

Ken Fabian
-
Posts
1035 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
7
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Posts posted by Ken Fabian
-
-
20 hours ago, Sensei said:
Of course it is feasible
I don't see any of course about it given the extreme distance, extreme costs of transport and the extreme conditions. We don't even have an inventory of what minerals are essential vs which are available there let alone what it would take to exploit them cost effectively - cost being about how much time and work people there must do to produce what is needed, which inconveniently includes what colonists can exchange for what they import.
It is possible that nations would make a space colony and commit to supporting it in perpetuity in the hope it can become a self reliant Planet B in order to preserve an independent remnant of the human race from distant global catastrophe but that is not currently the case and I am not convinced it would have widespread support - although I expect there are some with bunkers intended for preserving a remnant from much nearer term catastrophes.
Having to rely for day to day survival on large scale taxpayer support from very far away, that must persist unbroken for unforeseeable lengths of time doesn't sound like a sound plan.
0 -
I think that for wealthy and powerful - industrialists etc - the nation's good usually pares down to what is good for the near term profitability of their businesses and their interactions with politicians are largely transactional, making deals towards that end. Not surprising, they tend to oppose regulation or taxation and anything that they perceive as negatively affecting them (but they aren't necessarily good at the bigger picture and longer term; giving them what they think they want can end up worse, even for them, than not giving them what they want). Which makes politicians and parties that espouse such things - Right leaning - usually more to their liking, but not always if the deals others offer are good enough.
The transactional nature of mixing politics and business has a "soft" corruption element (legal means of influence - advertising, PR, tankthink, lobbying, strategic donating, tactical lawfare, post politics payoffs) ultimately means influencing the making of the rules including ensuring the nature of legislation intended to limit corrupt influence doesn't limit their influence. I think corrupt influence and the inability or unwillingness within political parties to address it is one of the greatest impediments to improved governance - and we need governance that is capable of dealing with the profoundly serious challenges we collectively face.
1 -
It got noticed and exposed. In a roundabout way that has to be good news.
Science is built around documentation and making it widely available for evaluation and critique by their peers. In fields with few participants and little outside interest I suppose data tampering can go unnoticed for longer but cheaters who have to document their lies will always be at risk of exposure.
1 -
We are adding CO2 at higher rates than ever - and would probably be even higher without growth of renewable energy - so I am not surprised that we see the scale of real world impacts growing. Whether this el Nino brings record global temperatures with it isn't certain but if not this one, the next one probably will.
I do think we are on the cusp of achieving zero growth of fossil fuel use but a lot of economic dependence on it is built on so reducing it's use is still dependent on a lot of still relatively new power stations aging before reaching retirement. But whilst renewables are cheaper to build for electricity generation - I think most of the growth is because they are cheaper, not for emissions reductions - that circumstance may not persist; we still need the kinds of commitments to actions that may make things more expensive in the near term in order to avoid the costs of climate impacts in the medium to longer term (not just longer term anymore).
0 -
10 hours ago, Bob Cross said:
Compare 2023 vs. 1923. Compare that to 1923 vs. 1823, etc. It’s advancing exponentially
Much like how I don't believe in gods, I don't believe in exponential progress either. I expect the progression is more like an S-curve. They can look very similar... for a while. Let us hope it is not a U-curve.
I don't want to die - although that may change as my body and mind deteriorates from age - but not enough to set aside experience and reason in favor of religious faith in an afterlife. I doubt a technological version is possible but I'm not much attracted by it; seems that whoever it is achieves consciousness in that body won't be me, even if he thinks otherwise. So I struggle to feel any attachment to his fate, apart from a vague "good luck".
Better medical care for the life I have - with or without a capability to extend it - will remain a better goal in my view
0 -
With a Mistermackian classification scheme there is just one species - everything living is descended from it and by that definition is all the same species and it takes abiogenesis to have a different species. But I think it is arguing etymology - what the word species means - rather than biology. For convenience we go with the usual definition - which isn't as clear cut as "can interbreed".
We have a lot of (unfortunately named) homo erectus DNA, that lives on in homo sapiens - we are indeed descendants - but sapiens has significant differences too, more than enough to rate being a separate species, the naming of which is to some extent a judgement call.
