-
Posts
276 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Posts posted by Edgard Neuman
-
-
hi,
- What is curvature of space time ? it's a variation of relative lengths (metrics)..
- Would a physical system be invariant if we scale it up or down ? (and why?)
- what if we consider general relativity as a field in space that define the scale of matter... the "graviton" would transmit scale variation between two spaces
- matter would always tend to accelerate where scale is smaller (picture a circle around which scale varies, just as with curvature, some part of the circle would contains "more" space is the scale is smaller). So a particle at the center of the circle would have more chance to change state in that direction (that would be the gravitational force)
- energy/mass would define the scale around it.. at large scale it would be the gravitational field, at microscopic scale it would define particles as topological singularities (knots of spacetime, where dimension is higher than the surrounding space.. somehow like chord theory, only the space would be of higher dimension only locally as the effect of local extreme scale variation)
- if the scale is relative, that would allow laws of physics to be invariant by homothetic transformation
- the would allow the whole universe to be fully invariant by homothetic transformation (which is required for us to not have any information about what's outside of it)0 -
17 minutes ago, Strange said:!
Moderator Note
Do not hijack other people's Speculation threads with with your won Speculation
hi,
right !
sorry0 -
I think it's simpler than that.. my theory is that we share with mammals a language based on frequencies... frequencies going up imply a positive message or a danger, action to do.. frequencies going down imply end of danger, sadness/negative message..
we find this in two things in human :
- the tones (interrogative / assertive etc) of phrases
You can hear it in dog and cats, in babbling toddlers mimicking a dialogue etc... Just take a dialogue and remove the meaningful sounds to keep only base tone and rythm and you get the music of it, expressing emotions
- and in music..
music allow to express stories using notes :- going up or going down note express sentimentals values of events (positive negatives etc)
- repetition and rhythm to express strength and resolution of events, contextualization and relations between the forces in place (little events or big events etc.. a lasting note imply a lasting effect, repeating a note imply hammering effort)
- most stories goes from a situation of stability to an other situation of stability, that's why most melodies start and end with the same note..
- a succession of note going up meaning a positive event, and note going down or under the mean note imply set backs and adversities..
- a repetitive background melody imply the setting of the story, while rhythm breaks imply unexpected events
- instruments can than be use to impersonate different characters or forces etc (mostly in orchestral music)
- all of the above can be done at different time scale (for instance a music can repeat a whole section with a note up or down) and the story can have different parts with variable notes and various rythmes
-
chords (notes with resonating harmonics) make all of it much more subtle
I can analyse most melodies this way and I often find a relationship with the lyrics associated
0 -
Hi,
This post is about suggesting a (maybe new ?) kind of maths with a different start for integers to your appreciation (that's why I put it speculations)
The idea is to modify Peano, to create a set, with a start and a end, (no, it's not really modular arithmetic with unknown modulus)
So we create two extremum :- 0 at left, inf at right
-
the function succ(x)
- exist y=succ(x) for x != inf
-
the function prec(x)
- exist y=prec(x) for x != 0
We have addition etc, subtraction multiplication etc. all within the limit for "succ" that imply that operations are have no solutions close to inf
every relation between elements have a "anti" counterpart, using the function y= inf -x
so we have anti multiplication, anti addition etc:- x '* y = inf - ((inf-x) * (inf - y))
- x '+ y = inf - ((inf-x) + (inf - y)) = x+ y - inf
- 0 is a multiple of any x (and anti-multiple)
- inf is a multiple of any x (and anti-multiple)
etc etc
And then we can extend numbers on both side :
-
negative numbers as solutions for
0 - x
on the left -
some other numbers as solutions for
inf + x
on the right
we have "antiprimes" ( { inf - primes } ) ... antifractions etc
such a symmetrical axiomatic has to be useful in some ways.. ?
0 -
17 minutes ago, taeto said:
Okay then, I will attempt to give the standard answer. I assume x(0)≠0 and x(0)≠1 as otherwise the answer is trivial, say with taking y=1/2.
