^2 Ft=Frp E=6x10^-9x9.54 E= 5.7x10^-8J E=mx v^2/2 V^2=5.7x10^-8/3x10^-18 V^2=1.9x10^10 V=1.37x10^5m/s To confirm: Centrifugal force Fc=m x v^2/r Fc=3x10^-18x1.86x10^10/69.7x10^8 Fc=0.08x10^18 (Fg=8.2x10^-18)******** The mirror is “pushed” in straight line by radiation pressure force - crated by reflected light from surface of Jupiter and “pulled” towards the sun by sun gravitational force. The angle of sun gravitational lens(angle) formula is used to calculate mass . Opinions ?
-
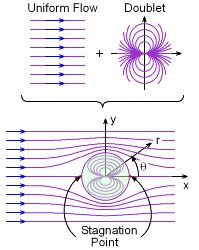
Doublet flow
Here is theoretical example : Two cylinders with diameter of d=1m And height h=1m are positioned at distance of r1=1m. Speed of wind moving against the cylinders is V2=0.4m/s At this distance measured speed in between cylinders is V1=3m/s At distance r2= 2.75 m between cylinders measured speed V2=0.4m/s Doublet flow has two concentric circles moving around each cylinder. In cylinder to the left the direction is CWand for cylinder to the right the direction is CCW. The radius of first concentric circles is Cr1=1m(from the center of cylinders) Cr2=1.875m The Average angular speed of fluid traveling in Cr1 is Av1=V1x Cr1 Av1=3x1 = 3rad/s Av2=V2xCr2 Av2=0.4x1.875 = 0.75rad /s The stagnation pressure - the speed in “hollow “sphere is not 0,so we can calm it pressure P1 is calculated : Po=Ps+0.5 x D x V^2 D=1kg/m3 density of air V=V2=3m/s Po=10^5Pa P1=100000-4.5=99995.5 This pressure is uniformed through Cr1 The pressure P2 P2=100000-0.16=99999.84Pa This pressure is uniformed in area around Cr2 From difference between Po,P1 and P2 (potential energy of fluid)we can calculate force difference between the Force at distance r1 compared to force at distance r2. The cylinders are balloons with plastic skin of negligible mass filled with air . The mass of cylinder is Mc1=Mc2=v(volume )cad Mc1=3.14kg=Mc2 The wind tunnel is positioned inside the diving aircraft so gravitational force of earth is not involved. The pressure difference P3: P3=P2-P1=E E=99999.84-99995.5 E=4.34J E-energy(work ) which creats the force difference between Cr1 and Cr2. E=Fxs S=2.75-1=1.75m F=E /s=4.34/1.75 = 2.48N This is the force which can be created by different potential energy of moving fluid between Cr1 and Cr2. Negative acceleration a=(V1-V2)/t F=mxa F=Mc1x(V1-V2)/t t=F/Mc1x(V1-V2) t=2.48/2.6=0.95 sec The force needed to “push” cylinders apart has to be minimum 2.48N and it would push the cylinders apart in 0.95sec. Now if we put two of these “new bigger hollow cylinders “ at distance Lx The same doublet flow will happen And we can call it fractal nature of doublet flow . Or dipole flow .
-
Doublet flow
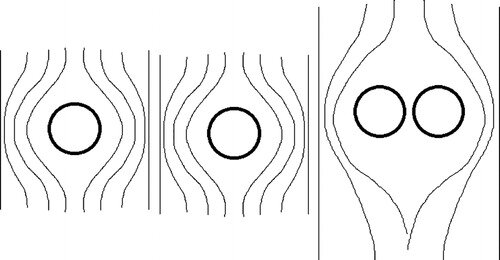
Here is a bit better explanation of what I would like to hear your opinion about. The shortest distance between spheres (picture to the right ,above) is point where distance between source and sink is shortest. The area above the line to the top of spheres is source of flow and sink is area from the line to the bottom of the spheres. The distance between source and sink is virtually 0m(or maybe the size of atom or two of material the sphere is made of). Instead of spheres let’s use cylinders to observe the doublet flow in 2D only. This is the “top”view of flow. The doublet flow around lower cylinder moves in CW direction .The doublet flow around upper cylinder moves in CCW direction . The fluid inside doublet flow around spheres is partially flowing in concentric circles (static wave)and partially going from source through the sink and out to uniform flow(wind). The uniformed flow of wind flows around this new “single cylinder “ with bigger diameter . The diameter of this “bigger “ cylinder is created by static wave like movement of fluid inside concentric circles of doublet flow. For this to happen the wind is non compressible and friction. The stagnation point for single cylinder is the point where speed is 0m/s. For two cylinders - newly created sphere is “hollow”in the middle and flow is not totally stopped. The split in doublet flow happens because speed at stagnation point of pressure between two spheres is not 0. The stagnation pressure formula Po=P+0.5xDxV^2 The speed between spheres is Vmax and pressure Po=10^5Pa The density of air id D=1.2kg/m3 Later comes a practical example .