Actually would not surprise me if sapiens and erectus could interbreed - no living apes are nearly so closely related - and the successful variants on the road to a different species would have done so with gene flow as an evolutionary mechanism. Like wolves being able to breed with dogs it doesn't make them the same species.
Erectus had descendants that had significant differences and ultimately those survived whilst the descendants that stayed much the same did not. We are descendants but we are not homo erectus.
0 -
For technological progress I expect S-curves, not exponential ones - they just look similar... for a while.
Even aside from the physical impossibility of endless exponential growth there are limits - like limits of physical properties of materials, like limits to return on investment.
Aircraft can exceed the sound barrier - it is not an absolute limit - but it costs too much to become widely used. We may get working fusion power plants but if the engineering requirements are too exacting they may be too costly. We can launch people and materiel into space but as long as it costs too much and delivers too little there won't be space colonies.
I suspect we are already overshooting the environmental limits of our world and unless clean energy tech advances a lot more (and quickly) the economic impacts of climate change will impose limits on how much nations can afford for far reaching R&D. Those impacts are going to get a lot more serious over the next few decades given total emissions are still rising and opposition (out of ignorance and apathy and out of being misinformed) to taking sufficient aggressive action remains strong.
Living within our means means setting aside some aspirations whilst some are just made a lot harder.
2 -
12 hours ago, Genady said:
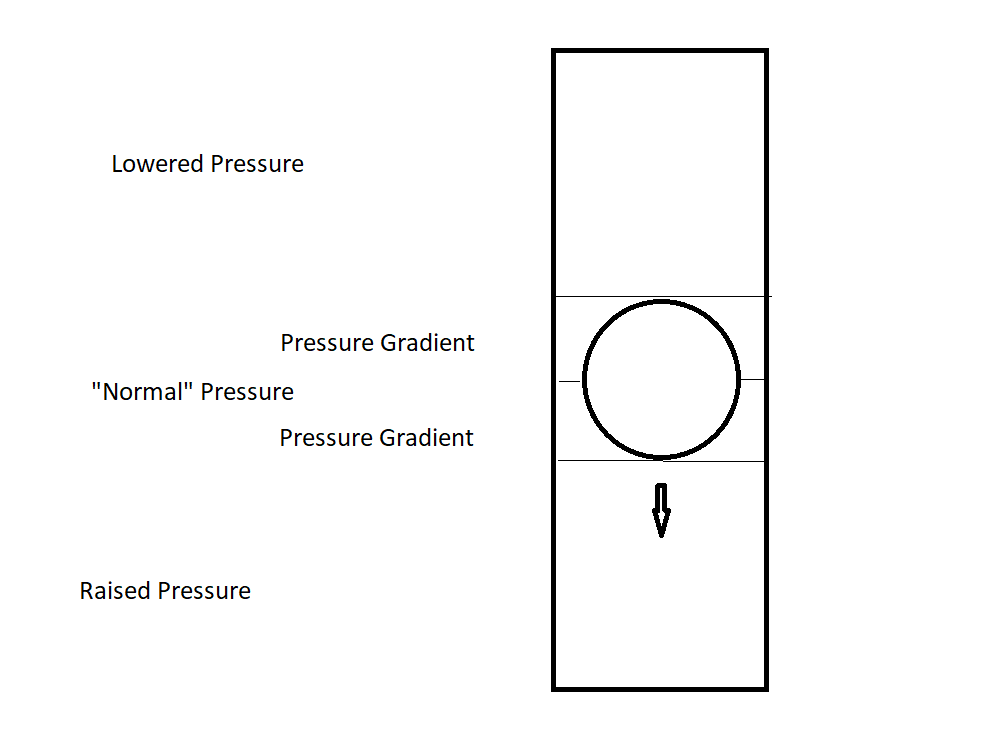
I think you're right and I see where some decrease in pressure above the sinking piston might come from.
Funny, I was thinking maybe you are right and I have been wrong!
At this point I think there is a negative pressure effect above - a negative pressure/suction - but it isn't equal to the pressure increase below. Take a falling weighted piston (thanks) with a tight fit and slow liquid flow past it and that effect will be very small; the growing weight of water above would act more like you said, being (I think) very close to the "normal" static state pressure. Close because I think there is a suction effect, but it is not going to be equal to the positive pressure in a vessel open to air, not without making it a closed vessel. Depth dependent? But I need to think about that some more.