The key is to realize that every real number in [0;1] has a representation, a "name" if you will, as a binary string preceded by a zero and a "decimal" point, such as the representation of the fraction 3/4 as the string 0.11, meaning 1/2 for the first digit after the decimal point added to 1/4 for the second digit. The fraction 1/3 has a representation which looks like 0.10101010… etc., hence the representation is not of finite length for every number.
You say that your x(n) is always in [0,1], for every n. In which case it has a representation as described.
Now we construct a number y in [0,1] that has a representation which is different from the representation of any one of the numbers x(n).
For each n=1,2,3,… let the n 'th binary digit of y be the one that is different from the n 'th binary digit of your x(n).
Then the y just constructed cannot be equal to any one of the numbers x(n), since in the n 'th digit it is different.
thanks a lot !
0 -
58 minutes ago, studiot said:
Why would you expect the sequence function to converge to other irrational numbers than your parameter?
Irrational numbers are not, in general algebraic expressions of other irrational numbers.
in that case you have products of x * (1 - x) that are all irrational
but I understand that you don't reach the sequence starting from another irrational (unless the expression if infinite)Ok so no bijection !
So you have a family of number (that are irrational) for each irrational and the expressions using them (like sqrt(2)* p /q for instance are all irrational of the family of sqrt(2)).
That's the object my other question :Thanks a lot.
0 -
4 hours ago, taeto said:
What do you mean by "build these numbers"?
For any sequence we can easily construct an element of the interval [0,1] that is not in the given sequence. This is standard, and I can guess that you most likely know the answer already.
I don't 😩
For instance, with :
x[n+1]=r * x[n] * (1-x[n])
With r = sqrt(2)*2.6 for instance
X[n] is always in [0 ; 1]
How do you find y in [0 ; 1 ] that is not in { x[n] } ?
Thanks for your help
0 -
nobody answered that question, but I think it's important.. if logistic map sequence never repeat and still stay in the interval [0 ; 1], and if we can prove than any x in [0;1] eventually is in it, then it's a way to build a bijection between N and [0;1]..(that wouldn't surprise me, but you probably)
I suppose some real in [0:1] are not in the sequence, but how can we build these numbers ?0 -
On 12/19/2019 at 11:20 PM, Enthalpy said:
I haven't grasped from you text where past/present/future makes a difference.
Picture the family tree of a specie (that's an analogy)... at any point in time you have several versions of the prototypical individual (each version of the DNA of the specie) living concurrently.. but as time pass, every branches eventually die off. Until you get to a point where only one ancestor is still represented by its descendant.. (the last common ancestor). At each point in time there are several individuals simultaneously, but far enough in the past, only one of them is needed to explain the present.
Now replace "individuals", by "alternate universes" (concurrent versions of the Feynman diagram).
I love this analogy, because it also understand how branches that died off are still necessary to explain what happened in the past, just as you need all the concurrent Feynman scenari to compute the probability of the final state..0 -
On 11/27/2019 at 12:51 PM, swansont said:
They always have a wave function. The collapse is a loss of superposition of states, not the loss of having a wave function.
You can send particles through multiple sets of slits and you will have interference, as long as you create a new superposition.
Hi,
I'm going to loose some other reputation points.... (I invoke the 1st amendment)
Everything is made of particles, the human, the brain, the air, the photomultiplier..
So maybe the only way of seeing the difference between multiple states and single states is relative to the present.. all states of photon hits the screen, maybe its only when it is multiplied into macroscopic world than states are selected...
Imagining that reality as a big tree of consequences made of various states branching into multiple new states at each moment.
- suppose simultaneous realities can always only differ to a certain extant (so the universe doesn't split into parallele stories).. (that is not limited by distance, allowing all the entangled things)
- but still at each point in time, there's always multiple state for each particles..
- stories always divides into several branches, but some branches constantly dies... (That's really what need to be solved in my opinion)
- so from the present, when we look far enough in the past (relatively to the scale of what we are looking at), what remains is only the common ancestors of all current states.. the states who branched into the reality that remains when all the others died.