-
Doublet flow
Yes The force of attraction between spheres is F. What if distance of source and sink is constant for one pair of spheres and distance between spheres is L1 Then we add one more pair of spheres(same L1 ) But they are positioned at L 2 distance from each other (side by side ) at distance L2 . Is there the possibility the flow of fluid (wind ) create bigger doublet flow around these pairs but the attracting force between them F1 is smaller ?
-
Doublet flow
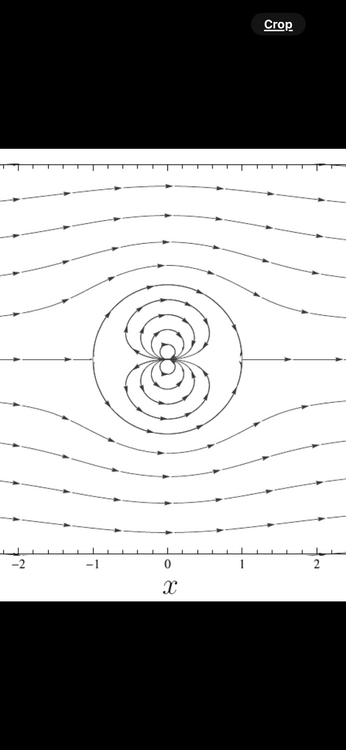
I would like to hear how many people are familiar with doublet flow ? Doublet flow in fluid dynamics refers to the flow pattern created by combining a source and a sink (an inflow point) placed very close to each other. When these two singularities are brought infinitesimally close while maintaining a constant product of their strength and separation distance, they form a doublet. This configuration creates streamlines that resemble the flow around a cylinder in two dimensions or a sphere in three dimensions. When two spheres move close to each other inside a fluid, the flow pattern between them can be approximated by a Rankine oval. This is because the combination of source and sink flows, induced by the moving spheres, can be superposed to create a closed streamline shape resembling an oval. The shape and characteristics of this "Rankine oval" are influenced by the relative size and separation distance of the spheres, as well as the fluid's velocity. The statement "sphere moving inside fluid is reversed bernoulli pipe" refers to a thought experiment or a way to visualize the relationship between fluid pressure and velocity, as described by Bernoulli's principle. It's not a literal reversed Bernoulli pipe, but rather a conceptual analogy. In a typical Bernoulli pipe, a fluid speeds up in a narrower section, causing a pressure drop. In this conceptualization, a sphere is used to create a local constriction in a fluid flow, similar to how a narrower pipe section would. This constriction, according to Bernoulli's principle, would cause a localized increase in fluid velocity and a corresponding decrease in pressure. The "reversal" refers to the fact that the sphere's presence is causing the pressure drop, not the pipe's geometry itself. In a fluid system, the fluid's speed is fastest when flowing through the smallest diameter section. This is due to the principle of continuity, which states that the volumetric flow rate (volume of fluid passing a point per unit time) must remain constant in a closed system if the fluid is incompressible. Two spheres (white circles) in the center in a picture above are positioned in wind tunnel The flow of wind(fluid ) is marked lines with arrows. The space in between spheres is acting like source and sink- and doublet flow is created - the wind travels in concentric circles in direction opposite of main flow. These concentric circles have different speed and consequently pressure is different. This can be called waves . The flow of waves can be described with wave function . The point where main flow “wraps” around waves(concentric circles) is called stagnation Point. The main flow traveling around stagnation point “circle “ is layered and has different speed (and pressure ) in each layer . This is perceived as distortion of fluid field . The attractive forces crated between two spheres are product of static and dynamic pressures of wind (potential and kinematic energy of moving fluid (wind). Opinions ?