Huh, @zetetic56 's topic has engaged my brain (even though I'm still stuck on the initial scenario) and I am not there yet but I think I will get to some better comprehension in the end.
0 -
@Genady I need to think about it. I note there is pressure reduction behind an object moving through water, at the extreme you get cavitation, but I don't know, your reasoning seems sound too.
0 -
43 minutes ago, Genady said:
I'll think about the suction, but regarding this:
I suggest a mental experiment. What happens if there is vacuum above the piston? When it moves down, the pressure under it gets higher, but the pressure above remains zero. Thus, the overall pressure gets higher.
Interesting. Initially I thought that scenario was too different to be instructive. After thinking about it I decided it is too similar to be instructive. Posit a liquid filled open vessel in air or posit it in vacuum and they are much the same. A perfect piston would not sink but the point is it isn't perfect and it does sink; the liquid flows around it as it falls and there will be liquid above it, with pressure; it displaces vacuum (or air) above and it starts being liquid above as per the initial scenario - with the pressure within the water above the question. It may simplify things to have a flat top/bottom piston with vertical sides - there will be no pressure gradient zone; I think the pressure around it as it sinks will be "normal", ie what it would be in it's initial or steady state.
I still think what happens with an immersed piston in motion making positive pressure below is that the inverse happens above, like a piston working in reverse, lowering the pressure. Whilst the top of the vessel looks to be open the liquid is contained, by gravity and as long as the piston is moving/sinking the pressure above will be lowered and below will be raised.
0 -
5 minutes ago, Genady said:
I don't think it will happen. Certainly not the reduced gravitational pull - the latter requires an accelerated fall, but the ball/piston rather moves in the fluid with a constant speed except momentarily at the very beginning.
I think, there is a higher pressure under the piston, a normal pressure above it, and a pressure gradient in the gap where the fluid moves up.
I don't see how the overall pressure can be higher whilst the ball falls than when at rest. But I stand corrected; it is not like less weight in a falling lift - as you say that depends on accelerations ie occupants of a lift falling at a steady rate will experience normal gravity - but I do think it will create suction above as it falls.
0 -
@Genady Firstly I expect there is a kind of conservation of pressure applying - that the total pressure within the container whilst the ball (or piston) drops is equal to the total pressure at rest.
Above the ball appears to me to be a case of the falling ball sucks - or perhaps better described as a case of reduced gravitational pull on that part of the water column whilst the obstruction below it is falling, a bit like we experience less weight in a lift as it falls. I'm not getting this from an external reference (or I would link) - it just seems (given the very basic things I have learned about gravity and fluids and pressure) logical to me - if wrong I am willing to be corrected.
0 -
My take on the original question is - there won't be a pressure ring (?) around the most constricted zone that follows the sinking ball; the zone that experiences the greatest increase in pressure is below the bottom of the ball and it will experience it equally.
 0
0 -
I don't think this will offer anything of significance for fixing global warming.
Does it require CO2 to be at high concentrations and or purity to work, ie separated from air or exhaust gases first? Where would the carbon go after? I note that the quantities are extremely large - 1 ppm is about 7 billion metric tons of atmospheric CO2 or 2.1 billion tons of Carbon. Global CO2 emissions are around the 40 billion per year mark.
Significantly, would the (clean) energy required to run it give better climate outcomes by extracting carbon from air than replacing fossil fuel use directly?
I am not a fan of Carbon Capture and Storage in - it doesn't address the principle problem (emissions from fossil fuel burning) and looks to me to be mostly promoted in order to NOT fix the dirty energy problem, by interests that won't care if it doesn't work.
0 -
Collateral damage would be a serious problem even if it might hypothetically work - except it won't.
Nuking the atmosphere to reduce CO2 is a new one to me. I've encountered use nukes to make a nuclear winter ie set fire to the world and all the smoke and ash will cool things down - but of course a nuclear winter will do a lot more than cool the climate. To be fair the global destruction and year or two of crop failures and livestock deaths along with the reduced economic demand from all that mass murdering and famines will sustain longer term emissions reductions! After the CO2 spike and renewed warming from all the burning subsides of course. Perhaps people in well prepared deep bunkers will be okay - if incapable of recovering an advanced technological society after.