In that views, (which I suppose is what the "quantum darwinism" is about), there's no need for "decoherence"0 -
As always, you seem to not understand my very complicated question, and give me very basic answers, that I understood a thousand times.
I'm challenging the theory. I try to understand it fully, and I thought of a specific case that seems (at least to me) to contradict it. I may be wrong, but I want to understand HOW.
Imagine a gas. In a perfect closed (or opened ?) chamber. All molecules of the gas are bouncing on the walls of the perfect chamber according to its shape. I'm a well aware of the laws of thermodynamics. That's not what I'm asking. My "vivid visual imagination" tells me (and some article I read about specific shapes that modify the density of things when they bounce in it), that, maybe for some specific shapes of the chamber, ordinary bouncing of particles could be altered in a certain way so that, from a state where all molecule are going in a random directions, they end up all going in the same direction and at the same speed. It's a box that SORT molecule and ORGANIZE them because of it's specific shape. It's a kind of maxwell's demon, doing so only with its shape. Because of the shape and the bounces.
You know that parabolas for instance, have specific properties.. I know you can create some chamber with very specific shapes where some place are only accessible after a certain serie of specific bounces (at least in 2D), or with forbidden area where a bouncing never goes. I'm thinking of very specific asymmetric shaped billiard that affect trajectories is a particular way.
Are you aware of that ? (the problem is I read a lot of articles and it's very hard to find this one back)
I understand, that in that very particular case, if in the end, (after the bounces in the very specific shapes) molecules effectively all go in the same direction, at the same speed, one could then argue that the entropy of the gas diminished. (because in their own shared frame of movement, they are not moving relative to each others, therefore their temperature is zero (may I remind you that "temperature" is not a mathematical object that exists by its own or is carried by space, but a statistical property of the molecules of a gas) ).
There's two possibility :
- such a shape does not exist (I don't see why but maybe for mathematical reasons). That would solve the paradox. In that case WHY NOT ?
- in that thought experiment, if the shape exist, did something gained entropy that I missed ? (we have to suppose the walls are perfect)..So in that case WHAT DID ?
I think I have the answer : the box necessarily gained some momentum in the opposite direction (the momentum of molecule that were redirected by the box), so for the law of thermodynamic to work, and the whole thing should have globally the same entropy : the box and the gas moving in opposite directions have globally the same entropy, because of their relative movement. That give me some insight (believe it or not )... so the entropy of a system of objects is proportional to the mass of the component of the system and to the disparity of speed around the barycenter.. (because speed is relative to the frame, but the disparity of speed is the invariant)... it's like the "n object gas" and a zero entropy box turned into "2 object" gas with high entropy (because the high mass)..
)... so the entropy of a system of objects is proportional to the mass of the component of the system and to the disparity of speed around the barycenter.. (because speed is relative to the frame, but the disparity of speed is the invariant)... it's like the "n object gas" and a zero entropy box turned into "2 object" gas with high entropy (because the high mass)..
Don't bother answering, I have my answer.. -3
-3 -
hi,
that may be a stupid question, but I'm not sure about the answer.. is it really impossible to reduce the entropy of a gas ?
Picture a cavity with a special shape (probably parabolas) where molecule would preferentially bounce in carefully selected directions.. it could also be some sort of tube, where when you put some gas at one end, molecules end up going all parallel at the other end.. I suppose what would be difficult is to make the speed of the particles uniform, but maybe if you use some material with a specific bouncing properties (i mean that molecules would bounce to different direction varying with their speed, and so you can filter them using only geometry)
is it really impossible ?0 -
Hi,
I have a lot of experience in coding, and this is a common problem, ranking objects (usually you need ranking to store them in a tree that you can request fast, using a "index", the index need ranking).. if what you need is just a way to rank objects.
A usual way is simply to sort them using each of their properties sequentially : compare them using the first method, and if they are equal, then use the second method.. it's what we all do with word with more than 1 letters (we compare the first letter, then if it fails, we compare the second letter etc..)
but if the methods must have the same importance, there is no method that wouldn't give equality, because your values are symmetrical.