-
Deuterium atom simulation
The Bernoulli formula: P1+1/2DV1^2=Pe +1-2Dve^2=Po Po-static pressure of fluid acting on electron cloud (pressure bubble of deuterium atom). P1=static pressure acting in the middle of deuterium atom Ve=0.088m/s(at average radius 5.4x10^-11) Pe=static pressure working on electron surface P1=F/A(strong force over area of proton/ neuron cross section- static pressure). P1=9x10^33Pa P1+ 1/2DV1^2-1/2DVe^2 The dynamic pressure from (which is equal to portion of fluid acting on the proton and electron ,respectively ) for proton neutron dynamic pressure is in 10^-9 and for electron 10^-27 magnitude . This is the dynamic energy of fluid acting on proton electron pair .It is negligible to energy of static pressure of fluid . From calculation from above - simulation confirmed that electrostatic force between proton and electron is equal to to force created by static pressure Pe acting on area of electron Electrostatic force (force produced by equilibrium of pressures Po and P1) Fe=8.25x10^-8N Ae=F/Po Ae=8.25x10^-8/9x10^33 Ae=9.1x10^-40m^2 Ae=2.44x10e-20m********* The volume of electron is V=6x 10^-59 me=VxD me=6x10^-59x 0.74x10^-27 me=4.44x10^-86kg******** The electron made of fluid (probably “vortex”the size re=2.44x10^-20) Is capable to produce force equal to electrostatic force. By the way what is the size of electron ? Mass is known - but size ? To answer your question where the fluid is coming from - i do not know . It has density very close to density of dark matter. It is theoretical term ,but it was calculated that dark mater interacts with gravity . 25% of universe is made of dark matter. From this simulation the dark matter interacts with strong force and electrostatic force . In this simulation fluid /dark alter Interacts with baryonic matter through Bernoulli principle. And we know that it interacts with gravity. So- in this simulation all 4 forces of nature have the same origin. Cheers
-
Deuterium atom simulation
Sorry I was interpreted The electrostatic force is equal to force created between electron and proton by moving fluid between them The gravitational force - 10^58 pressure bubles of atoms will create pretty big pressure buble . Inside smaller bubles are creating atractive and repulsive forces - depending on relative position to each other) the big outside bubble will interact with other (plante) the same way proton and neutron interct - fractal nature of universe Al forces have the same origin - fluid movement between baryionic matter r
-
Deuterium atom simulation
Omg I apologize Swansont. The ruler is traveling at the same speed - the atoms inside the ruler are contracted ,too? This simulation is using data from calculations done by quantum mechanics . That is simplicity of this simulation . I use formula from Newtonian physics. Two of them. And the results work. The super fluid which baryonic matter is moving throughput ,has density of dark mater . The matter which is 25 %of universe The speed of gluon of C is confirmed to be true The distance between center of atom and electron in any position inside the cloud can be calculated. The length contraction high speed explained without Einstein- like Lorentz predicted it ?
-
Deuterium atom simulation
Swansnot Centripetal force is governed by Newton's Second Law (F=ma), specifically, it's the force that causes an object to move in a circular path, and its direction is always towards the center of that circle. Centrifugal force, on the other hand, is an apparent force experienced in a rotating frame of reference, and it's an equal and opposite reaction to the centripetal force, according to Newton's Third Law. On the other hand Newton's laws of motion, including his first, second, and third laws, are applicable to objects within moving fluids, but with some considerations. The first law, the law of inertia, applies, meaning a fluid element will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. However, in fluids, this can be influenced by pressure gradients, viscous forces, and drag from the surrounding environment. Newton's second law, which relates force to acceleration (F=ma), still holds, but the forces acting on a fluid element can be complex and include pressure, viscous forces, and buoyancy. Newton's third law, the law of action and reaction, also applies, meaning a fluid particle exerts a force on a body moving within it, and the body exerts an equal and opposite force back on the fluid. Swansnot You are very knowledgeable in many aspects and I respect annd listen to every question and suggestion you have made ,not only in this thread ,but in all of them. Luckily in space there is no friction to worry about. So every formula and every value in this simulation is used form real world,both Newtonian and quantum physics . Without strong force graph,fine structure of deuterium page ,the probability of electron position I would not be able to do anything in this simulation . The key value and fact in all of this is gluon ,carrier of strong force , traveling at speed of light. Any similarity between results of simulation and the real world is coincidental (I joke - it is more than welcome ). Have you had time to have a closer look at calculations ? They are so simple but effective . Especially the length contraction - this was predicted by Lorentz long time before Einstein.
-
Deuterium atom simulation
I wanted to tell swamsnot that classical centrifugal and centripetal forces created by mass and gravity for example are not the way to think about the same forces inside moving fluid . One more thing The contraction of length at speed close to speed of light can be explained using This simulation : From formula r1^2 v1=r2^2xv2 if deuterium atom is moving close to C The flow in between proton and neutron will be C - not cahnged. The speed on the other sides will increase to C From formula above the distance between and outside of proton and neutron will be the same . So bubble “height “ will be 4x10e-15m Instead of height of 4.5 x10e-15 m This is in the direction of flight . The bubble width will stay the same in both case 6.5 x10e-15.
-
Deuterium atom simulation
In fluid mechanics, centripetal force refers to the force required to keep a fluid particle moving in a circular path, and it is always directed towards the center of the circular motion. This force is often associated with rotational motion, like in a vortex or when a fluid is forced into a curve. In a rotating fluid, the pressure on the inside of the curve is lower than on the outside. This pressure difference creates an inward force (centripetal force) that keeps the fluid moving along the curve. Just from the definition of centrifugal force - one can assume that centripetal force is the opposite phenomena . The “common “ Clasic Newtonian physics is not the way to go with fluid mechanics .

jv1
Senior Members
-
Joined
-
Last visited