Like that, and with the assumption that nuking the atmosphere would actually reduce CO2 (except that it won't) the other impacts of nuking the atmosphere are just too horrendous.
Dunno why, but my response to most "just do X" easy fix shortcuts (that somehow avoid the inconvenience of dealing with the cause ie fossil fuel emissions) is head scratching - "seriously?". I keep coming back to building as much clean energy as our most effective - and cost effective - climate change response.
2 -
@Genady Ah, yes, thanks.
SpoilerFor some reason I got stuck on thinking multiples of 100km, not fractions.
0 -
-
Spoiler
I got the obvious one. Less obvious - took me a while - there is a line of latitude around the South Pole with a circumference of 100km. Starting point is any point 100km North of that line - a 100km leg South, then 100km West in a circle to return to the same place, then North.
0 -
1 hour ago, mistermack said:
Putting a man back on the Moon isn't going to tell us much new stuff, that automation wouldn't.
For survey and exploration I think machines do it much better. But I think there is not much we do in space that requires or especially benefits by having astronauts - and having astronauts in space to advance the capacity to support humans in space seems a bit circular to me. Of course my pessimism around most space ambitions ought to be well known here.
Not sure laying claim to the moon is a driving factor for crewed missions to the moon - there are no resources of any value to exploit, or to seek to deny to enemies - but rather that developing and demonstrating the capacity to do it at all demonstrates technological superiority in areas highly relevant to military defense capabilities. China doing it would probably be seen as threatening to the USA, not for moon missions being in any way threatening but as evidence of China closing the gap on US technological superiority, which threatens the US military's "all theater domination" position.
Water for rocket fuel? Besides the need to demonstrate benefits of more distant space missions that require it - and deal with the problems of Hydrogen/Oxygen as rocket fuel - I think establishing the infrastructure needed on the moon would eat into any potential benefits. And for providing water in space maybe mining a near Earth asteroid - there are some that should have much lower delta-v requirements, that ought to have carbonaceous materials that water can be extracted from - could be more cost effective. I think asteroid mining is one of the few activities beyond Earth orbit with actual commercial potential, from resources that are known to be abundant.
1 -
On 5/4/2023 at 12:01 PM, sethoflagos said:
One pumping method that may be worth considering is Gas Lift. By sparging compressed air perhaps 200 - 300 m below the top of the pipe via an array of nozzles, the density of the mixed fluid above is substantially reduced generating the pressure difference necessary for the desired flowrate.
That would create suction below that level, so either rigid walls or else pumping the air in at the base.
11 hours ago, sethoflagos said:PS: I was going to say something about whether polyethylene was up to handling the considerable tensile forces involved, but perhaps we can save that for later.
Yes, I'd had that thought - wind and wave pushing the surface installation, tides and currents at different depths pushing the pipe, would make a lot of tension. Interesting as a thought experiment - as a first look, to identify the issues.
@mistermack - good point about the density differences from compression being in balance with surrounds - the effective weight of the column would be less than my rough estimate. I've learned things in this discussion.
Data on how much nutrient and plankton and subsequent fish stocks from ocean overturning may exist (or be derivable) in journals about marine science and provide some idea of how much deep water overturning for how much benefit and avoid the need for expensive experiments. Someone more interested in it and more optimistic about it than me would have to do that. I expect - strongly suspect that is - the volumes will have to be extremely large - but am open to being shown incorrect.
Of course I still think it is a non-starter for marine fisheries enhancement as well as for carbon capture. It can still be worth putting some numbers to, if that can be done, to be sure.
.
0 -
The deep water nutrients this is intended to bring back to the surface are the ones that are potentially headed for sedimentation, if not the sediments themselves, something I missed before; ironic that doing it would reduce ocean carbon sedimentation.
As for pumping (and using that last graph of Mistemack's) - I make a rough estimate of 5 kg per cubic metre averaged over a 1,000m lift. A 10ft/3m diameter pipe, 7 cubic metres and 0.035 metric tons per metre, so 35 tons lifted 1,000m for 7,000 cubic metres delivered to the surface. That sounds like a lot of water but for this purpose, maybe not that much.