0 -
-
I realize maybe we would have to define them each as a unique "set" of integer powers of a specific irrational number between ]0;1[ but the idea remains the same
0 -
Hi,
Here is a math question :
First I'm going to define some things (some names may already exists that I don't know of, so please take my definition into consideration)
- let's call p[n] the nth-rank prime number p[0]=1, p[1]=2, p[2]=3, p[3]=5 etc
- as you know, each integer >0 can be written as a product of integer powers of prime numbers.. let's call it the "prime writing" of a number... i'll write u[n]
so for any integer X we have
X = product( p[n] ^ u[n] )
- we can extend this to rational numbers, simply by allowing u[n] <0
My question is : can we define a set of irrational numbers in ]0 ; 1[ that extends p[n] when n<0 and are the building blocks for irrational numbers ? Let's call them subprimes..
Those numbers would have the properties following :
- they are not power/products of primes and other sub-primes and of course integer powers of some other real number (other than themselves)
Are they already known ? Do they exist ? How to construct them ?
I have some (very faint) clue :
When you elevate these numbers to positive powers , you get closer and closer to 0.. so the more you go close to 0, the more likely to find a power of a bigger subprime.. so the density must decrease closer to 0.. you get some sort of sieve, but closer and closer to 0.0 -
36 minutes ago, dimreepr said:
My maths is equivolent to yours, but it won't work because "so in our universe, we would have only one half of the loop.." that's like trying to dig half a hole or trying to make half a sandwhich.
First : thanks for taking the time to actually think.
Allow me to answer and disagree (because I can) :
No but, when I wrote this, I supposed the bridge had some internal length.. (and half of the loop would be in it). I admit I don't exactly know the topology of a einstein rosen bridge.
But it's not necessary. The rope (or the particle loop) can just be straight, go from left to right.. (it would be a loop but straight)..
I don't know either if you can make some ER Brigde with entries face to face.. (if you can't that would ruin everything.. that why I supposed you would have to make a topological inversion of one end)..
It's a very simple and stupid idea really.. If you played portal , you'll understand instantly the topology of the room. (Somebody probably had it before, but i've never heard of it)
(sorry for the poor quality of the schematic, i don't have photoshop)0 -
19 minutes ago, Bufofrog said:
You can submit what you call an idea but it ain't science, it is uniformed idle speculation.
I'm sick and tired of all your peremptive general answers :
- "math or it's nothing"
- "you're not a genius"
- "it's not math."
- "you know nothing"
bla bla
I've heard it all. I won't waste another full day talking about "my/your legitimity" "the importance of math", "the rules of the forum". I have a life. I'll make a list of people who are not objective, try to waste my time and discourage me of having ideas (what a absurd thing to do really) and who I will answer only once.
Who care "who I am" ? You do, because you don't know what "science" is about (obviously)
This idea is very simple. So spare me the b*llshit, and criticize the idea or leave me alone.
Your next answer can only be one of those :
a) "It wouldn't work because .... XXX (math if you want)"
b) "that's a good idea, I don't see why it won't work"
c) "I don't know, but it's worth thinking about it"
The rest is absurdity, misplaced ego and noise.
-1 -
38 minutes ago, Strange said:
If you are going to invoke science-fiction then you can do anything. Perhaps best to stick to science. (And if you are going to say "but an Einstein-Rosen bridge is science", then I require you to show the full mathematical analysis that your idea works.)
... now that's just absurd sadism.
(of course I know we can't make a einstein rosen bridge)..
From now on, I won't even answer to you, and only to people who have a brain. I wonder how many good ideas you throw to the bin because of your abusive self-importance. Learn about objectivity, it will do good to you.And the idea that i can't submit some idea without doing the math. That's absurd. A idea is a idea. Math is math. I'm not here for a medal in math. I don't do math, I hate math. I submit a idea. You need the math ? YOU DO the math, you seem to like it. I just submit the idea. The idea isn't wrong because I didn't do the math. You need math, I don't. It's just a very simple idea rightfully written in the "speculation part" of the forum. Contrary to you, I'm here to "share", not to make myself believe i'm important.
The math here is as simple as the idea ER-brigde math + linear particle accelerator math, so you can figure it out.-4 -
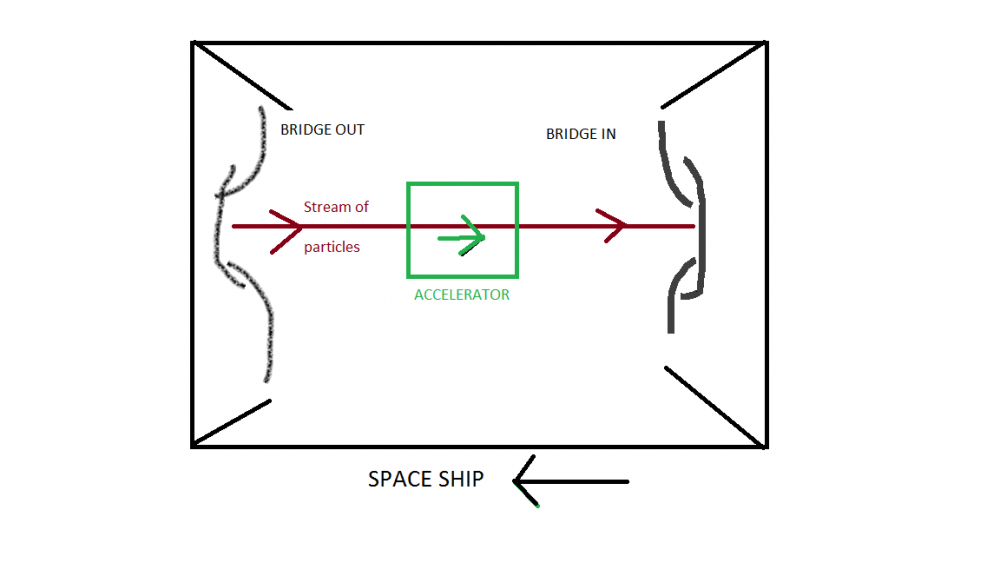
and what about the idea it inspired me ? somebody please tell me it's a good idea ! ?

You put two ends of a einstein-rosen-bridge face to face in a ship (Portal style), and you put a very simple (linear) particle accelerator between the two.. (you could also just put a rope, and pull it, but I figured a particle sized ER bridge would be easier).. I don't see any flaw in this idea..
Relative to space the mass going flowing the bridge would have some momentum/kinetic energy in a direction and the ship would have the opposite (so the laws won't be broken).. it's really a linear inertia wheel (a straight wheel)..
0 -
2 hours ago, SergUpstart said:
This system of equations is written on the hypothesis of Jamie Farnes, according to which the space of the universe is filled with electric dipoles with negative mass. Gravity from positively charged matter attracts negative mass, so in areas of space where gravity is stronger, the permittivity will be higher. Based on this, the curvature of space by gravity can be replaced by a change in the dielectric constant of the vacuum, and electromagnetic waves will move in this space along curved trajectories in accordance with the law of refraction of light.
It also tackles the question of whether gravity has mass. On the one hand, the gravitational field has energy, so it must have mass, but if you give it a positive mass, it will inevitably pull itself to a point. But if we remember that in physics textbooks gravitational energy is written with a minus sign, it is logical to recognize the mass of the gravitational field as negative. This also solves the issue with the balance of divergences in the dif.the equation for the gravitational field.
More detailed
https://www.yuniverse.org/eng/negativemass.aspx
http://www.yuniverse.org/eng/curvespase.aspx
https://www.yuniverse.org/eng/unifield.aspx
the system of equations is as followsbut how to explain curvated trajectory of particles that are not charged and not photons like the Z boson..
0 -
19 hours ago, Robert Wilson said:
Of course that this object is being tracked, how exactly does it contradict the Insect theory?