There will be pressure on the pipe walls, progressively more the deeper it goes - weight of water column plus additional pressure for making the flow. Can't use suction pumps without thicker walled pipes, it needs positive pressure (mentioned earlier in thread), either pump at base or possibly pumping water down a second pipe to provide positive pressure and flow - like some deep borehole pumps do?
As a thought experiment it was good of @mistermack to post the thread, but I think we can dismiss the potential for carbon capture adn there is a lot of preliminary research needed to establish benefits to fishery productivity - and what wider ecosystem impacts it may have.
I suspect it will need extremely large flow to be significant for fisheries but I don't know.
0 -
2 hours ago, mistermack said:
I have no reason to trust that estimate, or your interpretation of it, as it happens.
You put up the suggestion it would be a way to capture emissions - you need to show that it does. Throwing the burden of proof - that carbon sedimentation is too small, the amount it needs to expand too great and it won't work - onto me isn't helping your argument.
It is your claims about carbon sedimentation that are in question, not the validity of data from The Global Carbon Project in diagram form. It is clear to me what the numbers represent and the diagram provides it's own context - the Carbon Cycle and the values of sinks and fluxes.
If those numbers should not be trusted and are wrong, you are invited to show that.
1 -
21 hours ago, StringJunky said:
Even so, we are not suggesting it is the only solution. Even if it is the one under discussion, it is plainly obvious that a multi-pronged approach is required. You using numbers as if that is the only solution to be used.
No, I'm suggesting using the numbers to decide not to waste significant effort on something with so little potential and to move on to those other solutions.
I do think actual emissions reductions - changing to low emissions energy - is our most significant and effective action, deserving the most support and investment (which is the case), but I don't recall ever saying it should be our only action.
11 hours ago, mistermack said:It would help if you posted a link to verify your claim, rather than a diagram.
But would it help? Do you have any reason to think that estimate used by the Global Carbon Project for carbon sedimentation rate is wrong?
2 hours ago, mistermack said:4 hours ago, TheVat said:So how did that work out for the planet's biosphere?
Ok so far. 🙂
A novel use of "Ok", usually reserved for sarcasm. Should I ask you to post a link to verify your claim or provide one myself, that appears to contradict it?
This is a link to the IPCC Impacts, Adaptation and Resilience report -
https://report.ipcc.ch/ar6/wg2/IPCC_AR6_WGII_FullReport.pdf
So far -
QuoteHuman-induced climate change, including more frequent and intense extreme events, has caused widespread adverse impacts and related losses and damages to nature and people, beyond natural climate variability. Some development and adaptation efforts have reduced vulnerability. Across sectors and regions the most vulnerable people and systems are observed to be disproportionately affected. The rise in weather and climate extremes has led to some irreversible impacts as natural and human systems are pushed beyond their ability to adapt. (high confidence)
And in the future -
QuoteApproximately 3.3 to 3.6 billion people live in contexts that are highly vulnerable to climate change (high confidence). A high proportion of species is vulnerable to climate change (high confidence). Human and ecosystem vulnerability are interdependent (high confidence). Current unsustainable development patterns are increasing exposure of ecosystems and people to climate hazards (high confidence).
1 -
1 hour ago, StringJunky said:
Your criticisms are misplaced because there isn't a single solution we are gunning for, so you are just puttintg up irrelevant numbers.
It is the "solution" under discussion.
Irrelevant numbers? Natural carbon sedimentation being so small compared to emissions - 1/930th by the numbers in the diagram I posted - seems relevant to me. The numbers do matter and me pointing them out and suggesting with high confidence that makes this a non-solution should not irritate you. Blame the numbers.
1

Global warming (split from Atmosphere Correcting Lamp)
in Climate Science
Posted
Not that substantial - there has been three times as much warming in the 70 year 1950 to 2020 period than during 1880 to 1950, which began with about 3 decades of global cooling. I don't see much room for significant missing natural elements that would support doubt of the attribution of current global temperatures and weather consequences of that to raised GHG's.
The warming trend increasingly stands out above natural variability and adds it's influence to the weather events we experience - and attribution studies are confirming the expectations that were based on shifting the bell curve distributions of extremes.