The system see an object on the screen and it's tracking it, it doesn't know if it's a flying airplane or if it's a bug on the lens that looks "flying" when it Integrates with the view behind it. It's sees a spot in the frame and it's following it.
Please explain why doesn't it move when the airplane rotate? Why the horizon line (that you can see behind the clouds) move perfectly in correlation with the artificial horizon of the aircraft, but the object stays Exactly in the same possition?
https://i.ibb.co/zx2WhbP/Toggle-3-4.gif
Only object that is attached to the airplane can explain that.
In your gif, it kind of moves a little... if the thing was a distant disk, it seems still plausible
But, in the case of a insect what we need to know is the orientation of the camera relative to the plane.. if the insect is inside the glass thing, the camera wouldn't have to move at all.
Maybe some of the numbers on the screen are the angles of the camera.0 -
I've a better idea about it : if you played the game "portal".. (it all depends of the laws of bridge orientation if they exist, you would probably have to flip one entry of the bridge to make it face the other one).. you can imagine a ship having two ends of the bridge, facing each other (like in the game). In the middle, you put a particle accelerator.
When you accelerate the particle in one direction, the local reaction push the accelerator and the ship in the other direction, and when you decelerate the particles, the opposite happens. You would have some sort of inertia wheel, but linear thanks the topological inversion of the bridge. (I even suppose the parity of the particle would alternate each time they pass the bridge, the whole being the equivalent of a mobius strip)0 -
On 10/9/2019 at 12:10 AM, Robert Wilson said:
Hi all,I would like to refer to the following video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1THwiaXZfzA
which implies that what we see here is some kind of an "aliens spaceship" from out of space.
I think that this is Ridiculous.
Check minute 0:50 and minute 1:15 in the video - that is the so called "UFO" that they saw.
I claim that this is just a small insect on the camera lens, and I don't understand how people can be so blind and not see it.
The aircraft's infrared camera sits inside a pod as you can see here:
https://www.raytheon.com/sites/default/files/inline-images/rtn_475606.jpg
The insect probably got inside when maintenance was done on the aircraft , and it sits either on the camera lens, or on the inside window of the pod through which the camera looks out (and obviously, the insect is not exposed to the outside wind).
That explains why it is SO STABLE in relation to aircraft sight (an external object like another airplane will NEVER be that stable) and it also explains why it is So Blurry... that is because it is adjacent to the camera lens so it is out of focus... Also, take again a good look at the video, you can see pretty clearly the Legs of that insect! can't you see it?
It looks like an insect, it moves like an insect, and that's exactly what it is! just an insect!
Also, why do they shows us the same video from the same aircraft all the time? Where is the video from the same event taken from the OTHER aircraft? let's see it and compare between the two videos. If it's really an external object to the airplanes, then we should see it moving EXACTLY the same way second by second in both videos! So where is the video from the second plane? Or maybe the camera of the other aircraft just didn't see the object? As expected if I'm right.
Also, I don't know what they saw on the radar, but from my experience, especially in a sea environment, radars have LOT of false alerts for many things - Bird bands, fish bands jumping out of the water, sea turtles and even just sea waves. I think that what you see in the infrared's camera screen is NOT what they saw on the radar.
I have no doubt a that what you see in this video is just a small insect walking on the camera's lens.
Your opinion please.
I don't think the insect theory works... the object is in the center of the view because the camera has a pursuit system that detects objects and centers it.. (the two lines right next to the object are indicator of that system state) .. At the beginning the lines are bigger because the object is not in it, so the detection area is big. Once the system catch the object, it puts it in the center. In other videos you see the pilots trying to "catch" the object, meaning they orient the camera to it until the pursuit system takes control and start to automatically orient the view to maintain the object right in the center of the image.
Personally, I thought these object could simply be light plastic objects carried by the wind.. a simple plastic bag could fly as fast as the wind.. and we don't know the distance and the scale of the objects. I also suppose in some specific conditions a very steady wind could carry and sustain a light object flying straight near the surface for a relatively long period.1


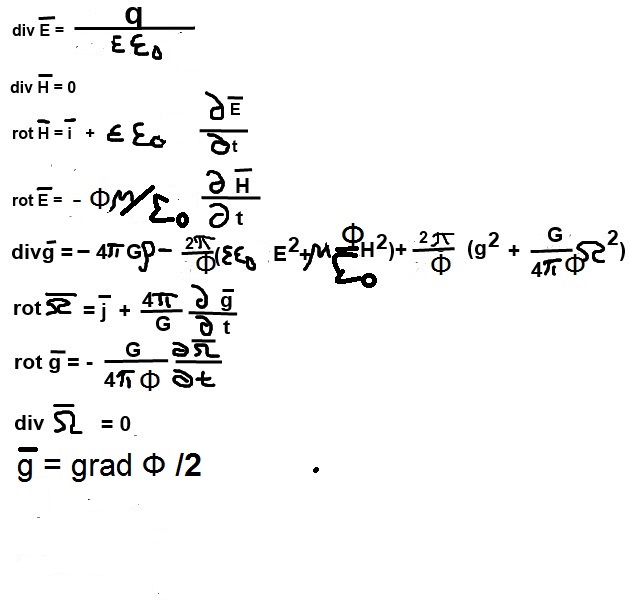
Could General Relativity simply be the "scale" field
in Speculations
Posted · Edited by Edgard Neuman
hi,
of course, GR is a succesfull theory, I certainly won't try to contradict its countless predictions.. and yes it would be the variation of the metrics as defined by general relativity (so space/time).. but my idea was just that it was in fact the measurement of "scale" of physics.. it would just be a more profound way of understanding general relativity.. It has to be equivalent or my idea wouldn't fit experiment results..
I understand why you don't understand. Things like "distance / time" etc.. are really defined relative to one an other, in my model..
I suppose here that relationship between length time are entirely defined by relativity. (the maximum speed of information across space, relative to the scale of structures in it, and the rate of events in structures)
The speed of light is defined in « m / s ».. a second is a measure of the rate of events in a structure (that is necessarily relative.. ), and a meter is defined by the scale that a certain quantity of energy in a certain state « choose » to occupy.. (for instance : the size of a given atom at rest is a constant)..
What I mean by scale, is ultimately the variation of size the same atom would have in two part of space (but it's the equivalent of speed of time variation).
That means : if everything if defined by the speed of light (length and time relative to structures), that mean that you scale up the universe by 2, it's distinguishable with the universe you get if you slow time by 2, or if you divide the speed of light by 2.. you have to see those measurement as relative to each other to understand what I'm talking about..
Speed of light is only measured relative to structures (like a atom.. it defines the length (the size of it), and the speed of time (the speed of electrons for instance) )
The main reason for me to have this idea is from a metaphysical consideration : if the visible universe is really "all the information we can get"... if it's "closed" .. meaning if trully no information can be known from outside of it, it means that there must be some "equivalence principle" for each and every measurement..
We know that physics is
- invariant by translation, (we can't measure "where" the universe is)
- by variation of speed (we can't measure the speed of the universe)
- but also by variation of the speed of information (that's not obvious, but that's what i'm talking about : the speed of information ultimately defines the scale of structures) that would be special relativity.... information (and light) would always travel at the same speed in a given isolated structure (we can't measure how fast the universe is evolving)
- invariant by changing the orientation of the universe, (we can't measure the specific orientation of the universe)
- invariant by changing all the electric charges of the universe (we can't measure how charged is the universe)
- invariant by changing the angular momentum of the universe (that would imply some sort of inertia attenuation at higher scales...some sort of "MOND" theory would do the trick) ...the inertia attenuation would prevent the rotating universe from experiencing centrifugal forces (we can't measure if the universe is rotating)
- and also the "scale" of the universe (that works if the scale if defined by matter itself, and it's relative, meaning there is a field, and gravitation would be the gauge particle of the field) (we ultimatly can't measure "how big is the universe", but only relative to structures inside of it)